The initiative is part of NamPost’s digital transformation program. Called “Project Sky,” it aims to enhance the organization's operational efficiency, optimize the customer experience, and promote financial inclusion.
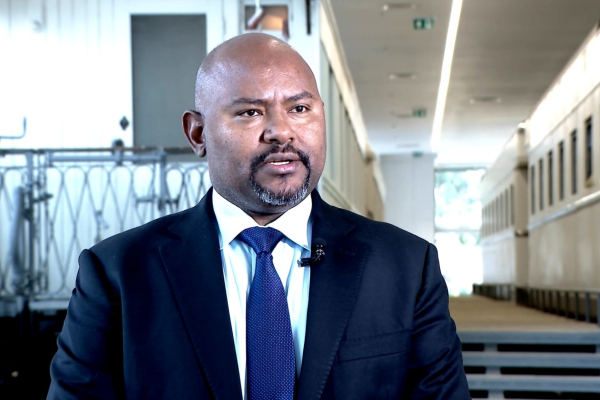
NamPost, Namibia's national postal operator, launched a mobile app and online banking services last week to expand access to its financial services. Customers of the state-owned enterprise can now check balances, make payments, and transfer funds electronically from their smartphones or any internet-enabled device without visiting a post office.
“The MyNamPost Banking App and Internet Banking are not just technological upgrades—they represent a commitment to bringing modern financial services to the people of Namibia, wherever they are. Our customers now have more control over their finances with digital tools that are simple, affordable, and convenient,” said Festus Hangula, NamPost’s Managing Director.
Emma Theofelus, Namibia’s Minister of Information and Communication Technology, acknowledged that innovative platforms like NamPost’s are crucial for financial inclusion. According to the World Bank, 71.35% of Namibians over the age of 15 had an account with a financial institution or mobile money provider in 2021, out of an estimated population of 2.5 million. However, she emphasized the need to equip all citizens “with the necessary skills to take advantage” of these services, noting the limited access to smartphones and the internet.
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) reports that 79.6% of the Namibian population owns a mobile phone. Although the proportion of smartphone users is not specified, the ITU indicates that internet penetration in Namibia stands at 62.2%, with 63.2% of households having internet access at home.
However, the cost of internet access in Namibia remains relatively high compared to ITU standards, which recommend costs below or equal to 2% of gross national income (GNI) per capita. Namibians currently spend 2.6% of their GNI on mobile internet and 8.7% for fixed internet. According to the World Bank, Namibia’s GNI per capita was $12,170 in 2023.
Isaac K. Kassouwi
Last July, Ethiopian Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed launched a program aimed at training young people in digital skills. A few months after its launch, authorities are now assessing its progress.
Ethiopian authorities have trained 31,000 citizens in coding within three months, according to a recent statement by Belete Mola, Ethiopia’s Minister of Innovation and Technology. He made this announcement while reviewing the results of the past fiscal year.
Belete Mola stated, “Over 246,000 citizens have enrolled in the training, and 31,000 of them have been certified. The young people trained as coders and the tech startups with creative potential will receive special support.”
The "5 Million Ethiopian Coders" initiative, launched last July by Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed in partnership with the United Arab Emirates, is part of the "Digital Ethiopia 2025" plan. Its aim is to provide training in programming, Android app development, data science, and fundamental digital skills in artificial intelligence.
This initiative aligns with Ethiopia’s broader goal to establish itself as a major tech hub in East Africa. The World Bank estimates that nearly 230 million jobs in Sub-Saharan Africa will require digital skills by 2030. Through the "5 Million Ethiopian Coders" program, Ethiopian youth are being prepared to meet this demand.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
South African digital transformation company Obami's Tech in Kind initiative is offering up to R1 million ($62,300) in pro bono digital services to South African non-profits and SMEs.
Selected organizations will receive up to R100,000 each in digital transformation services, including access to content digitization, course and program design.
Applications are open until October 31, 2024, and winners will also receive expert guidance and ongoing technical support to enhance their digital operations and efficiency.
