After supporting the development of around twenty promising startups, global accelerator Techstars has announced its withdrawal from Nigeria, a country where the startup ecosystem is experiencing rapid growth.
Techstars, a global startup accelerator and venture capital firm, is ending its operations in Nigeria after two years. The decision follows the conclusion of its partnership with ARM Labs, the Nigerian innovation entity with which it launched the ARM Labs Lagos Techstars Accelerator program.
“Techstars’ partnership with ARM Labs has ended, and we will not proceed with a third ARM Labs Lagos Techstars Accelerator Program. The first two cohorts featured outstanding companies and founders, supported by a dedicated group of mentors.We remain optimistic about collaborating with the local startup community to maintain our presence in this vibrant innovation hub,” said Matthew Grossman, Techstars’ global Chief Brand and Communications Officer.
Techstars and ARM Labs partnered in December 2022 to create an accelerator program to support early-stage African startups. Over two cohorts, the program added 24 startups to the Techstars portfolio, each receiving up to $120,000 in funding.
Techstars’ exit from Nigeria comes as the accelerator adjusts its finances, recently cutting 17% of its global workforce. This move raises concerns about the impact on Nigeria’s startup ecosystem, particularly regarding access to crucial resources and support. However, startups already funded through the ARM Labs Lagos Techstars Accelerator will remain part of Techstars’ portfolio and continue to benefit from its global network.
Samira Njoya
Dans plusieurs pays, le service postal occupe une place clé dans l’économie. Cependant, cette institution publique a progressivement perdu de son influence en raison d’un manque de vision stratégique. Aujourd’hui, grâce aux TIC, il devient possible de la réinventer pour répondre aux besoins actuels.
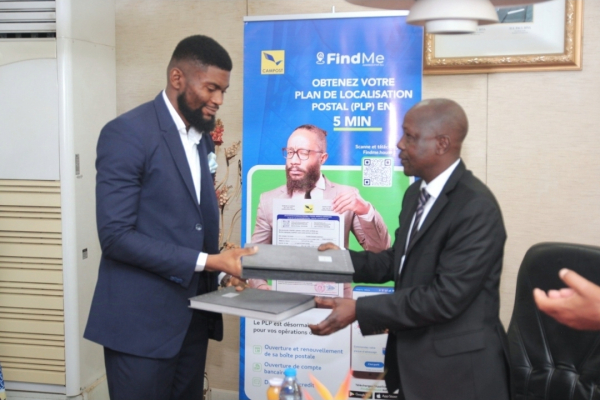
La Cameroon Postal Services (Campost), un opérateur public postal du Cameroun, a signé le vendredi 1er novembre un partenariat stratégique avec FindMe, une start-up camerounaise spécialisée dans l’identification et la géolocalisation. Cette collaboration vise à résoudre le problème de localisation au Cameroun, où une grande majorité de la population ne dispose pas d’une adresse postale officielle.
« Avec le boom de l'e-commerce, il est important pour le service postal de se réinventer afin de mieux satisfaire les clients, en répondant aux besoins de livraison jusqu’au dernier kilomètre et en optimisant nos services financiers grâce à une meilleure identification de nos clients bancaires, en conformité avec les exigences de KYC (Know your customer) », a déclaré Pierre Kaldadak (photo, à droite), directeur général de la Campost.
L'initiative s'inscrit dans la vision de modernisation et de transformation de la poste camerounaise. Elle fait suite à plusieurs mois de collaboration entre la Campost et la start-up FindMe, permettant l’implantation de cette solution au Cameroun depuis juillet 2024. Les premiers travaux ont également permis au gouvernement de créer des codes postaux couvrant l’ensemble du territoire national. Grâce au partenariat, chaque citoyen camerounais et chaque entreprise camerounaise peuvent désormais générer gratuitement une adresse postale en seulement deux minutes via l’application mobile de FindMe. Cette adresse fournit des informations précises, notamment le numéro d’occupation, le nom de la rue, le code postal et la ville.
