A computer scientist and trainer specializing in AI and machine learning, he is committed to solving problems, making a positive impact on society, and strengthening communities.
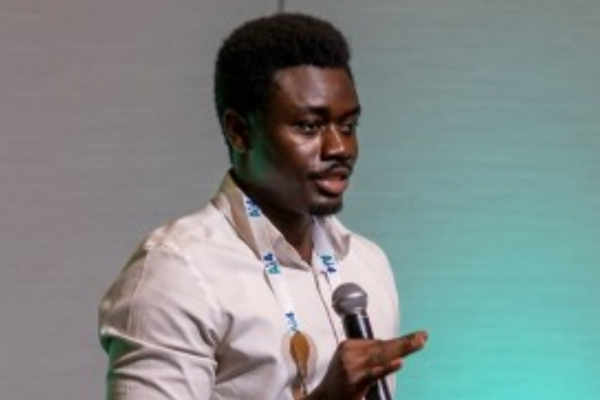
Emmanuel Acheampong (photo), a tech entrepreneur passionate about artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), is the co-founder and CEO of yShade.ai, a startup focused on developing AI solutions. Founded in 2020 by Acheampong alongside Derby Chukwudi and Rofy Okyere-Forson, yShade.ai aims to address the needs of diverse skin tones and types through custom algorithms. These advanced algorithms enable accurate recognition, analysis, and matching of skin characteristics.
yShade.ai is built on a unique database containing over 10 million images and covering 100 different skin tones, which allows it to deliver tailored solutions for its partners. The technology also adjusts for variations in lighting and environmental conditions, ensuring precise and adaptable analyses.
In addition to his work with yShade.ai, Acheampong shares his expertise as an AI instructor on Maven, an online learning platform that offers courses in AI, marketing, design, and engineering. In 2020, he co-founded ROBO-Bootcamp, an educational platform that uses AI to address gaps in technical skills.
Academically, Emmanuel holds a bachelor’s degree in computer science and mathematics from Berea College (U.S.), earned in 2019, and a master’s degree in engineering, science, and technology from the University of Notre Dame, completed in 2021. Between 2021 and 2023, he also served as an instructor on Coursera, one of the world’s leading online learning platforms.
Melchior Koba
International money transfers play a key role in the global economy, facilitating financial exchanges worldwide. In Africa, the rise of mobile money has revolutionized these transactions, significantly boosting financial inclusion.
Mobile money transfers between countries were among the fastest-growing services in Africa in 2023. The total amount sent reached nearly $29 billion, a 33% increase from $22 billion in 2022, according to the GSMA.
In The State of the Industry Report on Mobile Money 2024 , published last April, the GSMA explains that this growth was largely driven by the Covid-19 pandemic. During this period, diasporas worldwide widely adopted mobile money transfers to meet the urgent needs of family members in Africa.
This practice, born out of the necessity for quick, secure, and affordable transactions, has endured, especially given the continent’s low banking rate. Mobile money has thus become a critical alternative to traditional banking services. International transfers via mobile money grew from $16 billion in 2021 to reach $29 billion in 2023.
In 2023, international mobile money transfers accounted for 3.18% of the $912 billion transacted through mobile money in sub-Saharan Africa. Although modest, these transfers play a vital role in the sector. Merchant payments, another significant component, reached $74 billion, or roughly 8.11% of the total mobile money transactions, up 14% from 2022. Additionally, transfers between banks and mobile money services (in both directions) rose 15% year-on-year, reaching $210 billion in 2023, according to the GSMA.
Challenges and Recommendations for Further Development
Despite this strong growth, the expansion of international mobile money transfers in sub-Saharan Africa faces structural challenges. One key issue is the relatively low adoption of mobile financial services, even though mobile phone penetration is high. In 2023, the region counted 856 million mobile money subscriptions out of 980 million mobile phone subscriptions.
To accelerate growth in this sector, the GSMA recommends increasing partnerships between telecom operators and banks to enhance interoperability and lower transaction costs. Meanwhile, governments could support these efforts by investing in digital infrastructure in remote areas and adopting favorable regulations. These actions would make mobile money services even more accessible, amplifying their impact on financial inclusion globally.
