Telecom (147)
With the rapid global shift toward the digital economy, equipping young people with digital and business skills is essential for fostering innovation, entrepreneurship, and economic growth.
Zambia has launched an Online Entrepreneurship Learning Program to foster digital innovation and entrepreneurship. The initiative, launched on March 31, was unveiled by Hon. Felix Mutati, Minister of Technology and Science, alongside Mr. Ville Tavio, Finland’s Minister for Foreign Trade and Development. It aims to equip young Zambians with critical digital and business skills.
During the launch event, the Zambia Information and Communications Technology Authority’s (ZICTA) Director General, Eng. Collins Mbulo highlighted how the initiative aligns with ZICTA’s mission to build an inclusive digital society.
The program is implemented by Nokia in partnership with Airtel Networks Zambia PLC. It is designed to empower aspiring entrepreneurs by leveraging technology for business growth and job creation.
Youth unemployment remains a significant challenge in Zambia. Data from the Zambia Statistics Agency shows that in 2023, the youth unemployment rate was 12%, leaving many young people struggling to find formal jobs. This underscores the importance of entrepreneurial skills, enabling young individuals to create their own employment opportunities rather than depending solely on traditional job markets.
By providing access to essential digital skills, the Online Entrepreneurship Learning Program is expected to drive economic growth, foster innovation, and create opportunities for Zambia’s youth in the evolving digital economy.
Hikmatu Bilali
Over the past four years, Cameroon, Gabon, Chad, the Central African Republic, Congo, and Equatorial Guinea have collaborated on a project designed to enable seamless communication for their citizens traveling within the region, eliminating the need to change SIM cards. This initiative seeks to foster greater sub-regional integration.
Central African citizens could soon communicate freely across borders without incurring extra charges, as regional telecommunications ministers have issued a three-month deadline to finalize a free roaming project.
The decision followed a meeting of Telecommunications Ministers of the Central African Economic and Monetary Community (CEMAC) held last week in Bangui, Central African Republic. During the meeting, participants discussed obstacles hindering the initiative, which seeks to eliminate disparities in roaming costs that lead to expensive communications and impede the telecommunications sector's development.
In November 2021, CEMAC countries signed bilateral agreements to implement free roaming. However, the project has faced substantial delays. In April 2024, the Assembly of Telecommunications Regulators of Central Africa (ARTAC) reported that only two of the 213 planned interconnections had been established. These connections involved MTN Cameroon and MTN Congo, and Airtel Gabon and Orange Cameroon.
While the specific obstacles to free roaming were not disclosed, ARTAC's objectives for a 2024 seminar aimed at accelerating the process shed light on potential issues. These include delays in finalizing minutes, including tariff agreements between regulators, late signing of interconnection and roaming contracts, potential technical and legal difficulties for the involved parties, issues related to the separation of roaming and traditional international traffic on direct interconnection links, and the selection of technology for those links.
By Isaac K. Kassouwi,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
A new cycle of transformation is underway in the African telecom market. Under growing pressure, only the most decisive operators with an ambitious vision will be able to seize the opportunity, paving the way for a new phase of growth.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is generating growing interest across various sectors in Africa. Google estimates that its adoption could contribute up to $1.5 trillion to the continent’s economy by 2030. In the telecommunications sector in particular, AI has the potential to act as a growth catalyst, a key tool for addressing numerous challenges, and a gateway to new opportunities. This comes at a time of profound market transformation, marked by increasing operational challenges (network maintenance costs, energy, marketing, and commercial services) and rapid technological changes.
Over the past fifteen years, the market has witnessed increased consolidation and multiple divestments, reflecting the strategic repositioning necessary for players facing fierce competition, margin pressures, and increasingly stringent regulations. In 2014, Etisalat reorganized its presence by selling its subsidiaries to Maroc Telecom. In 2016, Orange acquired Millicom’s (Tigo) subsidiary in the Democratic Republic of Congo, as well as Bharti Airtel’s subsidiaries in Burkina Faso and Sierra Leone, while withdrawing from Kenya. In 2021, the sale of its operations to the Ghanaian state marked Millicom’s complete exit from Africa. Several acquisitions, divestments, and bankruptcies have followed over the years, including Vodafone’s sale of its Ghanaian operations to Telecel Group in 2023 and MTN Group’s withdrawal from Guinea and Guinea-Bissau in 2024.