Intra-African trade encounters numerous obstacles, including the absence of a unified payment system. The adoption of Papss addresses these challenges by streamlining payment processes and reducing dependence on foreign currencies, thereby promoting increased trade within Africa and enhancing economic integration.
Kenyan President William Ruto has called on commercial banks to expedite their adoption of the Pan-African Payments and Settlement Systems (Papss), urging them to transition away from using the U.S. dollar for intra-African trade. The president revealed this at the launch of the Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises Accelerator programme at the Kenyatta International Convention Centre, Nairobi, on Wednesday, October 16.
Ruto emphasized the need to reduce transaction costs on the continent, which currently result in Africa losing over $5 billion annually. “With Papss, we can conduct transactions in our local currencies, significantly lowering exchange rate challenges and reducing transaction costs for businesses across Africa,” he noted, further encouraging banks to sign on to the system to enhance regional trade.
Raimond Molenje, acting CEO of the Kenya Bankers Association, confirmed that the association is actively working with the Central Bank of Kenya to implement a national switch to the Papss system, which would facilitate smoother trade with neighboring East African countries. This development aligns with Papss's goal of creating a single market for Africa and increasing intra-continental trade.
Papss, which was introduced by the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) in 2019, facilitates seamless payments in local currencies across African nations. Initially piloted in the West African Monetary Zone, it was formally rolled out by Afreximbank in September 2021, with full operations beginning in early 2022.
The AfCFTA creates a single market for goods and services, allowing Kenyan businesses to access a market of over 1.3 billion people and a combined GDP of over $3.4 trillion. This significantly expands their customer base and revenue potential.
Hikmatu Bilali
Investing in digital infrastructure positions Africa for significant economic advancement by opening up opportunities for e-commerce, tech startups, and improved public services. Governments can leverage this trend to create jobs for its population
Governor Hyacinth Alia of Benue State signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with EVNT Technologies, a leading Saudi Arabian IT firm, aimed at transforming the state's digital landscape. The signing took place during the 2024 GITEX Global Summit in Dubai which ended on October 18.
The governor highlighted that this initiative “is a critical step towards realizing our vision of a truly digital Benue. It is about creating opportunities, empowering our people, and laying the groundwork for sustained economic growth."
Through the Benue Digital Infrastructure Company PLC (BDIC), the partnership will focus on expanding digital infrastructure, skills training, and digital policy development.
Hamad Al Saleh, founder of EVNT Technologies, expressed enthusiasm for making Benue a model for digital transformation in Nigeria. The implementation is expected to begin within 90 days, focusing on infrastructure development, capacity building, and digital innovation.
This move aligns with the National Digital Economy Policy and Strategy 2020 – 2030 (NDEPS), which aims to “transform the country into a leading digital economy providing quality life and digital economies for all.” Benue, by becoming a model for digital transformation, can leverage this trend to create jobs for its population.
Hikmatu Bilali
AI is projected to contribute significantly to the global economy. Africa’s investment in AI ensures the continent can tap into this booming sector, increasing its global competitiveness and fostering local innovation.
Zambia is establishing a second Artificial Intelligence (AI) Centre of Excellence in Lusaka. Felix Mutati, Zambia’s Minister of Science and Technology, announced this on October 20 while speaking at a solar panel handover and AI training event for teachers at Katoba Secondary School in Chongwe District.
Mutati revealed that the Katoba Secondary School will be transformed into an AI hub to advance AI-assisted learning and technological skills across schools nationwide. He emphasized the potential of AI to revolutionize Zambia’s education system, saying "AI will help teachers prepare lesson plans more efficiently and track student progress," highlighting its ability to make education more responsive to students’ and teachers’ needs.
This AI center complements the one launched a month earlier at the University of Zambia in collaboration with Google, aimed at fostering tech-driven solutions to the country's social challenges. This new hub will function as a training ground, enabling other schools to adopt AI-driven educational tools.