Samira Njoya
Africa hosts a growing number of startups fueled by increasing digitalization. However, many struggle to scale due to limited resources and mentorship. Targeted programs are essential to enhance their growth and competitiveness locally and globally.
The National Agency for Science and Engineering Infrastructure (NASENI) has partnered with AfriLabs to launch the NASENI Innovation Hub, aimed at empowering Nigerian innovators and startups. The partnership was forged at the 2024 AfriLabs Annual Gathering (AAG) held from November 5 – 8 in Cape Town, South Africa. It aims to bridge the support gap for young creators, providing resources to commercialize groundbreaking technologies and drive sustainable economic growth.
NASENI’s Executive Vice Chairman, Khalil Suleiman Halilu, emphasized the hub’s role in advancing Nigeria’s technological and industrial goals, saying: “At NASENI, we are committed to transforming Nigeria into a global leader in technology and industrialization. The establishment of this innovation hub marks a pivotal step in fostering homegrown solutions, nurturing local talent, and creating a dynamic ecosystem that will drive sustainable development through science and engineering.”
The hub will offer infrastructure, mentorship, and capacity building to nurture ideas, foster industrialization, and position Nigeria competitively in the global tech space. It will run specialized programs, including the NASENI Reverse Japa Programme, which supports Nigerian researchers abroad in commercializing innovations locally, and the DeltHer Expansion Programme, which empowers women in engineering. FutureMakers by NASENI will nurture young innovators through grants and mentorship, while the Placeholder Programme addresses public sector challenges with innovative solutions. NASENI Xceler8 will accelerate startups in science, engineering, and manufacturing.
Nigeria has a vast pool of talented innovators, but a lack of infrastructure, funding, and mentorship often stifles their potential. According to the Global Innovation Index 2024, which captures the innovation ecosystem performance of 133 economies, Nigeria ranked 113th, highlighting the urgent need for focused investment in science, technology, and innovation ecosystems.
This partnership establishes a foundation for a sustainable innovation ecosystem to drive Nigeria’s industrialization and economic transformation. By empowering innovators and fostering collaboration, NASENI and AfriLabs are building a future where Nigerian innovations thrive locally and impact the global stage.
Hikmatu Bilali
A young entrepreneur, she is fighting to reduce school dropout rates among African children. She offers innovative, tech-driven educational solutions.
Wiem Ben Mahmoud (photo) is a Tunisian tech entrepreneur and the founder and CEO of KidzRise, a startup dedicated to empowering children to actively contribute to their communities. Established in 2023, KidzRise uses an AI-powered detection system to identify and develop the unique talents and aptitudes of children between 5 and 17 years old. The company offers e-learning programs that transform these talents into concrete, marketable skills. KidzRise awards badges and certificates for achievements, aiming to make education more inclusive and equitable.
“At KidzRise, we believe every child is gifted. Each child has unique abilities and strengths that set them apart. Our mission is to uncover and nurture these hidden gems, ensuring each child reaches their full potential and shines in their own unique way,” reads the company’s website.
Wiem Ben Mahmoud graduated from the Institute of Higher Commercial Studies in Sousse, Tunisia, with a bachelor’s degree in business management and advanced commercial studies in 2021. She also holds a master’s in digital management and information systems, earned in 2022 from Esprit School of Business.
She began her career in 2016 as the media and communications manager for the Sousse International Festival. In 2020, she worked as a market research officer at Sarraj Immobilier before joining VERMEG for Banking & Insurance Software, a software provider for banks, capital markets, and insurance companies, as a business analyst in 2021.
Melchior Koba
He has years of experience working in construction companies. With a focus on digital transformation, he helps modernize industry practices.
Nabil Hassoune (photo) is a Moroccan investor and serial entrepreneur, founder and CEO of GRO’INO, which connects construction industry operators with the supplies and services they need.