A Decisive Turning Point
Today, AI is seen by several telecom players in Africa as an opportunity to be fully leveraged. It promises greater efficiency and cost reduction. At the Northern Africa OTF event organized by Huawei during the Mobile World Congress 2025 in Barcelona, Spain, Bruce Xun, president of Huawei’s global technical service, identified AI as a major inflection point. According to him, AI will optimize operations, enhance decision-making, and create new sources of value, paving the way for innovative and high-performance telecom solutions in the digital age. This is why the Chinese technology company has been investing for several years in AI research and integration into its new services and infrastructures, particularly telecom towers that adjust their capacity based on network traffic.
Huawei is not the only company to recognize AI’s transformative potential. In an interview with CIO Mag in 2024, Jocelyn Karakula, chief technology innovation officer at Orange Middle East and Africa (OMEA), highlighted that the company had already adopted AI for various applications. “AI is a strategic priority for Orange, given its ability to accelerate value creation and enhance performance across multiple domains. In terms of networks, which are primarily mobile in Africa, we manage increasingly complex technologies (2G, 3G, 4G, and now 5G) in countries facing energy challenges. To ensure optimal network performance, AI provides additional capabilities that guarantee the quality of service and customer experience,” he explained.
A study published in 2024 by Nvidia reveals that nearly 90% of telecom companies worldwide use AI, with 48% in the pilot phase and 41% in active deployment.
A Wide Range of Applications
In several countries, notably Nigeria and South Africa, MTN Group has made AI a cornerstone of its customer service. Through the Zigi chatbot and virtual assistants, the company has reduced response times to customer inquiries and improved satisfaction levels. Vodacom, in collaboration with Nvidia, is developing a virtual network management platform that uses AI to facilitate decisions on network performance improvements. In Kenya, Safaricom has deployed Nokia’s AVA energy efficiency software, which utilizes AI and machine learning algorithms to automate the shutdown of inactive equipment during low-usage periods, thereby reducing energy consumption and costs.
Hicham Ennoure, executive vice president of Moov Money Gabon, recently revealed in Barcelona that the rapid modernization of the platform, combined with targeted marketing strategies based on data analysis, allowed the company to increase its user base by 84% and its revenue by 85% in 2024.
Operational Efficiency
Major strategy consulting firms are also optimistic about AI’s positive impact on telecoms. McKinsey cites the example of a European telecom operator that increased its marketing campaign conversion rates by 40% while reducing costs, thanks to AI-generated personalized content. Another example is a Latin American operator that improved customer service productivity by 25% and enhanced the quality of customer experience, with the potential to reduce costs by 15% to 20%.
“Our experience working with clients indicates the potential for telcos to achieve significant EBITDA impact with gen AI. In some cases, estimates indicate returns on incremental margins increasing 3 to 4 percentage points in two years, and as much as 8 to 10 percentage points in five years, by enhancing customer revenue through improved customer life cycle management and decisively reducing costs across all domains,” writes McKinsey.
Challenges to Overcome
While AI offers considerable opportunities, its adoption in Africa is not without obstacles. IBM indicates that integrating any new technology requires investment. Modern AI investments are costly, even though they promise long-term profitability. However, not all operators have the financial capacity to undergo this transformation.
The American firm also notes that AI adoption fundamentally transforms businesses, requiring many employees—if not all—to acquire new skills to integrate AI tools into their work. Yet, Africa still faces a shortage of specialists in advanced technologies. Moreover, ethical and regulatory issues related to AI usage, particularly regarding data protection and privacy, require special attention.
To overcome these challenges, the GSMA recommends close collaboration between governments, operators, and technology players. Public authorities must establish policies that encourage AI-driven innovation and investment while ensuring a balanced regulatory framework. Meanwhile, operators must invest in training and developing local talent to maximize the benefits of this technology.
