Smartphone adoption remains relatively low in Uganda. According to the latest official statistics, the country has 16.7 million smartphones for 38.5 million active mobile subscribers.
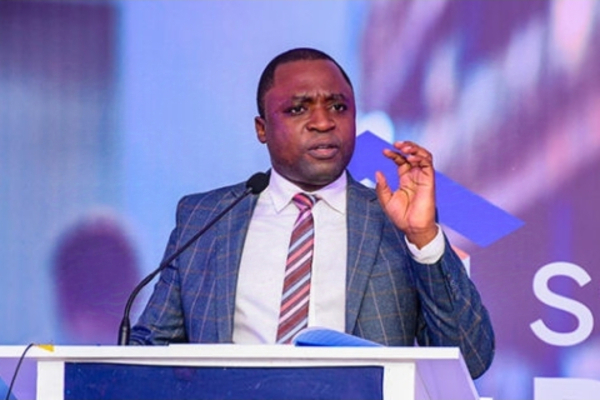
The Uganda Communications Commission (UCC) has launched an initiative in partnership with the Federation of Small and Medium Enterprises (FSME) to equip owners of micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) with smartphones. The initiative aims to reach 2,720 beneficiaries by the end of the year, with a target of distributing 60,000 devices over three years.
“The government covers 50% of the cost of each phone, while the FSME covers the remaining balance. The sh50,000 contribution by recipients is to ensure a sense of ownership. We don’t want them to sell off the phones,” explained John Walugembe, Executive Director of FSME.
This initiative comes at a time when Ugandan MSMEs are struggling to access smartphones and lack digital skills, despite the fact that, according to Mr. Walugembe, “digital technology has the potential to transform businesses.” Smartphone adoption remains low across the general population. According to the latest UCC data, Uganda has 16.7 million smartphones for 38.5 million active mobile subscribers.
The program is expected to boost the productivity of MSMEs in Uganda. For example, Aisha Nalule, a hairdresser benefiting from the initiative, believes her smartphone will help her promote her services on platforms like Facebook, X, and TikTok.
t Uganda has 1.1 million MSMEs, according to data from the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD). These businesses account for 80% of the country’s GDP and 90% of its private sector, according to the same source.
Isaac K. Kassouwi
E-commerce is flourishing in Africa, driven by its youthful, tech-savvy population and ongoing efforts to integrate economies across the continent.
In 2017, only 13% of Africans shopped online. However, according to a July 2024 report by cross-border payments company Nikulipe, this figure could soar to 40% by the end of 2025. This growth positions e-commerce as a key driver for strengthening intra-African trade.
Nikulipe's report, "Payments and E-commerce in Africa 2024," forecasts the African online commerce market to increase by $15 billion by 2028, representing a nearly 49% growth over four years. Data from Statista supports this trend, predicting an average annual growth rate of 11.7% between 2024 and 2028. This implies that the market size could double compared to 2023, when revenues stood at $16.1 billion.
Driving this expansion is a young, digitally connected population. With a median age of 19.7 years and over 1.4 billion people, Africa has significant demographic potential. Furthermore, internet usage has increased dramatically over the past decade, rising from 16% in 2013 to 37% in 2023, according to the International Telecommunication Union.
Despite this potential, intra-African e-commerce faces several challenges. According to a Trade Organization (WTO) report, inadequate infrastructure complicates cross-border trade. Additionally, the lack of harmonized e-commerce regulations between African countries adds to the complexity of cross-border transactions.
Toward Continental Trade Integration
Several initiatives are underway to facilitate intra-African trade. The African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) has introduced a digital trade protocol aimed at harmonizing regulations and simplifying online exchanges between African countries. Regional projects, such as the COMESA Digital Free Trade Area, also encourage e-commerce and digital integration among member states.
More African e-commerce players are expanding their reach across the continent. Jumia, a pan-African online retail company, operates in 11 countries and attracts 5.7 million active consumers worldwide. Anka Africa, based in Côte d'Ivoire, hosts over 20,000 online stores across 46 African countries, drawing more than one million visitors per month.
These platforms facilitate trade between African countries by providing a digital showcase for local producers and simplifying cross-border logistics.
Melchior Koba
Entrepreneur en série, il se distingue par ses solutions technologiques innovantes. A ce jour, il a fondé trois entreprises spécialisées dans des secteurs variés de la technologie.