Founded in 2022, GRO’INO is a B2B e-commerce platform tailored to professionals in construction and hardware. It provides merchants with centralized access to a wide range of supplies, competitive pricing, and flexible payment options. The platform offers an extensive product selection, including paint, sanitary materials, and various plumbing and carpentry tools, all with delivery service included. For exclusive hardware and DIY manufacturers and distributors, GRO’INO serves as a direct sales channel, providing targeted marketing tools and payment terms not exceeding seven days.
Hassoune is also the founder and CEO of AXURYS, an IT services startup, and an investor in PECSYS France, a company specializing in IT consulting, services, and digital transformation.
In 2018, he founded Nomalis International Group, a startup he led until 2023. This company focused on digitizing processes like logistics, B2B marketplaces, and integrated financial and insurance services.
Hassoune graduated from the Ecole Nationale Supérieure d'Électricité et de Mécanique in Casablanca, Morocco, earning an engineering degree in mechanical design and manufacturing in 2001. He also holds a master’s degree in management from Ecole Hassania des Travaux Publics, obtained in 2014.
Before his entrepreneurial career, he worked from 2002 to 2004 as a B2B business development manager for southern Morocco at Total Petrochemicals. In 2004, he joined OCP Group, a fertilizer supplier, as operations manager. By 2012, he had become CEO of Prefamar SA, a construction materials manufacturer and distributor, while also serving as CEO of BigMat Morocco, a retailer selling construction materials.
Melchior Koba
Between 2022 and 2024, African countries saw their average scores on the E-Government Development Index rise by 4.8%, from 0.4054 to 0.4247. Djibouti is keeping pace with this trend, ramping up efforts to digitize as many services as possible.
Djibouti announced, on November 14th, the pilot phase of a digital building permit platform. The platform is designed to streamline and speed up the permit process for both individuals and businesses. This move follows the May 2024 announcement at the 8th session of the Council of Ministers, where plans for an e-permit system were first unveiled. The platform is set to integrate into the national online services portal, which already offers a variety of digital public services.
To support this initiative, the Djiboutian government has sought technical and financial partnerships. Earlier this week, they reached out to the European Union as part of the "Global Gateway" investment strategy. The e-permit implementation is part of the broader "Djibouti Digital Foundation" project, which aims to accelerate the country's digital transformation.
A United Nations report released in September categorized Djibouti as a country with a medium E-Government Development Index (EGDI), scoring 0.2911 out of 1. However, Djibouti's Online Services Index, a component of the EGDI, remains low at 0.2092 in 2024.
During the pilot phase, building permits will be issued within seven days, as stated on Djibouti's national online services portal. Applications can be submitted from Saturday to Thursday between 7 AM and 2 PM.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
An IT professional by trade, she is passionate about no-code development. She now uses this technology to create digital solutions in Madagascar.
Amboara Rabe-Harinoro (photo) is a Malagasy software developer and entrepreneur. She serves as the CEO of Misaina Incorporation, a company specializing in digital solutions.
Founded in 2017, Misaina Incorporation is an innovative startup in the no-code sector, providing solutions tailored to the specific needs of businesses. Its mission is to support the digital transformation of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and startups, allowing them to focus on their core activities.
Misaina Incorporation also offers no-code training courses aimed at entrepreneurs and freelancers, in addition to providing software development services.
In March 2024, Amboara Rabe-Harinoro launched NoCode Madagascar, the first no-code community in the country. She is also the lead developer of PayFacile, a platform that facilitates entrepreneurs' access to online payment solutions and subscription services. Simultaneously, she teaches software development at the IT University of Madagascar and serves as an IT consultant for BICI, a software development company.
She holds a bachelor's degree in computer science, obtained in 2017 from IT University Andoharanofotsy. She also graduated from Université Côte d’Azur, where she earned a master's degree in Mobility, Databases, and System Integration (MBDS) in 2019.
Amboara Rabe-Harinoro began her professional career in 2017 as a software developer at Madagascar Airport (ADEMA). In 2018, she joined BICI as a full-stack developer, where she also held the role of project manager. In 2019, she became a full-stack developer at iFox Code, a Mauritian mobile and web application development company, where she worked for three months.