Muriel EDJO
Kenya: Communications Authority Takes Action Against TikTok Following Child Exploitation Allegations
Kenya’s crackdown on TikTok’s content moderation failures is a significant step toward safeguarding digital spaces in Africa, with broad implications for the continent’s development.
The Communications Authority of Kenya (CA) has launched an urgent investigation following a BBC report alleging that minors in Kenya were involved in sexualized livestreams on TikTok, with the platform reportedly profiting from digital gifts sent by viewers.
Expressing serious concern, the CA emphasized, in a release dated March 6, that such activities violate both Kenyan and international laws on child protection. Kenya’s existing legal framework—including the Computer Misuse and Cybercrimes Act, the Films and Stage Plays Act, the Children Act, and the Data Protection Act—strictly prohibits online child exploitation. These laws align with global standards such as the United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child (UNCRC) and the African Charter on the Rights and Welfare of the Child.
In response to the BBC report, the CA has ordered TikTok to remove all explicit content involving minors, explain how it bypassed moderation, and present a plan to strengthen child protection measures. TikTok will also face a formal investigation with potential sanctions for legal violations. Meanwhile, the CA is increasing public awareness by educating parents on online safety and promoting parental control tools.
The CA also reminded TikTok of its previous commitments to improve content moderation and establish a local office in Kenya, following government directives in 2023. The latest revelations suggest that significant gaps remain in TikTok’s enforcement of its policies, necessitating stronger regulatory action.
The CA has urged all online platforms operating in Kenya to comply with the country’s legal and regulatory requirements, particularly regarding the protection of minors and the prevention of harmful content. Parents and guardians are also encouraged to utilize online child protection resources at https://cop.ke-cirt.go.ke/.
The authority reaffirmed its commitment to ensuring a safe, ethical, and secure digital space for all Kenyans and vowed to hold digital platforms accountable for any violations.
Kenya’s decisive response to online child exploitation could set a precedent for stronger social media regulation across Africa, where digital platforms have increasingly become spaces for abuse, including child exploitation, hate speech, defamation, and misinformation.
Online child exploitation is a growing concern in Africa. A 2024 report by ChildFund International and the African Child Policy Forum revealed a significant increase in online child sexual exploitation and abuse across the continent, with over 60% of unidentified victims being young children, including infants and toddlers, and 65% being girls.
Hikmatu Bilali
Africa's mobile internet market is rapidly expanding, fueled by rapid digital growth, a young and connected population, and substantial investments in telecommunications infrastructure.
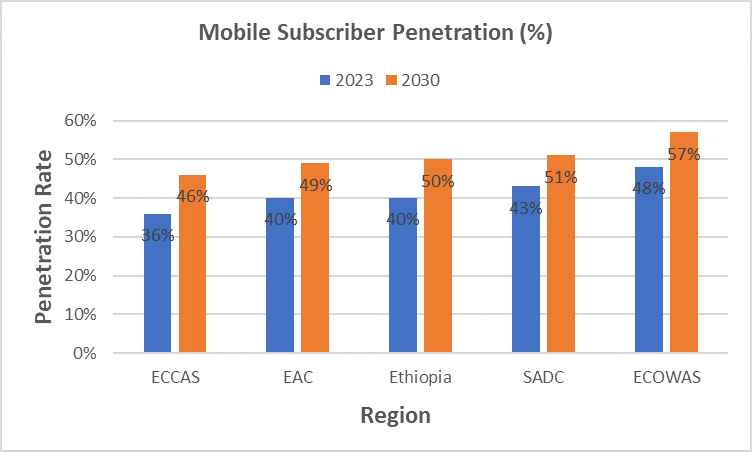
Sub-Saharan Africa's monthly mobile data traffic per connection is projected to nearly quadruple by 2030, increasing by almost six gigabytes (GB), according to the GSMA. This growth will be driven by the expansion of high-speed mobile network coverage and rising demand for data-intensive content, such as gaming and video streaming.