The initiative is funded by Ecobank, with Managing Director Aina Moore emphasizing the importance of providing students with access to modern technology and sustainable energy sources. This is part of Zambia’s larger effort to integrate AI into its educational system, positioning the country as a leader in tech-enabled learning in Africa.
Additionally, Zambia’s move towards AI integration comes in the wake of scholarships awarded by the Czech Republic for Zambian professionals to study AI, as well as calls from the Chamber of Mines for AI to be included in the Technical Education, Vocational, and Entrepreneurship Training (TEVET) curriculum.
These efforts are crucial, given that Zambia’s education system faces quality and access issues. In Zambia, the allocation for Early Childhood Education (ECE) has consistently remained low, with only about 0.4% of the education budget allocated to it between 2016 and 2020, according to the Zambia Education 2024 Budget brief by UNICEF. This falls significantly short of the recommended 10% investment. As a result, many children are deprived of crucial early learning experiences, entering primary school underprepared and at a disadvantage for Grade 1, hindering their ability to catch up with their peers. AI-driven tools could significantly improve lesson planning, personalized learning, and the monitoring of student progress, helping to close these educational gaps.
Hikmatu Bilali
A technology and finance entrepreneur, he has founded and led two companies. His solutions and works have earned him numerous awards and recognitions.
Muriuki Collins is a Kenyan IT specialist and tech entrepreneur, renowned for his expertise and contributions to Africa's finance sector. He is the co-founder and CEO of Terra, a company offering innovative digital wallet services.
Founded in 2012 by Muriuki Collins and Martin Nyaga, Terra enables African businesses to achieve their financial goals through a platform that centralizes and simplifies access to various financial services. By integrating features such as payments, loans, and identity verification (KYC), Terra provides a comprehensive solution for managing and deploying digital wallets across the continent.
Today, Terra operates in over 25 countries and manages more than 5 million mobile wallets. Among its key clients are the Kenya Tea Development Agency, which serves at least 650,000 farmers, and Food for Education, a mobile platform supporting one million schoolchildren.
Beyond Terra, Muriuki Collins founded SwypePay in 2017, where he also serves as CEO. This startup focuses on automating business operations for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in Africa, helping them grow and develop more efficiently.
Muriuki holds a bachelor's degree in Computer Systems Technology from Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology, which he earned in 2013. He began his professional career in 2011 as a systems engineer at Novel Technologies EA Ltd. From 2014 to 2019, he served as a fintech consultant for the Kenya Tea Development Agency.
In 2023, Muriuki Collins was named one of the Top 40 Under 40 by Business Daily, recognizing influential and progressive figures in Kenyan business. He was also recognized by The Founder Africa as one of the continent's most promising entrepreneurs.
Melchior Koba
Tech company Yango Group and Zindi, which connects organizations with data scientists, will host the 2024 Lusaka Mobility Prediction Hackathon on October 26. The competition will focus on predicting traffic patterns affected by weather.
The event will bring together data scientists and tech enthusiasts in Zambia to tackle real-world urban mobility challenges.
The hackathon aims to inspire Zambia's data science community by offering prizes to the top three participants. It is part of Yango’s commitment to driving urban solutions through data and technology.
A screenwriter, director, and writer, he became an entrepreneur to support rural farmers. By leveraging technology, he helps them sell their products to a wider audience.
Abdulai Barrie, a Sierra Leonean entrepreneur, is the founder and CEO of Salone Agro Market, a technology platform focused on agriculture. The platform’s primary goal is to empower farmers while improving their market access across Sierra Leone.
Founded in 2019 and registered under the startup SALGRO Ltd., Salone Agro Market connects buyers and sellers of agricultural products. It provides small and large farmers alike with a marketplace to sell their produce, while also facilitating access for commercial businesses and large enterprises seeking to purchase these products.
In addition to connecting buyers and sellers, Salone Agro Market supports small farmers by providing access to inputs, processing equipment, transportation solutions, and information systems. The platform is accessible offline via USSD codes, ensuring maximum inclusivity. It also offers real-time information on market prices, weather forecasts, and facilitates direct transactions between sellers and buyers.