Melchior Koba
In a context where access to technology remains uneven, countries are seeking innovative solutions to improve connectivity. International partnerships, particularly in satellite technology, are essential levers to bridge this digital divide.
The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), on Tuesday, November 12, signed a memorandum of understanding with Monaco's leading satellite operator, Monacosat, to expand satellite infrastructure in the country. The agreement, signed by Congolese Minister of Posts, Telecommunications, and Digital Economy Augustin Kibassa Maliba (photo, left), aims to bridge the digital divide in rural and remote areas.
The partnership will involve discussions to finalize the details of deploying a satellite telecommunications network in the DRC, leveraging Monacosat's satellite capacity. According to a statement from the Congolese Ministry of ICT, the initiative aims to bridge the digital divide in rural and hard-to-reach areas by leveraging Monacosat’s satellite capabilities to expand connectivity. “We have decided to work closely together and consult on matters of mutual interest, focusing on the deployment of a satellite telecommunications network in the DRC through the acquisition of satellite capacity from Monacosat,” the statement read.
This initiative aligns with DRC's “Horizon 2025” National Digital Plan, which seeks to develop a robust digital infrastructure to connect the country. It follows a recent cooperation agreement signed with the Polish government to support digital infrastructure expansion in the DRC.
Despite government efforts, the country continues to show low connectivity rates. According to the Congo Post and Telecommunications Regulatory Authority (ARPTC), as of June 30, 2023, only 30.79% of Congolese had access to mobile internet, and a mere 0.0174% had fixed internet access. The United Nations' latest "E-Government Survey 2024," published in September, highlighted this gap, noting that the DRC’s telecom infrastructure development index stands at 0.1591, well below the African average of 0.4534.
If negotiations succeed, Monacosat would extend its coverage across the DRC using its TurkmenAlem52E/MonacoSAT satellite, which already operates in Africa. This initiative could not only connect millions of Congolese but also facilitate access to education, healthcare, and digital public services, contributing to the country’s overall development. It could also help offset delays in the fiber optic network expansion, which is estimated to require nearly 50,000 kilometers of additional coverage.
Samira Njoya
Insufficient information about market supply can fuel inflation. Sometimes, unscrupulous merchants exploit shortages to artificially inflate prices. Preventing such practices is crucial for economic and social equity.
The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) has unveiled a new mobile app, TALO, developed by local talent to improve economic oversight. Presented to the Council of Ministers, last Friday, by Deputy Prime Minister Daniel Mukoko Samba, the app aims to improve transparency and price regulation through real-time monitoring of commercial practices and stock flows.
TALO comprises two modules: a mobile module for field investigators to collect and centralize price data weekly, and a platform for businesses to directly submit information on inventory, pricing, and pricing structures. The system aims to enhance transparency in commercial practices and strengthen economic regulation.
Its adoption demonstrates the Congolese government’s commitment to enhancing transparency and restoring trust in economic oversight for both businesses and the public. According to Mukoko Samba, the initiative seeks to turn oversight functions into genuine regulatory tools, free from abuses, to ensure a fairer and more reliable business environment.
TALO aligns with broader efforts to improve economic regulation in the DRC. By enabling more transparent and effective management of economic controls, the app supports adherence to standards, strengthens control missions, and safeguards due process for businesses. It also facilitates complaint collection and the detection of potential irregularities.
With this system, the government aims to create a more equitable economic framework that fosters transparency and strengthens the trust of economic actors. Raising operator awareness, through the distribution of a guide on economic oversight, is also essential to securing a more regulated and investment-friendly business environment in the DRC.
Africa's pharmaceutical market faces supply chain issues and counterfeit drugs, but technology offers a solution. Leveraging digital tools can address these challenges, create economic opportunities, and strengthen healthcare infrastructure - making a lasting positive impact on public health and economic growth.