The Economic Community of Central African States (ECCAS) will see particularly strong growth, with monthly mobile data traffic expected to increase sixfold. Countries like Angola, Chad, and Equatorial Guinea could see a tenfold increase. However, mobile data consumption in the region is projected to remain below the Sub-Saharan African average of eight GB due to lower 4G and 5G penetration rates.
The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) is expected to have the highest mobile data traffic in Sub-Saharan Africa by 2030, reaching 10.1 GB.
The GSMA also indicates that the growth of mobile data traffic in Sub-Saharan Africa will be fueled by greater smartphone adoption. It estimates smartphone adoption rate will rise from 51% in 2023 to 81% in 2030. ECOWAS is expected to be the most dynamic region due to its swift implementation of necessary actions to develop the telecom sector. Its smartphone adoption rate, which stood at 54% in 2023, is projected to reach 83% by 2030.
By then, the five largest smartphone markets in Sub-Saharan Africa are expected to be Nigeria (230 million connections), South Africa (140 million), Ethiopia (97 million), Tanzania (92 million), and Kenya (72 million).
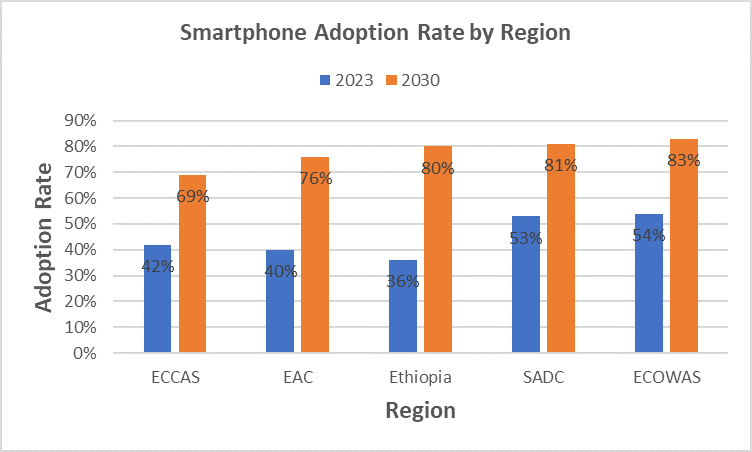
The number of mobile phone service consumers will also be highest in the ECOWAS region.
“By 2030, the economic contribution of mobile telecommunications in Sub-Saharan Africa will reach $170 billion. This growth will primarily stem from the continued expansion of the mobile ecosystem and its spillover effects on other sectors, as they increasingly benefit from the productivity and efficiency gains driven by mobile service adoption,” the GSMA stated. In 2023, the mobile industry contributed $140 billion to Sub-Saharan Africa’s economy.
However, for all of GSMA’s projections to materialize, Sub-Saharan African governments must take the necessary measures to encourage telecom operators to invest in networks. Otherwise, mobile network investment is expected to decline after 2027, despite relatively increasing revenues.
Special attention must also be given to smartphone affordability to promote its adoption and facilitate internet access for populations. GSMA recommends eliminating sector-specific excise duties on mobile telecommunications services, including customs duties on mobile phones, reducing VAT rates, and scrapping fixed consumer taxes (such as activation or numbering taxes) that make these services less affordable.
Muriel Edjo
Mobile payments are rapidly expanding across Africa, significantly increasing access to financial services. Leading providers like Orange Money are at the forefront of this digital shift, delivering innovative and accessible solutions tailored to the local population.
Orange Money Burkina Faso announced the upgrade of its mobile financial services platform with Mobiquity® Pay X, a next-generation solution developed by Comviva, at the Mobile World Congress (MWC) in Barcelona on Wednesday, March 5. The evolution aims to enhance innovation and provide an improved user experience for Orange Money customers in Burkina Faso.
"Orange Money is one of our key growth drivers, contributing significantly to economic and social development in Burkina Faso. We are particularly impressed by Mobiquity® Pay's microservices architecture, open design, and API-first philosophy, which will enable us to significantly expand the Orange Money ecosystem in the region and provide disruptive services to our customers," said Christophe Baziemo, CEO of Orange Money Burkina Faso.