Au Cameroun, ce système numérisé devrait notamment améliorer l'efficacité des services de secours et des forces de sécurité, accélérer le développement de l’e-commerce et des services postaux, et faciliter les opérations des services fiscaux et fonciers, contribuant ainsi au développement économique national. L’objectif plus large est de créer un référentiel national d’adressage sur lequel les services publics pourront s’appuyer pour déployer leurs diverses opérations.
Samira Njoya
Lire aussi:
Guinea is making strides in digitalizing its public administration, but there's still room for improvement. According to the United Nations, the country's digital governance score increased from 0.2955 in 2022 to 0.4006 in 2024. Despite this progress, Guinea remains behind and is working to accelerate its digital transformation.
The Guinean Ministry of Commerce, Industry, and Small and Medium Enterprises recently announced the upcoming launch of an administrative document management platform (PLAGED) on November 13. This platform aims to simplify administrative procedures for citizens, marking a significant step toward digital governance in Guinea.
This initiative follows Guinean Prime Minister Bah Oury’s recent call for a concerted push to improve the country's digital administration, where progress has lagged. Oury attributes this delay to limited familiarity with the rapid evolution of digital technologies. According to the United Nations' report "E-Government Survey 2024: Accelerating Digital Transformation for Sustainable Development," Guinea scored 0.4006 out of 1 on the E-Government Development Index (EGDI), ranking 29th on the continent. This is an improvement from a score of 0.2955 in 2022, reflecting gradual progress in online government services.
The report also noted Guinea’s Online Service Index score of 0.4808, which assesses the technical features of national websites as well as policies and strategies for online service delivery across general and sectoral levels.
Earlier this year, in April, Guinean authorities launched “e-Learning” and “e-Consulting” initiatives to modernize administrative processes with innovative training and management tools. The introduction of PLAGED aligns with these efforts, supporting the government’s digital strategy to improve service delivery and accelerate the adoption of digital tools across public administration.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
Bitcoin Events is organizing The Blockchain Africa Conference 2024. This 10th edition aims to showcase advancements in Africa’s blockchain and cryptocurrency sectors.
The event will convene blockchain developers, investors, and industry leaders at the CSIR International Convention Centre in Pretoria on November 20, 2024.
Speakers include Charles Hoskinson, Founder of Cardano, Ernest Mbenkum, CEO of Interstellar Inc., and Stafford Masie, former CEO of Google Africa. A special fireside chat will feature blockchain pioneers Elizabeth Rossiello and Ernest Mbenkum reflecting on a decade of industry growth.
Pan-African venture capital firm Janngo Capital has finalized its second fund at $78 million, it announced on October 30. This further advances its commitment to early-stage tech startups across Africa.
Janngo distinguishes itself as a "gender-equal" investor, with 56% of its portfolio companies being women-led, given that Africa has the highest rate of female entrepreneurship globally, yet receives minimal VC backing for female founders.
The firm’s investments target diverse sectors including healthcare, logistics, financial services, retail, agritech, mobility, and the creator economy.
Social media plays a key role in election integrity by enabling citizens to report incidents, share information, and foster transparency. Civil society organizations have raised concerns that restrictions can harm both democracy and economic growth, underlining the long-term impacts on citizens’ rights and national development.
Mauritius's Information and Communication Technologies Authority (ICTA) has directed all internet service providers to block access to social media platforms from Friday November 1 through November 11. The announcement was made in a communique dated November 1, by the authority.
The restriction comes in response to “concerns regarding illegal postings that constitute a serious threat to national security and public safety," the communique reads.
This scenario in Mauritius is part of a broader trend in Africa, where several countries have implemented internet shutdowns or social media restrictions during elections or periods of civil unrest in recent years. For example, in Uganda’s 2021 election, social media was restricted, with authorities citing security concerns.
Between 2020 and 2023, at least 22 African countries enforced full or partial internet shutdowns, resulting in an estimated $3.9 billion in economic losses, according to consulting firm Africa Practice, which advises investors and development partners across the continent.
Hikmatu Bilali
Investing in digital skills accelerates regional tech development and prepares African nations for a digital future. This approach helps address critical challenges. Additionally, it tackles the region’s high youth unemployment, creating more opportunities for the next generation.
