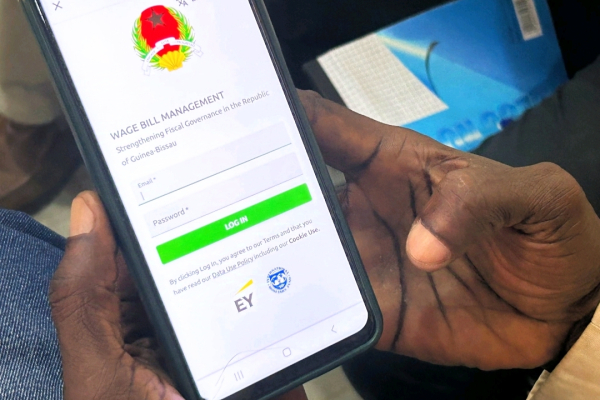
By adopting blockchain technology in May 2024 to modernize and optimize several of its state operations, Guinea-Bissau made a bold decision. This ambitious move aimed to enhance transparency, security, and efficiency in administrative and financial processes.
Guinea-Bissau is set to expand its blockchain-based salary management platform to cover all public sector employees. By November 2024, the solution could track the data of the country’s 26,600 civil servants and 8,100 retirees, according to Concha Verdugo Yepes, lead economist for Africa at the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and head of the institution’s Blockchain Solution program. She shared this information in an interview published on Wednesday, October 2, by IMF Country Focus, the IMF's news platform.
“The platform offers a secure, transparent digital ledger for managing the public service’s wage bill data, enabling almost real-time monitoring of salary and pensions eligibility, budgeting, payment approvals, and salary and pensions disbursements. It significantly improves data integrity and supports the production of timely and accurate fiscal reports for use by policymakers and the public. It’s one of the first platforms in sub-Saharan Africa to use blockchain technology to improve government operations, particularly in managing salaries and pensions,” Verdugo Yepes explained.
When the project was first conceived in 2020, 84% of the state’s tax revenues were used to pay the salaries of Bissau-Guinean public servants—the highest ratio in the region, according to José Gijon, the IMF’s mission chief for Guinea-Bissau. He noted, “For every hundred dollars collected in taxes, eighty-four dollars were spent on salaries. This ratio has now declined to 50 percent—a huge improvement, but still high compared to the West Africa Economic and Monetary Union (WAEMU) regional fiscal convergence criteria of wages not exceeding 35 percent of tax revenues.”
The government of Guinea-Bissau adopted blockchain technology to combat various issues, including poor governance in state finances, embezzlement, and corruption. The system aims to eliminate ghost workers, payroll fraud, and other schemes that persisted due to poor traceability of public funds. The platform securely records, stores, and shares information in a way that prevents tampering. Every transaction is inviolable, and the system detects any discrepancies in salary data, flagging them for the relevant authorities.
For the IMF, the solution offers additional benefits by simplifying audit reporting and reconciliation processes. It also provides reliable, up-to-date, and high-quality data for artificial intelligence models.
According to the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), governments must have credible public finance management frameworks to build trust with international donors and local and foreign investors. A crisis of confidence in government threatens the financial resources it needs for the country’s economic and social development.
Adoni Conrad Quenum