The mobile financial services market in West Africa is experiencing strong expansion, driven by the rise of digital payments and operators' initiatives to strengthen financial inclusion. According to the financial results of the Orange Côte d'Ivoire Group, which includes Orange Burkina Faso, the group closed 2024 with consolidated revenue of 1,084.1 billion CFA francs ($1.8 billion), a 6.6% increase. This performance is primarily fueled by key sectors such as mobile data, Orange Money, and fiber, illustrating the growing demand for mobile financial services in the region.
The new cloud-based platform represents a cutting-edge solution offering a comprehensive suite of information management services, particularly for digital money, wallets, and payments. Its robust and scalable architecture ensures a secure and user-friendly experience, while enhanced modularity enables faster market deployment of new services.
With over ten years of expertise in digital payments, Comviva has deployed its Mobiquity® Pay platform in more than 60 projects across 45 countries. This modernization is expected to enable Orange Money Burkina Faso to launch new services more quickly, improve interoperability with other financial systems, and enhance transaction security. Ultimately, the initiative will help boost the mobile payments ecosystem and promote greater financial inclusion in the country.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
Africa, with its vast territories and growing population, faces an urgent need for digital connectivity. Despite progress made, many regions remain excluded from Internet access, hindering their economic and social inclusion in an increasingly digital world.
Orange Africa and Middle East (OMEA) and French satellite company Eutelsat announced a partnership on Tuesday, March 3, to accelerate the deployment of satellite internet across Africa and the Middle East. The goal is to reduce the digital divide in these regions by providing reliable and affordable high-speed access, particularly in underserved "white zones" lacking connectivity.
"This partnership illustrates our commitment to connecting all territories and bridging the digital divide in Africa and the Middle East. Today, Orange serves more than 160 million customers in the region, and is pursuing its ambition to provide digital access for all," said Jérôme Hénique, CEO of Orange Africa and Middle East.
The partnership leverages the Eutelsat Konnect satellite, an advanced technology enabling download speeds of up to 100 Mbps. Initial deployments will focus on Côte d'Ivoire, Senegal, and the Democratic Republic of Congo, with plans to gradually expand across the region. The initiative aims to bridge the connectivity gap in remote areas by providing tailored solutions for both individuals and businesses.
The agreement reflects a shared commitment to reducing the digital divide by offering high-speed access to currently underserved regions. According to the "The Mobile Economy Sub-Saharan Africa 2024" report by the GSMA, Sub-Saharan Africa is the world's least connected region, with only 27% of the population using mobile internet services, leaving a 13% coverage gap and a 60% usage deficit.
By combining Orange’s telecommunications expertise with Eutelsat’s technological innovation in satellite services, the partnership is expected to deliver tailored offerings for both individuals and businesses, ensuring secure, reliable, and high-performance connectivity. The complementarity of fixed, mobile, and satellite technology solutions will help connect isolated areas and meet the growing demand for internet access in the region.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
Orange's financial results from last year highlighted a strong revenue surge in the Middle East and Africa (OMEA) region. This demonstrates the success of the French company's substantial investments in these emerging markets.
French telecommunications group Orange recently indicated its Africa and Middle East division (OMEA) was the primary driver of group growth in 2024.
OMEA, encompassing 16 African subsidiaries and Jordan, generated 7.683 billion euros in revenue, up 11.1% from 2023. This performance contrasted sharply with other markets: France saw a 0.4% increase, while Europe and Orange Business each reported a 2.1% decline.
The division accounted for nearly 19% of Orange's total revenue, which reached 40.26 billion euros in 2024. Earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, amortization, and after lease costs (EBITDAaL) for OMEA rose 13.1%, signaling strong financial health.
"The Africa & Middle East region once again delivered a robust performance, driven by its growth engines, namely mobile data, fixed broadband, B2B and Orange Money. Orange now has over 160 million mobile customers and almost 40 million Orange Money customers on the continent,” Orange wrote in a release.