Julius Mbungo (photo) est un entrepreneur technologique tanzanien. En 2023, avec Ebenezery Kimaro et John Mwapinga, il a fondé une entreprise visant à révolutionner les services de maintenance automobile. Leur objectif est de résoudre les défis auxquels sont confrontés les propriétaires de véhicules et les mécaniciens.
Spana propose un réseau de mécaniciens agréés, de fournisseurs de pièces détachées, ainsi qu’une application qui facilite la réservation, le paiement et la mise en relation avec des mécaniciens. Grâce à cette application, les utilisateurs peuvent demander divers services automobiles, que ce soit pour des réparations ou de l’entretien régulier, ainsi que des pièces de rechange à des prix abordables.
En parallèle, Julius Mbungo est également le fondateur et président-directeur général de Toolboksi, une plateforme numérique lancée en 2019. Toolboksi offre aux travailleurs du secteur informel des opportunités de travail stable, ainsi qu’un accès à une formation continue et à une évolution professionnelle. La start-up a pour mission de formaliser le processus de recrutement afin de permettre aux personnes défavorisées d’accéder à des emplois ou, au minimum, de nourrir l’espoir d’en obtenir.
Avant ces initiatives, en 2016, Julius avait cofondé la start-up Click n’ Cart, où il occupait le poste de directeur des opérations. Cette entreprise offrait une plateforme de commande et de livraison d’épicerie en ligne, permettant aux utilisateurs de se faire livrer leurs produits préférés en moins d’une heure.
Julius Mbungo est titulaire d’un diplôme d’administration des affaires option innovation commerciale et gestion de chaîne d’approvisionnement obtenu en 2015 à la School Business de la Mzumbe University. En juillet et août 2024, il a également suivi une formation en entrepreneuriat à la Clark Atlanta University, aux Etats-Unis.
Melchior Koba
Lire aussi:
Irene Phoebe Kiwia promeut les start-up spécialisées en IA, IoT et blockchain
A trained computer scientist, he specialized in developing fintech solutions. His goal is to make everyday life easier for Africans.
Ayo Akinola (photo) is a Nigerian business developer with a background in computer science, business intelligence, project management, and sales. He is the co-founder and CEO of Pocket, a financial app.
Founded in 2019, Pocket simplifies sending, receiving, and managing money for Africans. The app offers three types of wallets, called "pockets." The personal pocket allows users to transfer, spend, buy, and pay bills quickly. The business pocket helps users create an online store and manage professional payments. The group pocket allows users to manage funds with friends, colleagues, or family members.
Pocket is developed by Piggyvest, a startup Ayo Akinola also co-founded and where he serves as Chief Operating Officer. Established in 2016, Piggyvest helps individuals and businesses manage their finances, save, and invest easily.
Prior to Piggyvest, Akinola co-founded PuchCV in 2014, where he led business development until 2019. PuchCV connects talents with recruiters through a dedicated platform.
Ayo Akinola graduated from Covenant University in Nigeria, earning a bachelor's degree in computer science in 2012. In 2008, he interned with the IT department at Meyer PLC, a Nigerian paint manufacturer and distributor. In 2011, he served as assistant to the Chief Technology Officer at Fasyl Technology Group, a company specializing in IT services for financial operations.
Melchior Koba
As digital technology becomes essential in public service, many civil servants lack the necessary skills. This limits the government's ability to deliver efficient, tech-driven services. Addressing this skills gap will enhance productivity and service quality in sectors.
Kenya is set to launch a Centre of Excellence to train public servants in digital skills. Announced by the Ministry of Information, Communications & The Digital Economy on October 3, the center is hosted at the Kenya School of Government (KSG). It is part of a joint initiative with the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP).
The Centre will offer training in technology adoption and digital infrastructure to improve service delivery and promote job creation, officials said. Information, Communications, and the Digital Economy Cabinet Secretary, Margaret Ndung’u, met with UNDP and KSG officials to discuss the Centre’s governance and operational framework.
The project will incorporate a multi-sectoral approach for curriculum development and is expected to provide training to both local and international public sector professionals.
In an increasingly digital world, developing skills -particularly digital skills- is vital for economic growth and reducing unemployment, especially in emerging economies. In Kenya, this effort aligns with Vision 2030, which seeks to make the country industrialized and middle-income by 2030. The digitization of the civil service is an essential component of this vision. It aims to enhance the speed and efficiency of government services for users.