Alongside his work at Salone Agro Market, Abdulai Barrie is the editor of the Commonwealth Youth Council newsletter, an organization focused on youth development within the Commonwealth. He also serves as a project manager at Sierrapreneurs, an initiative promoting youth entrepreneurship in Sierra Leone. Since 2018, he has been the co-founder and creative director of Creative Media Network SL, a multimedia production company.
Abdulai Barrie holds a certificate in entrepreneurship, financial management, and reporting for innovators, awarded in 2021 by the Institute of Public Administration and Management at the University of Sierra Leone. A former screenwriter and director, he also worked as a writer for Hidden Voices Africa, a platform publishing human interest stories, from 2023 to 2024.
In recognition of his commitment to innovation and social development, Abdulai Barrie secured third place in the 2024 Orange Social Venture Prize in Africa and the Middle East (POESAM) in Sierra Leone. He will represent his country in the continental phase of the competition.
Melchior Koba
The entertainment industry is thriving across the continent. Tech entrepreneurs are creating innovative digital solutions to streamline various aspects of event management, among other things.
Akwaaba is a digital solution developed by a Ghanaian startup that offers users venue recommendations, the ability to purchase event tickets online, and the chance to earn rewards by sharing the app and referring others.
Founded in 2012, it features an iOS and Android app, with the Android app boasting over a thousand downloads on the Play Store. Through those mobile apps, users can create their accounts to, among other things, make reservations at places like restaurants, cinemas, and fast-food outlets in the cities of Accra and Kumasi.
Event organizers and venue promoters can also leverage Akwaaba to sell tickets, manage bookings, and benefit from marketing support. To boost engagement, the startup has launched a rewards program aimed at "generating more user involvement and revenue for local businesses, helping them thrive in an increasingly competitive market."
Additionally, the startup has partnered with social media content creators to enhance its visibility. “By leveraging the power of social media, the Influencer Programme will engage a wider audience and increase app downloads, further solidifying Akwaaba’s position as the viable event platform in Ghana," explained Kingsley Kordie, Akwaaba’s director.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
More...
African youth stand at the brink of a transformative era, requiring a collective effort to harness their potential for leadership and innovation. By investing in their education and training, they can become a driving force for the continent's development.
On Monday, October 21, Gabon's Deputy Prime Minister, Alexandre Barro Chambrier (photo, center), inaugurated the Gabonese Innovation Center (CGI). This initiative aims to transform the country's tech and entrepreneurial ecosystem, positioning Gabon as a key player in Central Africa’s technology sector.
"The Gabonese Innovation Center is not just a tool for technical development; it’s a catalyst for digital and social transformation. It will undoubtedly help develop our strategic economy with a single goal in mind: to be ready to address future threats. It is a guarantee of success," stated General Bonjean Frédérik Mbanza, the Minister of Digital Economy.
The CGI hosts several innovation-focused spaces, including a certification center for acquiring recognized digital skills, a FabLab (a creation and innovation space equipped with advanced technologies), a media lab for digital media collaboration, and a digital acclimatization hub (crucial for preparing Gabon for innovation and digital transformation).
This new center is part of Gabon's ongoing digital transformation, which seeks to make digital technology a driver of economic and social growth. As a result of these initiatives, the country ranks 10th on the continent with an ICT development index of 74.7 out of 100, according to the latest 2024 report from the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). In 2023, Gabon also held this position with a score of 72.9, reinforcing its progress in this strategic field.
The CGI will provide young people with opportunities to acquire certified skills in digital technologies, enhancing their employability in an increasingly digitized economy. By facilitating access to these new skills, the center is also expected to contribute to youth empowerment and their active participation in the country’s economic development.
Samira Njoya
Like many countries, Tunisia has embraced digital technology to modernize its operations. This initiative aims to enhance the efficiency and accuracy of processes, particularly when it comes to data collection.
Tunisia is set to conduct its thirteenth General Population and Housing Census from November 6 to December 31. This census, fully digitized, marks a shift from traditional paper-based methods. The government formalized the announcement with a decree issued by the head of government on Wednesday, October 16.
