Equipe Publication
La fintech Cauridor lève 3,5 millions $ pour se développer en Afrique
Cauridor, une fintech spécialisée dans les infrastructures de paiement, a récemment annoncé la réussite d’un tour de table d’un montant de 3,5 millions USD. Déjà présente en Guinée, au Sénégal, en Côte d'Ivoire, en Sierra Leone et au Liberia avec plus de 25 000 agents, elle utilisera ces fonds pour renforcer ses infrastructures de paiement et s’étendre à de nouveaux marchés en Afrique.
Lire aussi:
Cameroun : Jean-Patrick Ketcha forme et finance les jeunes entrepreneurs
Le Rwandais Felix Rubanda facilite la recharge de véhicules électriques en Afrique
Diplômé en génie civil, il choisit de s’orienter vers le secteur de la mobilité afin de rendre le transport durable plus accessible en Afrique. Pour y parvenir, il mise sur la technologie et encourage l’adoption de véhicules électriques sur le continent.
Felix Rubanda (photo) est un entrepreneur technologique originaire du Rwanda. Il est le fondateur et le président-directeur général de Feru Energy, une start-up spécialisée dans l’infrastructure de l’e-mobilité en Afrique.
Fondée en 2022, Feru Energy a pour mission de développer et de déployer des solutions d’e-mobilité abordables et fiables pour les entreprises ainsi que les conducteurs de véhicules électriques sur le continent. Parmi ses innovations figure SafariCharger, une solution complète pour l’optimisation de la recharge des véhicules électriques.
SafariCharger intègre un système de gestion des stations de recharge (CSMS) destiné aux exploitants d’infrastructures ainsi qu’une application mobile. Grâce à une surveillance et une analyse en temps réel, le CSMS fournit des données détaillées sur l’utilisation des chargeurs et permet aux opérateurs d’optimiser leur réseau de stations de recharge.
L’application mobile, quant à elle, informe les utilisateurs sur la disponibilité, les tarifs et l’emplacement des bornes de recharge. Elle offre aussi la possibilité de réserver un créneau et de payer directement via mobile money, un mode de paiement largement adopté en Afrique.
Parallèlement à ses activités chez Feru Energy, Felix Rubanda est responsable des stations de recharge chez Kabisa Electric, une entreprise rwandaise spécialisée dans la mobilité électrique. En 2021, il a également cofondé Punda Group, une société qui exploite la technologie pour transformer le secteur de la construction en Afrique.
Il est titulaire d’une bachelor en technologies de génie civil obtenue à l’université du Rwanda. Avant de se lancer dans l’entrepreneuriat, il a dirigé, de 2014 à 2017, Five Worlds, une agence rwandaise de voyage et de tourisme.
Melchior Koba
Edité par Sèna D. B. de Sodji
Lire aussi:
Blandine Umuziranenge améliore l’accès à la santé pour les femmes
Cirus Sumika Aims for a Digitally Self-Sufficient Africa
He began his entrepreneurial journey in 2019 while still a student, developing technological solutions to accelerate digital transformation in Africa.
Cirus Sumika, a Ugandan tech entrepreneur, is the founder and CEO of Sumic IT Solutions, a startup dedicated to narrowing Africa’s digital divide by providing sustainable technology solutions.
Founded in 2019, Sumic IT Solutions specializes in building professional websites for businesses, NGOs, hotels, and educational institutions, among others. The company also develops mobile applications, handling the entire process from ideation to delivery while offering ongoing support. Additionally, it provides digital marketing services, IT consulting, and training in new technologies.
"Our core mission is to facilitate the growth and self-sufficiency of businesses by providing them with affordable, standard, and sustainable technologies. We achieve this through a range of services including Website Design & Development, Domain Name Registration & Hosting, Mobile Application Development, Digital Marketing, IT Trainings, and IT Consulting," the startup states.
Sumic IT Solutions operates under Sumic Group, founded by Sumika, which also launched Sumic Online, a platform that facilitates buying and selling various products and services.
Sumika holds a bachelor’s degree in computer science from Makerere University, Uganda, which he earned in 2021. In 2020, he interned as an accountant at KPMG East Africa. Between 2023 and 2024, he was a partner at Black Leaders Worldwide, a business network for Black professionals in the U.S. and the U.K.