Mobile data revenue grew by 18.4%, fixed broadband by 19.5%, Orange Money by 20.4%, and B2B services by 12.5%. Several major investments in 2023 contributed to these strong results. OMEA continued expanding mobile network coverage, improving service quality, developing fiber optic networks, diversifying mobile financial services, strengthening business offerings (cloud, cybersecurity, etc.), introducing 5G in several markets including Senegal and enhancing its commercial strategy with the super app Max It.
Orange CEO Christel Heydemann emphasized that the 2024 successes “fully reflect the execution of our Lead the Future strategic plan.” Launched in 2023, this strategy is built on four pillars, including accelerating OMEA’s growth by deepening its local presence and expanding its role as a multi-service operator.
For 2024, Orange achieved its EBITDAaL targets, with a 2.7% increase from the previous year. Looking ahead to 2025, the group is aiming for approximately 3% growth and is counting on OMEA’s continued momentum to help achieve that goal.
By Muriel EDJO,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
In Africa, the advent of 5G is revolutionizing the telecommunications sector, delivering ultra-fast speeds, reduced latency, and enhanced connectivity. This technology paves the way for new applications in key industries, which Tunisia can now leverage to accelerate its digital transformation.
Orange Tunisia officially launched its 5G network on Friday, offering ultra-high-speed connectivity. This milestone marks a major turning point in Tunisia’s digital development and positions Orange Tunisia at the forefront of innovation in the telecommunications sector. The introduction of 5G addresses the growing demand for connectivity, benefiting both professionals and individuals while supporting the country’s digital transition.
"5G from Orange Tunisia delivers an optimized customer experience with ultra-fast download speeds, minimal latency, and increased connection capacity. With speeds three to four times faster than 4G, 5G meets the rising need for connectivity," the operator stated in a press release.
Apart from this major technological rollout, Orange Tunisia has introduced the MAXBOX 5G, a next-generation WiFi 6 router designed to provide an optimal home experience. With unmatched performance, the MAXBOX 5G includes a Turbo mode, specifically tailored for gaming and streaming enthusiasts, allowing users to fully harness 5G’s capabilities in their daily digital activities.
This initiative is also accompanied by the creation of a “5G Lab”, an innovation hub dedicated to testing 5G applications in key sectors such as Industry 4.0, healthcare, culture, and education. Open to businesses, startups, and academic institutions, this laboratory aims to foster collaborative innovation and explore how 5G can drive Tunisia’s digital transformation.
A Milestone for Tunisia’s Telecom Sector
The launch of 5G is part of a broader digital development strategy. With this deployment, Orange Tunisia becomes the fifth operator within the Orange Group to commercialize 5G in Africa and the Middle East. The network is already operational across 400 sites, covering multiple regions, and will progressively expand to reach all governorates in the country.
This launch aligns with the forecasts of the African Telecommunications Union (ATU), which, in its January 30 report titled “5G Readiness and Relevant Use Cases in Africa,” highlights 5G’s potential to transform the continent’s economy. According to the report, applications such as smart agriculture, remote healthcare, and online education could be revolutionized by 5G, significantly improving the quality of life across Africa.
The GSMA, the global association of mobile operators and manufacturers, goes even further, estimating that 5G networks could contribute $26 billion to Africa’s economy by 2030. This projection underscores 5G’s enormous potential to drive growth in key sectors and support economic development across the continent.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
In a global context where digital technology is becoming a key driver of economic and social development, the Liberian government is investing to ensure high-quality Internet access for all, including more affordable costs.
The Liberia Telecommunications Authority (LTA) is modernizing the Liberia Internet Exchange Point (LIXP), the country’s sole internet exchange point. Last week, the regulator acquired $39,000 worth of new equipment for the LIXP, which it said will improve internet quality.
“The main goal of an IXP is to improve the efficiency of Internet routing by allowing for direct interconnection between networks. This can help reduce latency, decrease bandwidth costs, improve network performance, and enhance overall Internet reliability and resilience" the LTA said in a Facebook statement.