Nigeria announced a N2.8 billion ($1.7 million) commitment from Google to support the digital economy. The investment was led by Matt Brittin, Google’s President of EMEA Business & Operations. Announced on October 31 by the Minister of Communications, Innovation, and Digital Economy, this commitment aligns with Nigeria’s Strategic Blueprint for Digital Transformation.
The minister of Communications, Innovation, and Digital Economy commented on the move saying, “I appreciate the entire Google team for betting big on our technology ecosystem and their continued support. I look forward to building on our partnership, as we continue on our path of Digital Transformation in Nigeria.”
Such investments come as digital growth becomes increasingly essential. According to the National Bureau of Statistics, Nigeria's digital economy contributed 16.36% to the country’s GDP as of Q2 2024, just behind trade and Agriculture. This underscores the strategic importance of fostering technological innovation and skills to further boost economic resilience and global competitiveness.
The investment will fund initiatives to train 20,000 Nigerians in AI and Data Science, introduce 125,000 young students to AI fundamentals, support over 1,000 public officials in AI-driven governance, and empower 10 Nigerian AI startups with funding, tools, and mentorship.
Google's support aims to strengthen Nigeria's role in the global digital economy by promoting technical skills and fostering innovation nationwide. This effort is part of a broader $5.8 million investment to advance AI skilling programs across Sub-Saharan Africa.
Hikmatu Bilali
A serial entrepreneur, he has already founded three companies in the science and technology sector. His latest startup aims to simplify payment processes for businesses.
Mohamed Abdelmottaleb (photo) is an Egyptian serial entrepreneur, managing partner, and founder of XPay, a fintech company focused on digital transformation and financial empowerment.
Founded in 2018, XPay aims to enhance quality of life by offering a suite of solutions to streamline financial management. The platform enables businesses to handle various payment types with ease, providing multiple transaction options and complete control through a unified dashboard.
XPay also simplifies end-to-end event management for organizers, covering everything from event creation to ticket sales and providing unique payment links to facilitate transactions. Its innovative payment gateway is adaptable for businesses of all sizes, enabling a smooth, simplified payment process for online operations.
Before founding XPay, Abdelmottaleb launched SabryCorp Ltd in 2006, a company dedicated to improving living conditions in developing countries through science and innovation. In 2011, he co-founded Trendak, a firm specializing in data analytics and artificial intelligence.
Abdelmottaleb graduated from Ain Shams University with a bachelor’s degree in chemistry in 1997 and earned a Ph.D. in nanotechnology from KU Leuven, a leading multidisciplinary research university in Belgium, in 2002.
In 2004, he joined Chemnitz University of Technology in Germany as a senior researcher, and in 2009, he became an assistant professor at Nile University in Egypt. There, he founded the Nanotechnology Center and led the university’s nanotechnology master’s program for five years.
Melchior Koba
The Ghanaian government is ramping up efforts to bridge the country’s digital skills gap. Officials recently announced plans to launch a $5 million fund aimed at fostering technological innovation.
Ursula Owusu-Ekuful (photo, left), Ghana’s Minister of Communications and Digitalisation, launched the “eSkills4Jobs” program last week. The initiative aims to equip over 5,000 young Ghanaians with essential digital skills, with a focus on supporting women from marginalized communities and people with disabilities.
The program is a partnership between the Ghanaian government, the World Bank, and the Ghana-India Kofi Annan Centre of Excellence in ICT.
“The digital economy is here to stay, and we must ensure no one is left behind. eSkills4Jobs will focus on creating tailored training programs, mentorship opportunities, and access to resources to enable participants to build relevant skills,” Owusu-Ekuful said.
The initiative aligns with the Ghanaian government’s broader goal of training one million young people in digital skills to meet the demand for a skilled workforce in a rapidly digitalizing economy. According to the International Finance Corporation (IFC), 20% of Ghanaian companies currently rely on foreign recruitment for digital skills, primarily because they cannot find qualified local talent. The World Bank estimates that approximately 625 million Africans will require digital skills by 2030.