His achievements include winning the Startup of the Year in Technology award at the 2022 Startup Uganda Awards. In 2023, Sumic IT Solutions received the Global Recognition Award. Most recently, in 2024, Sumika was named Young Entrepreneur of the Year by the Private Sector Foundation Uganda, the country’s top private sector body.
By Melchior Koba,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
Thierry Kientega Connects Tech Talent with Global Businesses
He helps businesses develop innovative products by building a community of information and communication technology (ICT) experts.
Thierry Kientega (photo) is a telecommunications engineer and tech entrepreneur from Burkina Faso. He is the founder and CEO of OUIcoding, a consulting firm specializing in information technology.
Founded in 2018, OUIcoding specializes in digital transformation, offering custom development solutions, NoCode services, and data and artificial intelligence-based tools. The company focuses on process automation and rapid application development. It also identifies, vets, and connects coders, designers, and engineers from Africa and emerging markets with businesses across the continent.
The startup has built a community of talents, where members can train, learn, share knowledge, and innovate. Its ambition is to create an ecosystem conducive to innovation and collaboration. Today, this community includes over 360 experts and has supported more than 158 projects, involving 46 companies.
Thierry Kientega holds a telecommunications engineering degree obtained in 2008 from the École Supérieure d’Ingénieurs de Rennes in France. He also earned a PhD in telecommunications in 2011 from the École Nationale des Ponts et Chaussées in France.
His career began in 2007 at France Télécom (which became Orange in 2013) as a telecommunications engineer. In 2011, he joined the international consulting firm Leyton as a senior consultant, helping companies identify financial levers to accelerate growth and drive sustainable progress. In 2014, he became director of the commerce division at CFAO France, a company specializing in international trade.
By Melchior Koba,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
Mastercard Opens First Office in Ghana to Strengthen West Africa Presence
Africa is experiencing a rapid shift toward digital payments, fueled by increased smartphone penetration and internet usage. Mastercard’s expertise in secure and scalable payment systems can complement and enhance these existing platforms.
Mastercard has opened its first office in Accra, Ghana, a key step in its West Africa expansion. This move, announced yesterday January 13, reflects its commitment to supporting Ghana’s digital economy through innovative financial products and services tailored to the local market.
“Opening our office in Ghana marks an important milestone in our commitment to deepening relationships across the region. Our growth strategy for West Africa is ambitious, and establishing a formal presence here allows us to better serve the specific needs of our customers,” said Mark Elliott, Division President for Africa at Mastercard.
The new office underscores Mastercard’s dedication to fostering stakeholder relationships and promoting inclusive growth. By establishing a presence in Ghana, Mastercard aims to enhance collaborations and accelerate the adoption of tailored financial solutions.
Beyond the office, Mastercard has collaborated with companies like Kalabash, KaiOS, Boost, and Smile ID, and partnered with banks such as Access Bank and Fidelity Bank to improve cross-border payment solutions. These efforts have empowered fintechs, expanded digital access for underserved communities, and strengthened Ghana’s position as a tech hub.
Mastercard’s office in Accra is a strategic response to the growing demand for secure, efficient, and inclusive financial solutions in Ghana and West Africa. By leveraging its global expertise and fostering local partnerships, Mastercard is set to play a pivotal role in transforming Ghana’s financial landscape and contributing to the region’s digital future.
The 2021 Financial Services Demand-Side Survey Report by the Ministry of Finance reveals that Ghana has achieved a remarkable 96% financial inclusion, leaving only 4% of the population without access to financial services. This significant progress is primarily driven by the widespread adoption of mobile money nationwide. It underscores the growing digitalization of Ghana's economy, creating opportunities for fintech innovation, e-commerce, and digital payments.
Ghana’s near-universal financial inclusion and thriving digital economy make it an ideal launchpad for Mastercard’s broader West African strategy. This milestone demonstrates the country’s leadership in financial inclusion within the region and its readiness to leverage digital solutions to drive economic development.
With offices across Africa, including in Cairo, Casablanca, Johannesburg, Lagos, and Nairobi, Mastercard’s expansion into Accra reinforces its commitment to building a sustainable digital economy across the continent.