To ensure the success of this digital-first initiative, the National Institute of Statistics (INS) developed a Tunisian-made application to centralize data collection and enable real-time processing. Additionally, 9,000 tablets have been procured for census agents, who will visit households across the country. The project has a total budget of 89 million dinars (approximately 28.8 million USD), with 24% dedicated to IT infrastructure.
This initiative aligns with the country’s 2026-2030 development strategy. It is also part of the digital transformation efforts outlined in the National Strategic Plan “Tunisia Digital 2020.” The government is leveraging digital technology to optimize various sectors, including the census, where data accuracy is critical.
The use of digital tools will not only speed up the census process but also improve its accuracy. Tablets and a dedicated app will help eliminate errors often associated with manual methods. Real-time data collection will provide reliable statistics, essential for public policy planning, and enhance overall efficiency. Preliminary results are expected to be published in February 2025, with detailed data available by September 20, 2025.
Samira Njoya
As Africa’s digital economy continues to grow, investments in the sector become crucial. These investments play a critical role in driving sustainable development across the continent.
Nigeria has announced a $119 million investment aimed at strengthening its tech hubs and supporting the growth of micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs). The announcement was made following a meeting between Nigeria's Vice President Kashim Shettima and Swedish investors in Stockholm on October 17.
Vice President Shettima highlighted the importance of the investments, noting that "The government's 'Renewed Hope Agenda' emphasizes creating a competitive business environment that attracts both foreign and domestic investments.”
A key portion of the investment—$100 million—comes from Gluwa, a decentralized financial platform, which has committed to enhancing digital skills in the country. Gluwa’s Director, Akinola Jones, outlined plans to train over 30,000 Nigerians in digital technologies.
Additionally, Ericsson's Managing Director for Nigeria, Peter Olusoji Ogundele, revealed plans to invest $19 million in building a technology hub. Ogundele emphasized that the initiative would help develop local talent, positioning Nigeria as a global player in tech services.
Nigeria continues to attract substantial investor attention. At the recent GITEX Global event in Morocco, the UAE demonstrated interest in the country’s burgeoning tech sector, aiming to support the growth of its dynamic startup ecosystem. This highlights the increasing recognition of Nigeria as a key player in Africa’s tech innovation landscape.
According to Nigeria’s National Bureau of Statistics (NBS), the information and communication sector contributed 13.12% to the total Nominal GDP in the 2024 first quarter, highlighting the importance of digital transformation.
Hikmatu Bilali
SMEs employ the majority of people on the continent. However, they face numerous challenges, including limited access to capital, markets, and digital resources, which hampers their growth and ability to scale. Addressing these challenges is essential for achieving sustainable socioeconomic development in Africa.
On October 16, Littlefish announced a partnership with Visa to enhance digital experiences for businesses, providing advanced solutions for both in-store and online transactions. The omnichannel platform offering business solutions to financial institutions aims to empower micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) across Africa.
Co-founder and CEO of Little Fish Brandon Roberts noted the importance of delivering “a seamless, cost-effective digital platform that empowers financial institutions to support sustainable growth in the MSME sector.”
The partnership also integrates Visa's CyberSource system, enhancing secure payment processing and opening the door for future products like remittance flows, lending, and loyalty programs. This collaboration marks a crucial step towards digital transformation for MSMEs in Africa, making commerce more efficient and accessible across the continent.
According to Forbes Africa, citing the World Economic Forum, MSMEs account for around 80% of businesses and more than 50% of the GDP in Africa. This underscores their importance to economic stability and job creation. However, these businesses often struggle with limited access to digital payment solutions and financial tools, which can hinder their growth potential.
As cash transactions continue to dominate daily business in Africa despite global digital payment trends, this collaboration addresses a significant gap. Visa and Littlefish will offer innovative payment solutions through traditional POS systems, mobile POS, Tap2Phone, and e-commerce channels, coupled with value-added services designed to streamline MSME operations and support growth.
Hikmatu Bilali