The Ghanaian government believes that the skills acquired through the eSkills4Jobs initiative will not only enhance individual employability but also contribute to the overall growth of Ghana’s economy. World Bank data from 2022 shows that 3.1% of Ghana’s active workforce is unemployed.
Isaac K. Kassouwi
High-quality, easily accessible multisectoral data enable a clearer understanding of countries’ macroeconomic situations. Achieving this, however, requires a technological leap that many countries have yet to make. Ethiopia has chosen to make the leap.
Ethiopia is accelerating the digital transformation of its statistics service to enhance data collection and analysis capabilities.
Planning and Development Minister Fitsum Assefa announced this during her opening address at the 9th African Statistics Forum on Wednesday, October 30. The goal is to improve data quality, accessibility, and leverage innovative technologies to diversify and optimize information sources.
"We must embrace technology and digital tools to improve the accuracy, accessibility, and timeliness of our data, ensuring that we meet the growing demands for high-quality information at both the national and global levels," said Fitsum Assefa, underscoring Ethiopia's commitment to becoming a key player in the field of statistics.
This initiative is part of Ethiopia's National Statistics Development Program, which integrates advanced technologies such as digital geospatial systems and mobile data collection tools. Supported by both national and international institutions, this modernization project aims to make Ethiopia's statistical infrastructure more responsive and better suited to the country's complex data needs.
The digitalization of statistics aligns with a broader continental effort led by the United Nations Economic Commission for Africa (UNECA), which has created a roadmap to modernize African statistical systems by 2030. By promoting the adoption of international standards, UNECA seeks to equip African countries with reliable data systems, crucial for guiding sustainable development and enabling informed, data-driven decision-making.
Samira Njoya
More...
Africa continues to grapple with some of the world's most pressing health issues. In this context, information and communication technologies (ICT) could be a game-changer in improving health and healthcare access across the continent.
Mauritania is set to implement a national digital health strategy by 2030. The draft document was presented on Tuesday, October 29, in Nouakchott at a workshop for review and adoption, overseen by Health Minister Abdallahi Ould Wedih and Minister of Digital Transformation and Administration Modernization Ahmed Salem Ould Bedda. Supported by partners like the European Union and the World Health Organization (WHO), this project aims to modernize healthcare services by integrating digital solutions.
“Digital health is an emerging strategic priority that will significantly strengthen national health policies and the National Health Development Plan (PNDS) to achieve universal healthcare coverage,” said Abdallahi Ould Wedih.
This initiative aligns with the electoral agenda of President Mohamed Ould Cheikh El Ghazouani, who considers digitalization the primary driver of the country’s economic modernization. By 2030, the administration aims to digitize key sectors of the economy through new technologies.
The e-Health strategy being introduced in Mauritania is expected to transform the healthcare sector by providing equitable access to quality health services, expanding coverage in remote areas, and enabling remote consultations through telemedicine. It will also help streamline healthcare costs.
According to a report published last year by McKinsey & Company, widespread adoption of digital health tools—such as teleconsultations, electronic medical records, and mobile apps for chronic disease management—could increase efficiency in African healthcare systems by up to 15% of total spending by 2030. This potential underscores the significance of digital transformation in Mauritania’s health sector.
Samira Njoya
Addressing youth unemployment in Africa is a top priority for many governments. Recognizing the significant challenges, these governments are turning to new technologies to revolutionize training programs. This approach aims to modernize teaching methods and skill development to better align with the evolving demands of today's job market.
Benin is taking steps to modernize its education sector by implementing a national strategy for the digitalization of technical and vocational education and training (TVET). The initiative was officially launched on Thursday, October 31, 2023, with a workshop led by Minister of Secondary, Technical Education, and Vocational Training, Kouaro Yves Chabi.
"The digital transformation of TVET seeks to build a pan-African network and ecosystem to accelerate the digital transition across the continent, improve the quality of inclusive education, and boost learners' employability," said Minister Chabi, highlighting the anticipated impact of this shift for young learners in Benin.