Prosper Africa, a Presidential-level national security initiative focused on strengthening strategic and economic ties between the U.S. and Africa, has launched a pilot project under its Africa Tech for Trade Alliance (AT4T). The initiative, announced on November 12, aims to digitize and improve transparency in Africa’s pharmaceutical supply chains. Launched in collaboration with USAID’s e-Trade Alliance, IBM Consulting, and the National Association of Boards of Pharmacy (NABP), it introduces the Pulse by NABP™ platform in South Africa.
British Robinson, Coordinator of Prosper Africa, highlighted the importance of partnerships in developing technology-driven solutions under the Digital Trade for Africa (DTA) initiative. “Through Prosper Africa’s Tech for Trade Alliance, we support partnerships that leverage technology to create products that yield both financial and social benefits for Africans and Americans alike,” he stated.
Designed to link U.S. and global pharmaceutical giants like Pfizer and Roche with African distributors and pharmacies, Pulse by NABP™ aims to foster transparency, improve communication, and establish a secure framework for medication distribution.
This initiative also includes AI-based training for African pharmacies and retailers through IBM’s watsonx.ai, empowering them with data-driven tools to optimize their sales strategies. The Pulse platform is set to address Africa’s complex pharmaceutical distribution challenges, paving the way for increased economic growth and access to healthcare across the continent.
Africa has one of the fastest-growing pharmaceutical markets in the world, valued at approximately $26.85 billion in 2023, according to the Africa Pharmaceutical Market Size, Industry Report, 2030 by research and consulting company Grand View Research. This market is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.4% from 2024 to 2030, fueled by an increasing demand for healthcare services as the population grows and ages.
However, the continent faces challenges, including fragmented supply chains, logistical barriers, and regulatory differences, which drive up costs and reduce product availability. The Pulse platform aims to address these challenges by increasing supply chain visibility, which could help African pharmacies minimize losses, maintain consistent stock, and forge profitable partnerships with international suppliers.
The initiative aligns with recommendations outlined in the African Development Bank Group's 2022 report, A New Frontier for African Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Industry. The report emphasizes that strengthening logistics integration is essential to developing Africa’s pharmaceutical industry, enabling efficient intra-African and international trade, particularly in pharmaceutical products.
Hikmatu Bilali
More...
He leverages his real estate investment expertise to help South Africans boost their income, utilizing technology to achieve this goal.
Ezra Rasethe (photo) is the founder and CEO of investRand, a South Africa-based investment firm. Through his startup, he aims to help individuals build sustainable real estate wealth.
Founded in 2021, investRand offers a marketplace connecting real estate investors with income-generating properties, reliable service providers, and various financing options. The company's goal is to enable individuals to generate passive income through real estate investment.
"Our platform is revolutionizing the real estate and PropTech industries by making it possible, accessible, and profitable for every South African to invest in property. We are proud to offer exceptional investment opportunities within every budget and area of interest, empowering our clients to make informed decisions about property investing," the company explains on its website.
Rasethe is also the founder and CEO of Infinity Property Group, established in 2017, which includes companies specializing in proptech, affordable housing, and student housing. These firms help South Africans make informed choices in real estate investment through technology.
Rasethe holds a degree in real estate development and investment from the University of Cape Town, obtained in 2022. He also serves as president of the 4thDimension Toastmasters club, where he helps members enhance their communication and leadership skills through public speaking.
Melchior Koba
The volume of electronic and electrical waste is growing in Africa every year. Successfully giving this waste a second life could help ease current environmental pressures while creating wealth for young people.
On Wednesday, November 13, Orange Middle East and Africa (OMEA) and German development agency GIZ announced the launch of the "Master Repair" project, backed by a joint €2.85 million investment. This initiative offers specialized training in electronic device repair, as well as in the installation and maintenance of solar panels and fiber optic networks. The program targets young men and women in Morocco, Tunisia, Senegal, and Egypt, with a particular focus on individuals with disabilities.
The project is positioned as an inclusive approach to enhancing youth employability and promoting the creation of micro-enterprises in electronic repair and sustainable technology sectors.