Hikmatu Bilali
Zepz, formerly WorldRemit, has secured $267 million to expand across Africa and other key markets. The funding round was led by Accel with participation from Leapfrog, TCV, Coller Capital, and a $20 million investment from the International Financial Corporation (IFC).
Since rebranding in August 2021 after acquiring Sendwave, Zepz has retained both the WorldRemit and Sendwave brands.
The investment will enhance Zepz’s position in Africa’s fintech market, supporting financial inclusion and the growing demand for cross-border transfers.
The ongoing digital transformation in Africa is impacting all sectors, including public administration, which plays a central role in the daily lives of citizens. By integrating modern technologies, the goal is to enhance efficiency and reduce bureaucracy, making government services more accessible and streamlined.
Liberian Minister of Commerce and Industry, Amin Modad (photo), recently announced the imminent launch of new online services as part of a broader strategy to modernize administrative services.
During a statement on Thursday, October 3, at the Ministry of Information, Modad outlined several services set to be digitized, including the Liberian Business Registry, the issuance of online import and export permits, and the introduction of a new business registration certificate with anti-fraud security features. He highlighted that the business registration process, which previously took one to two weeks, has already been shortened to three to five days, with the aim of further reducing this timeframe through a digital platform designed to eliminate corruption and simplify procedures.
This initiative is part of a modernization strategy to tackle bureaucratic bottlenecks and corruption, long-standing issues that have hindered the business environment in Liberia. Minister Modad has also secured funding to fully digitize the ministry's services, marking a critical step in the country's digital transformation.
The launch of these new services is expected to bolster the government's efforts to digitize public administration, though Liberia continues to lag in this area. The country currently ranks 182nd in the UN's 2024 e-government report, down from 177th in 2022, reflecting a decline in modernization efforts.
The digitization strategy led by the Ministry of Commerce is set to improve administrative efficiency, increase revenue from business registrations and permits, reduce processing times, enhance transparency, and improve Liberia’s international competitiveness.
Samira Njoya
He has over 10 years of experience in technology, data, and artificial intelligence. He is regarded as one of the most promising young tech entrepreneurs in Benin.
Luc Alapini (photo) is a serial entrepreneur and a prominent tech leader from Benin. He serves as the CEO of Bivariant, an inclusive platform that enables organizations and governments to accelerate the deployment of sovereign artificial intelligence (AI) across the entire supply chain.
Bivariant is an AI-focused platform designed for modern enterprises. The startup offers a variety of services, including AI strategies and data collection. It currently provides three main products. The first, Bivariant Studio, is an AI application development platform that allows businesses to seamlessly connect their AI applications to their data and create AI agents without any coding.
The second product, Bivariant Forge, is a platform for deploying and managing AI models, enabling businesses to implement large language models (LLMs) on their own infrastructure. Lastly, Bivariant Orbit serves as a centralized repository for storing, managing, and sharing AI resources, ensuring that teams have access to the latest AI innovations.
From Thursday, October 3 to Friday, October 4, Luc Alapini presented Bivariant at the FrancoTech exhibition in Paris, through the Benin Innov booth, an initiative of the Beninese government. The event, held at the Station F incubator, brought together 10 Beninese companies.
In addition to his role at Bivariant, Alapini is an advisor to Vocads, a startup that helps professionals in customer relations, marketing, and market research gather and analyze detailed feedback through voice surveys.
A seasoned entrepreneur, Alapini co-founded Tuniar in 2014, an inclusive mobile service for international money transfers and online payments. In the same year, he launched Enccore, a company specializing in modern cloud solutions and data intelligence. In 2020, he founded Oblic, a data engineering company.
Alapini holds a degree in statistical engineering from Benin's National School of Applied Economics and Management (ENEAM), which he earned in 2013. He also has a master's degree in applied mathematics from the University of South Brittany in France.
His career began in 2013 at Benin's Ministry of Health, where he worked as a data scientist. In 2014, he became the technical director of KYMA Ventures in Benin, a company specializing in innovation strategy and digital solutions. From 2020 to 2023, he served as technical director at Datexis Digital in France, a startup focused on data management and collection for businesses.
Melchior Koba
The digital transformation is progressing across the continent. Morocco is ramping up partnerships and investments in the digital sector, aiming to establish itself as a key player in the industry within Africa.
On Friday, October 4, in Rabat, Moroccan authorities launched a digital procedures and services platform. This project, developed in partnership with the International Labour Organization (ILO) and supported by the Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency, aims to streamline various administrative processes.