Improved internet connectivity could support the government’s “Digital Fast Track” program, which aims to accelerate Liberia’s digital transformation by improving digital infrastructure and services. The government considers digital infrastructure crucial for achieving national development goals.
The UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UN DESA) ranks Liberia 47th out of 54 African countries in e-government deployment, with an e-Government Development Index (EGDI) score of 0.2513 out of 1. UN DESA notes that Liberia has an average EGDI, “reflecting steady growth in digital integration despite various challenges.” The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) ranks Liberia 36th out of 47 African countries for ICT development, with a score of 37.1 out of 100.
Despite government efforts, Liberia faces significant digital infrastructure deficits beyond the internet exchange point. The country has only one fiber-optic submarine cable, which is frequently disrupted and affects internet access. According to Datacenterplatform, Liberia has only one data center. UN DESA gives Liberia a telecom infrastructure score of 0.1238 out of 1, a key component of the EGDI.
By Isaac K. Kassouwi,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
More...
Leveraging technology can accelerate Africa’s development, ensuring digital inclusion, economic resilience, and global competitiveness. Nigeria's leadership in connectivity and AI will likely inspire similar initiatives across the continent, positioning Africa as a key player in the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
The Federal Executive Council (FEC) has approved two major initiatives under the Federal Ministry of Communications, Innovation & Digital Economy (FMCIDE) to accelerate Nigeria’s digital transformation. This was during the council meeting on February 4, which was chaired by President Bola Tinubu.
The Minister of Communications, Innovation & Digital Economy Bosun Tijani remarked, “Access to connectivity is something many of us take for granted. Expanding mobile coverage through additional base stations will significantly improve the quality of life for millions of Nigerians in underserved regions.”
The first approval establishes the Nigeria Universal Communication Access Project under a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) funding model. This initiative aims to connect over 21 million people across 4,834 rural and underserved communities that currently lack basic mobile communication access. The project complements Project Bridge, Nigeria’s 90,000km Fibre Fund, by expanding connectivity to remote areas, improving digital inclusion, and enhancing economic opportunities for millions.
The second approval supports Nigeria’s ambition to become a global leader in Artificial Intelligence (AI) through the creation of the National AI Trust - a pioneering initiative designed to mobilize resources, provide oversight, and guide AI development across key economic sectors.
The National AI Trust, the first of its kind globally, will consist of 10 AI experts, the Minister of Communications, Innovation & Digital Economy, and the Minister of Science, Innovation & Technology. The Trust will play a strategic role in shaping Nigeria’s AI landscape, future-proofing investments, driving job creation, and attracting foreign direct investment (FDI).
According to DataReportal’s Digital 2024: Nigeria, only 45.5% of Nigerians have internet access, leaving a large segment of the population unconnected. The Nigeria Universal Communication Access Project seeks to close this gap by bringing connectivity to people in underserved communities and fostering digital inclusion and economic growth.
In parallel, the National AI Trust reinforces Nigeria’s ambition to lead in artificial intelligence. According to the National Artificial Intelligence Strategy, Nigeria’s AI market is expected to grow to $434.4 million by 2026, with a CAGR of 44.2%, highlighting the sector’s rapid expansion and potential.
These initiatives align with Nigeria's broader digital economy goals, aiming to enhance connectivity, foster innovation, and ensure inclusive growth across the nation. By prioritizing Connectivity Infrastructure and Artificial Intelligence, Nigeria is positioning itself at the forefront of Africa’s digital transformation.
Hikmatu Bilali
The government has ambitious goals for the digital economy this year, with expanding high-speed connectivity at the forefront. Improving and expanding high-speed internet access is a top priority. While fiber optics remain crucial, the government is also exploring other technologies to achieve this goal.
Guinea is moving closer to launching a satellite to strengthen its digital sovereignty and technological capabilities.
On Friday, January 24, Rose Pola Pricemou, Minister of Posts, Telecommunications, and the Digital Economy, met with a delegation from AirSAT Technology, a Chinese company specializing in commercial satellite solutions, to discuss potential collaboration on the project.