Jérôme Hénique, CEO of Orange Middle East and Africa, stated, “This partnership with GIZ illustrates our commitment to supporting young people, especially women and persons with disabilities, towards sustainable professional integration and a more inclusive economic future. Together, we invest in skills that not only create opportunities but also strengthen the foundations of a circular and resilient economy for tomorrow.”
Master Repair is part of the develoPPP program, commissioned by Germany's Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development (BMZ) and supported by the "Decent Work for a Just Transition" special initiative. The project aligns with the mission of Orange Digital Center to promote digital inclusion and support digital skill development for employment, particularly among youth and women.
According to Market Research Network, the global market for electronic maintenance and repair was valued at $98.1 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach $142.7 billion by 2030, growing at an average annual rate of 4.5% between 2024 and 2030. While specific data on Africa is unavailable, it’s evident that this market holds promise. With the World Bank reporting that a majority of Africans live on less than $5 a day, purchasing new devices often requires significant financial sacrifice, making repair a more affordable option than replacement.
Increasing the number of young people skilled in repair and maintenance is also expected to better meet the needs of households and businesses across the region.
Digital transformation is a top priority for the Djiboutian government, which aims to establish the country as a technology hub by 2035.
Djibouti wants to strengthen its cooperation with the European Union (EU) to accelerate its digital transformation. The goal was at the center of discussions between Mariam Hamadou Ali, Djibouti’s Minister Delegate for Digital Economy and Innovation, and Denisa-Elena Ionete, the EU ambassador to Djibouti.
This cooperation aligns with the EU’s Global Gateway investment strategy, which aims to drive both digital and green transitions while delivering reliable, sustainable connections for partner countries. Key projects under discussion include e-permits, e-cabinet systems, cybersecurity, and digital skills training.
According to the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), Djibouti currently ranks 17th out of 47 African countries in ICT development, with a score of 61.6 out of 100—down from 16th place in 2023, when it scored 63.6. Additionally, the United Nations places Djibouti among the countries with a mid-range e-government development index (EGDI), scoring 0.2911 out of 1.
In cybersecurity, Djibouti ranks as a Tier 4 country by ITU standards, reflecting a basic government-driven commitment to cybersecurity. Legislative measures are cited as a strength, but the ITU notes that additional progress is needed in technical measures, organizational frameworks, capacity development, and cooperative actions.
The EU’s support is expected to boost the Djibouti Digital Foundation project, which is already backed by the World Bank. This project is aimed at transforming Djibouti into a tech hub by 2035 through the expansion of digital services and the establishment of a supportive environment for private-sector ICT investment.
Isaac K. Kassouwi
Digital transformation and artificial intelligence are key to modernizing nations and boosting their competitiveness. By investing in these areas, countries can upgrade infrastructure, improve public services, and strengthen their digital economies.
Tunisia plans to implement a digital transformation strategy and an artificial intelligence (AI) strategy, according to Communications Technology Minister Sofiene Hemissi. The announcement came on the sidelines of the 10th International Forum for Chief Information Officers (CIOs), held in Hammamet from Thursday, November 7 to Saturday, November 9. The initiatives aim to boost digital usage and leverage Tunisia’s AI potential.
Hemissi explained that the national digital transformation strategy will be built on several core pillars: digitizing administrative and public services, fostering the digital economy, supporting innovation and entrepreneurship in digital fields, enhancing communication network infrastructure, and strengthening legislative and regulatory frameworks to secure cyberspace.
The AI strategy, set for launch in 2025, aims to integrate AI into key sectors, including health, education, environment, and transport, while advancing digitalization and promoting open data usage. It also emphasizes creating business incubators and support programs for promising tech projects at the local level.
The upcoming digital strategy will replace the 2022-2025 plan, which positioned Tunisia among Africa's digital leaders. According to the latest report from the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), released in December 2023, Tunisia ranks 8th in Africa with a score of 77.2 out of 100 in ICT development. In e-government, Tunisia leads in North Africa and ranks third continent-wide, according to the United Nations’ E-Government Survey 2024: Accelerating Digital Transformation for Sustainable Development. The report gives Tunisia a score of 0.6935 out of 1, surpassing the African average of 0.4247.
Samira Njoya