Younes Sekkouri, Minister of Economic Inclusion, Small Business, Employment, and Skills, highlighted that the objective is to digitize 55 administrative procedures and services. The platform will leverage data management and extraction technologies to optimize public policies, particularly in employment and skills development.
This initiative follows the launch of the "Digital Morocco 2030" strategy, which places e-government at its core. Morocco aims to become Africa’s leading digital hub by 2030. According to the "E-Government Survey 2024: Accelerating Digital Transformation for Sustainable Development," published in September, the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UN DESA) ranks Morocco 11th on the continent and 100th globally in the Online Service Index (OSI), with a score of 0.5618, above the African average of 0.3862.
The implementation of this platform is expected to improve interactions between the government and citizens, strengthen the relationship between businesses and employees by simplifying administrative procedures, reducing processing times, and enhancing productivity. It will also improve how businesses manage human resources and interact with public authorities.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
By adopting blockchain technology in May 2024 to modernize and optimize several of its state operations, Guinea-Bissau made a bold decision. This ambitious move aimed to enhance transparency, security, and efficiency in administrative and financial processes.
Guinea-Bissau is set to expand its blockchain-based salary management platform to cover all public sector employees. By November 2024, the solution could track the data of the country’s 26,600 civil servants and 8,100 retirees, according to Concha Verdugo Yepes, lead economist for Africa at the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and head of the institution’s Blockchain Solution program. She shared this information in an interview published on Wednesday, October 2, by IMF Country Focus, the IMF's news platform.
“The platform offers a secure, transparent digital ledger for managing the public service’s wage bill data, enabling almost real-time monitoring of salary and pensions eligibility, budgeting, payment approvals, and salary and pensions disbursements. It significantly improves data integrity and supports the production of timely and accurate fiscal reports for use by policymakers and the public. It’s one of the first platforms in sub-Saharan Africa to use blockchain technology to improve government operations, particularly in managing salaries and pensions,” Verdugo Yepes explained.
When the project was first conceived in 2020, 84% of the state’s tax revenues were used to pay the salaries of Bissau-Guinean public servants—the highest ratio in the region, according to José Gijon, the IMF’s mission chief for Guinea-Bissau. He noted, “For every hundred dollars collected in taxes, eighty-four dollars were spent on salaries. This ratio has now declined to 50 percent—a huge improvement, but still high compared to the West Africa Economic and Monetary Union (WAEMU) regional fiscal convergence criteria of wages not exceeding 35 percent of tax revenues.”
The government of Guinea-Bissau adopted blockchain technology to combat various issues, including poor governance in state finances, embezzlement, and corruption. The system aims to eliminate ghost workers, payroll fraud, and other schemes that persisted due to poor traceability of public funds. The platform securely records, stores, and shares information in a way that prevents tampering. Every transaction is inviolable, and the system detects any discrepancies in salary data, flagging them for the relevant authorities.
For the IMF, the solution offers additional benefits by simplifying audit reporting and reconciliation processes. It also provides reliable, up-to-date, and high-quality data for artificial intelligence models.
According to the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), governments must have credible public finance management frameworks to build trust with international donors and local and foreign investors. A crisis of confidence in government threatens the financial resources it needs for the country’s economic and social development.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
More...
Developed to simplify the ticketing process for events, the solution won the first prize of the NBA Africa’s Triple-Double accelerator program.
Tix Africa is a digital solution developed by the Nigerian startup Festival Coins, enabling users to purchase event tickets online with just a few clicks. Founded in 2019 by Folayemi Agusto, the Lagos-based startup raised an undisclosed amount in 2021 to support its growth.
Commenting on the funding round, Agusto stated, “The new capital will enable us to scale quicker and to integrate the currently separate products and services we offer, including an app offering event attendees a marketplace where they can buy, trade and resell tickets securely.”
Tix Africa offers a mobile app available on both iOS and Android, with over a thousand downloads according to Play Store data. Users can create an account and access various events on the platform, ranging from sports and wellness to arts, culture, spirituality, religion, music, and performances.
Event promoters can showcase their events on Tix Africa, with the ability to track ticket sales from a dashboard. “You can create events that repeat more than once within a specific period. Then, within a single checkout, attendees will be able to select the preferred date they’d like to attend your event. This feature allows you to manage single ticket pages for multiple events and make the same tickets available across multiple dates, thus saving you time and effort,” explains the startup.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
After several years of experience in tech companies, she is now specializing in the beauty and wellness sector. She leverages her technological skills to invigorate this industry.