This project aligns with the broader vision of the Pan African Initiative for Digital Transformation of TVET and Skills Development Systems in Africa, launched in 2021 by UNESCO and its partners as part of the African Union’s Continental Education Strategy (CESA 2016-2025), in line with the Education 2030 Agenda. The goal is to establish a strong foundation for modern, adaptable skills that meet the demands of a rapidly changing labor market.
In a context marked by high youth unemployment across Africa—where over 10 million young people enter the workforce each year, often without the necessary qualifications—TVET digitalization is a crucial response. This transformative program will not only modernize technical and vocational education but will also equip young people with skills aligned with international standards, integrating Benin into the global digital economy and preparing learners to face future challenges.
Samira Njoya
Passionate about entrepreneurship, he leverages technology to help farmers grow their businesses. He also provides communities with opportunities to invest in agriculture and livestock sectors.
Ntuthuko Shezi (photo) is a South African serial entrepreneur and the founder and CEO of Livestock Wealth, an agrifinance company.
Founded in 2015, Livestock Wealth offers a digital platform that connects potential investors with certified farmers who own cattle, macadamia trees, or farmland. The start-up facilitates investment agreements, ensuring transparency and trust between all parties involved. Through this model, Livestock Wealth recruits qualified farmers who, with the invested capital, manage assets on behalf of investors to achieve expected returns, allowing clients to invest in tangible, sustainable assets.
In 2020, the company introduced the Farmers Club Meat Box, an e-commerce service that allows customers to purchase grass-fed beef through its online platform.
Before founding Livestock Wealth, Ntuthuko Shezi co-founded Imfundo in 2003, serving as CEO until 2007. Imfundo was a math and science school offering supplementary Saturday education to students from Alexandra and Soweto.
Shezi graduated from the University of Cape Town in 2001 with a bachelor’s degree in electromechanical engineering. His professional career began in 2002 at Accenture, a global management and technology consulting firm, where he worked as a strategy consultant.
In 2006, he became CEO of Scratch Mobile, an airport-based car panel cutting and spray-painting business. From 2014 to 2016, he worked as a program manager at Connectivity, Entrepreneurship, Energy, and Education for Entrepreneurship (CE3), an initiative aimed at stimulating local economic activity in South Africa.
Melchior Koba
Africa can address critical educational challenges by leveraging scalable technology to provide quality education to millions. It will help build a more skilled, connected, and economically resilient generation in these regions.
Kenyan edtech innovator Eneza Education has joined forces with Pakistan's Knowledge Platform in a strategic merger that forms a pioneering educational technology venture spanning Africa and Asia. The cross-continental union, announced on October 29, is headquartered in Singapore. It brings together Eneza’s SMS-based learning solutions for underserved African communities with Knowledge Platform’s gamified digital learning tools popular across Asia.
Wambura Kimunyu, former CEO of Eneza and now Chief Growth Officer of Knowledge Platform, emphasized the merger's focus on inclusive learning. "With over three billion young people across emerging markets, this collaboration will fuel education equity for a sustainable future," he stated, highlighting how Eneza's direct-to-consumer model integrates with Knowledge Platform’s B2B approach to serve diverse learner needs.
Mahboob Mahmood, CEO of Knowledge Platform, praised Eneza's affordable, impactful learning model, which has a track record of delivering education through SMS to students without reliable internet access. "Eneza’s reach complements our gamified curriculum approach, creating a powerful blend of low-cost and high-impact educational solutions," he said.
Africa has around 98 million out-of-school children and youth, according to UNESCO, with many facing challenges like limited school infrastructure and teacher shortages. Edtech solutions, such as Eneza Education's SMS-based platform, make learning accessible even without internet, helping underserved communities stay connected to learning resources despite infrastructure challenges.
Eneza has been a pioneer in mobile-first education across Africa, allowing students to access educational content even in areas with limited internet connectivity. The scalable model, combined with Knowledge Platform's adaptive and interactive learning strategies, promises to extend accessible education across remote or underserved areas.
Hikmatu Bilali