Hikmatu Bilali
Nairobi to Host AI Kenya Breakfast Summit 2025
Nairobi will host the AI Kenya Breakfast Summit 2025 on January 29 at Mövenpick Hotel from 7:00 AM to 11:30 AM. The event, themed “Transformative AI From Efficiency Gains to Strategic Advantage,” will explore AI’s potential to enhance efficiency and provide strategic benefits for businesses in East Africa.
Topics will cover AI adoption in East Africa, partnerships to unlock AI’s potential, and using AI for efficiency and strategy. Attendees can network with leaders, explore partnerships, and gain actionable insights to drive AI-led innovation in 2025.
Mohamed Louati Offers Digital Solutions to Industrial Companies
As an entrepreneur and expert in digital transformation, he is committed to developing innovative solutions to optimize the management of companies in the industrial sector.
Mohamed Louati (photo) is a Tunisian data analysis expert and tech entrepreneur, serving as the co-founder and CEO of Logimes, a technology company that specializes in solutions for the industrial sector.
Founded in 2021, Logimes is a digital services startup that assists industrial companies in implementing production management systems for their workshops. The company enables real-time tracking of work-in-progress, evaluation of operator performance, and measurement of overall production efficiency.
"Our goal is to be the strategic partner that guides the transition to advanced production management systems, improving operational efficiency and competitiveness in the era of Industry 4.0. By leveraging innovation, commitment, excellence, and collaboration, our mission is to deliver customized solutions and drive our clients’ success for a more efficient and sustainable future," states the company’s website.
Among Logimes' offerings are Fastuz, a learning platform designed to provide practical training tailored to labor market needs, helping learners succeed in their careers, and DAS ERP, a comprehensive enterprise resource planning solution.
Mohamed Louati holds an engineering degree in statistics and information analysis, with a focus on data analysis, which he earned in 2004 from the Higher School of Statistics and Information Analysis. He also obtained a master’s degree in economic modeling and econometrics in 2005 from Tunisia Polytechnic School.
His professional career began in 2004 at Karmex, an industrial company, where he worked as an analyst and administrator of an enterprise resource planning (ERP) system. In 2011, he joined Logidas, an ERP solutions provider, where he advanced through various roles including business developer, operations director, and eventually co-CEO.
By Melchior Koba,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
Nigeria: Galaxy Backbone Expands Fibre Optic Network to Lagos, Ibadan, and Ilorin
The expansion of fibre optic network in Africa is a critical development in the journey toward digital transformation. This achievement supports key objectives, including bridging the digital divide, fostering economic growth, and strengthening the continent’s position in the global digital economy.
Technology services provider of the Federal Government of Nigeria, Galaxy Backbone (GBB), has successfully deployed its cutting-edge fibre optic network in Lagos, Ibadan, and Ilorin, it announced on December 16. This marks a major milestone in Phase II of the National Information and Communication Technology Infrastructure Backbone (NICTIB) project. The expansion reflects GBB's commitment to enhancing Nigeria's digital connectivity and accelerating its transformation into a digitally inclusive nation.
Prof. Ibrahim A. Adeyanju, Managing Director/CEO of Galaxy Backbone, hailed the achievement, stating: "The expansion of our fibre optic network to Lagos, Ibadan, and Ilorin is a significant step in bridging the digital divide and positioning Nigeria as a global leader in the digital economy. This infrastructure empowers us to deliver innovative, customer-focused solutions for both the public and private sectors."
With an extensive cross-country optical fibre backbone now spanning over 5,000 kilometers across 27 state capitals, GBB continues to solidify its role as Nigeria’s digital backbone. The project integrates the nation’s six geopolitical zones, enhancing digital inclusion and fostering economic growth.
The newly completed Abuja-to-Lagos route, which connects key cities such as Minna, Bida, Mokwa, Ilorin, Ogbomoso, Oyo, Ibadan, and Lagos, is a strategic development designed to bolster network reliability. This closed-loop network ensures service redundancy and reduces potential downtime, offering users a seamless, world-class digital experience.
The fibre optic network enhances high-speed, secure connectivity for government institutions and businesses, empowering them to thrive in an increasingly digital world. With this deployment, GBB reinforces its commitment to Nigeria’s socio-economic growth and its vision of a digitally inclusive society.