Maya Ammouche (photo) is an Algerian computer scientist and businesswoman. She is the founder and CEO of Izya, an app dedicated to the beauty, health, and wellness sectors.
Launched in 2022, Izya aims to connect professionals in these industries. The app lists top establishments and experts, offering personalized services for individuals either in a salon or at home as well as for companies focused on employee well-being. Its main feature allows clients to book appointments at the nearest establishment or request an in-home service provider.
“We offer a SaaS [Software as a Service] solution that helps businesses better manage their operations, while making it easier for clients to book appointments. Clients also benefit from a range of both qualitative and quantitative advantages. They will enjoy access to a directory of the best value-for-money services,” explains the founder of Izya.
Before founding Izya, Maya Ammouche co-founded the accelerator SprintHub in 2020, where she served as Vice President of Marketing and Sales until 2023. She holds an engineering degree in computer engineering, which she earned in 2007 from the Houari Boumediène University of Science and Technology.
Her career began in 2009 at Altex-Corp, an IT services company, where she worked as a consulting engineer. In 2012, she became Director of Sales Development at Corpotrade, a commercial firm. In 2018, she was appointed Director of Marketing and Partnerships at Yassir, a startup focused on ride-sharing and delivery services. In 2020, she joined Cleverzone, a technology company, as Director of Marketing, Sales, and Business Development.
Melchior Koba
Akwa Ibom state in Nigeria will host the Akwa Ibom Tech Week (AKTW) 2024 from October 28 to November 2, under the theme "Building a Resilient Innovation Ecosystem."
This year’s event aims to bring together local and global innovators to explore how the state can position itself as Africa’s next tech hub.
Innovate Africa, an early-stage investment fund will headline the event with a $2.5 million venture fund to support promising startups. Attendees will also have the opportunity to engage with Kristin Wilson, Innovate Africa's co-founder, through a series of curated fireside chats, knowledge-sharing sessions, and masterclasses throughout the week.
The issue of fake diplomas poses a significant challenge for Cameroon, as it does for many other countries. It undermines the integrity of the educational system and damages the credibility of institutions, as well as the local workforce.
On October 1, 2024, the Cameroonian government introduced a new digital platform aimed at verifying the authenticity of diplomas issued by universities, public administrations, and private institutions. The initiative was unveiled at the École Normale Supérieure (ENS) of the University of Yaoundé 1, during a ceremony co-chaired by the Minister of Higher Education (Minesup), Jacques Fame Ndongo, and the Minister of Public Service and Administrative Reform (Minfopra), Joseph Le.
The digital platform is described as an "essential tool" designed to streamline the often lengthy recruitment process within the public sector, which has been slowed by cumbersome diploma certification procedures. “This platform is not only a modern tool for verifying the authenticity of diplomas but also a guarantee of trust for citizens, employers, and especially public institutions,” said Joseph Le.
As per a joint circular from May 8, 2024, Minesup will provide Minfopra with a secure software interface, allowing access to diploma data. In return, Minfopra will be able to submit verification requests digitally, speeding up the process. A secure response confirming the authenticity of the diploma will then be sent back to Minfopra through the platform. According to Minister Le, the platform is “a crucial step” in the government's commitment to enhancing transparency and efficiency in public administration. The initiative is part of a broader modernization effort to improve the management of civil servant integration processes.
The platform aims to address the growing issue of fake diplomas in both the public and private sectors. For example, in June 2024, Defense Minister Joseph Beti Assomo announced the discovery of 1,312 fake diplomas during the recruitment process for young gendarmes and soldiers for the 2024 fiscal year. Similarly, in 2022, nearly 1,000 gendarmerie students were dismissed due to falsified credentials. This new platform is expected to help decrease such incidents by streamlining document verification.
The platform's launch follows an agreement signed between Minesup and Minfopra on April 6, 2023. It will be implemented in collaboration with the ministries that issue the most diplomas, including Minesup, the Ministry of Secondary Education (Minesec), the Ministry of Basic Education (Minedub), and the Ministry of Employment and Vocational Training (Minefop). Through this initiative, Minfopra aims to verify diploma authenticity more effectively and significantly reduce the processing times for recruitment and certification.
P.N.N.