According to a ministry statement, the satellite project aims to facilitate large-scale data transmission and lay the groundwork for technological skills transfer in the aeronautics sector. The initiative also includes plans to train local engineers to manage processes related to the operation and maintenance of satellite technologies.
This initiative aligns with Guinea's push for digital sovereignty. Such a project could be a turning point for the country, equipping it with a critical tool to modernize its telecommunications and reduce dependence on foreign infrastructure.
According to Space in Africa’s 2023 Annual Report on the African space industry, the sector was valued at $19.49 billion in 2021, with projected growth of 16% by 2026, reaching $22.64 billion.
By pursuing this ambition, Guinea could join the ranks of African nations leveraging space technologies to support their development. To date, nearly fifteen African countries have invested over $4.71 billion in 58 satellite projects, with further developments underway. Nations such as Nigeria, South Africa, and Kenya are already utilizing their satellite capabilities to enhance internet connectivity, monitor climate change, and optimize natural resource management.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
With over 120 million inhabitants, Ethiopia has an immense digital potential.
The country is actively working to expand internet access, modernize its infrastructure, and embrace innovative technological solutions.
Ethiopia is working to accelerate internet development and bridge the digital divide, Minister of Innovation and Technology Belete Molla said on Monday. Speaking at the opening of the Internet Development Conference (IDC), Molla emphasized the government's commitment to building an inclusive and dynamic digital ecosystem for all citizens.
The Digital Ethiopia 2030 strategy will serve as a roadmap for this effort, guiding the modernization of internet infrastructure, raising digital literacy awareness, and promoting responsible technology use. The government also aims to collaborate closely with member countries of the Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD) to improve connectivity in remote areas and ensure equitable and secure internet access.
Ethiopia has made significant progress in recent years. 4G coverage now reaches 34.8% of the population, and 5G services are available in 14 cities. The country currently boasts 80.5 million mobile subscribers and 45 million broadband users. Innovative solutions like Telebirr, a mobile payment service with 51.54 million users, demonstrate the potential of digital technology to drive financial inclusion and transform economic transactions.
The GSMA's Digital Economy Ethiopia Report forecasts further growth in connectivity, with more than 50 million Ethiopians expected to be connected to mobile internet by 2028, nearly double the current figure. This increased connectivity could contribute approximately $2.5 billion to the agricultural sector and $2 billion to the manufacturing industry by 2028.
These advancements are expected to solidify Ethiopia's role as a driver of digital transformation within the IGAD region while delivering sustainable economic and social benefits for its citizens.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
Interoperability between banks and non-banking financial service providers makes financial services more accessible to unbanked and underbanked populations. As many Africans remain unbanked, integrating digital payment solutions into everyday transactions can help bridge the gap between the banked and unbanked.
The Kingdom of Eswatini has launched the Eswatini Payment Switch (EPS), a platform enabling real-time, interoperable transactions across banks and non-banks. Paylogic, the provider behind its development, announced the rollout on January 7.
Commenting on the development, Mohamed Mekouar, Executive Chairman of PayLogic said, "We are honored to partner with the Central Bank of Eswatini in this transformative project. The Eswatini Payment Switch is a testament to our commitment to advancing digital payments and financial inclusion across Africa."
The EPS marks a significant step toward creating a cash-lite economy by reducing dependency on cash transactions. The system allows payments to be processed within seconds, ensuring seamless, 24/7 service availability, including weekends and holidays.
The EPS enhances interoperability among financial institutions, fostering a more inclusive and interconnected financial ecosystem. This innovation is expected to drive financial inclusion and digital transformation, enabling individuals and businesses to access faster and more secure payment services.
This initiative aligns with Eswatini's broader push to modernize its payment infrastructure, drive economic growth, and expand financial access for its citizens. The country has made notable progress in embracing digital payments, led by the Central Bank of Eswatini (CBE) through its National Payment System (NPS) Vision 2025, which focuses on achieving interoperable, real-time, and 24/7 payment capabilities.
By ensuring interoperability and real-time processing, the platform positions Eswatini as a leader in embracing digital financial solutions in the region.
Hikmatu Bilali