As Galaxy Backbone (GBB) extends its network, it reinforces its position as a key partner in driving Nigeria's digital economy, fostering innovation, and enabling sustainable development. This initiative aligns with GBB’s vision of building a smarter government, which will pave the way for smart communities, cities, and a more technology-driven nation. It also marks a significant step towards fulfilling its mandate of operating a nationwide IP-based network to provide a unified platform for connectivity and infrastructure services for all Government Ministries, Departments, and Agencies (MDAs).
The expansion aligns with Nigeria's National Broadband Plan 2020-2025 which aims to increase broadband penetration to 90% by 2025, a goal supported by GBB’s ongoing projects.
Hikmatu Bilali
Brij Technologies Launches BrijX Platform to Transform Intra-African Trade
Brij Technologies Inc. unveiled the BrijX Currency Swap B2B Digital Platform on Tuesday November 19. This will enable real-time mobile money currency swaps between Ghanaian Cedi and Nigerian Naira without traditional foreign exchange intermediation.
Supported by the U.S. Embassy in Ghana and licensed by the Bank of Ghana, BrijX is undergoing final integration with Mobile Money Limited Ghana and G-Money Financial Services. The platform is expected to go live before Christmas 2024.
Report Unveils Top 5 Digitally Advanced African Parliaments
African parliaments are increasingly turning to digital technologies to improve efficiency. However, the digital divide remains a significant challenge, hindering progress in many regions.
South Africa (8 out of 10), Zimbabwe (8), Burundi's Senate (7), Morocco (7), and Mauritius (7) lead the continent in digital maturity among African parliaments, according to a new report published in October 2024 by the Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU), a global organization of sovereign state parliaments. The report is based on responses from 115 parliaments or chambers across 86 countries, as well as from supranational parliamentary organizations.
Titled the "World e-Parliament Report 2024," the report offers a comprehensive analysis of digital technology use in parliaments worldwide through a digital maturity index, an innovative benchmarking tool. This index assesses parliaments across six key areas: governance, digital strategy and management; infrastructure; parliamentary systems; user support; digital content and publications; and citizen engagement.
“The purpose of benchmarking is not to create a league table of ‘good’ or ‘bad’ parliaments. Rather, it supports strategic decision-making on the use of digital technologies by highlighting the factors that can affect maturity,” the IPU stresses.
In addition to the leaders, Tunisia (6), Burundi's National Assembly (5), and Malawi (5) stand out with scores of 5 or higher. However, sub-Saharan Africa remains underrepresented among the top performers. According to the IPU, 50% of parliaments in the region rank among the 30 least digitally mature institutions, a situation attributed to a lack of modernization initiatives, insufficient investment in new digital systems, and an absence of ambitious digital transformation programs.
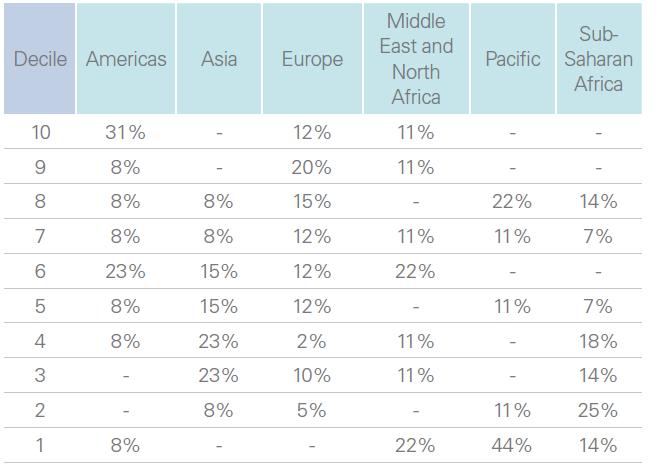
Distribution of parliaments by region for each decile ranking
At the bottom of the index, parliaments in countries like Djibouti, Lesotho, Madagascar, and the Central African Republic scored an average of 1 out of 10, reflecting significant gaps in digital adoption.
To address these gaps, the report recommends that institutions and governments develop clear strategic visions and comprehensive digital strategies; allocate adequate financial, human, and technological resources; establish robust governance frameworks; invest in capacity building; prioritize citizen participation; and strengthen inter-parliamentary collaboration.
Additionally, generative artificial intelligence is highlighted as a strategic lever to accelerate parliamentary digital transformation, offering the potential to deliver valuable insights and enhance the accessibility of parliamentary processes.
Samira Njoya
Lire aussi:











