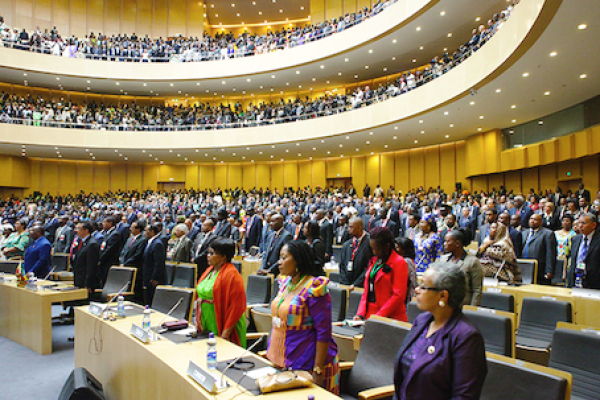
African parliaments are increasingly turning to digital technologies to improve efficiency. However, the digital divide remains a significant challenge, hindering progress in many regions.
South Africa (8 out of 10), Zimbabwe (8), Burundi's Senate (7), Morocco (7), and Mauritius (7) lead the continent in digital maturity among African parliaments, according to a new report published in October 2024 by the Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU), a global organization of sovereign state parliaments. The report is based on responses from 115 parliaments or chambers across 86 countries, as well as from supranational parliamentary organizations.
Titled the "World e-Parliament Report 2024," the report offers a comprehensive analysis of digital technology use in parliaments worldwide through a digital maturity index, an innovative benchmarking tool. This index assesses parliaments across six key areas: governance, digital strategy and management; infrastructure; parliamentary systems; user support; digital content and publications; and citizen engagement.
“The purpose of benchmarking is not to create a league table of ‘good’ or ‘bad’ parliaments. Rather, it supports strategic decision-making on the use of digital technologies by highlighting the factors that can affect maturity,” the IPU stresses.
In addition to the leaders, Tunisia (6), Burundi's National Assembly (5), and Malawi (5) stand out with scores of 5 or higher. However, sub-Saharan Africa remains underrepresented among the top performers. According to the IPU, 50% of parliaments in the region rank among the 30 least digitally mature institutions, a situation attributed to a lack of modernization initiatives, insufficient investment in new digital systems, and an absence of ambitious digital transformation programs.
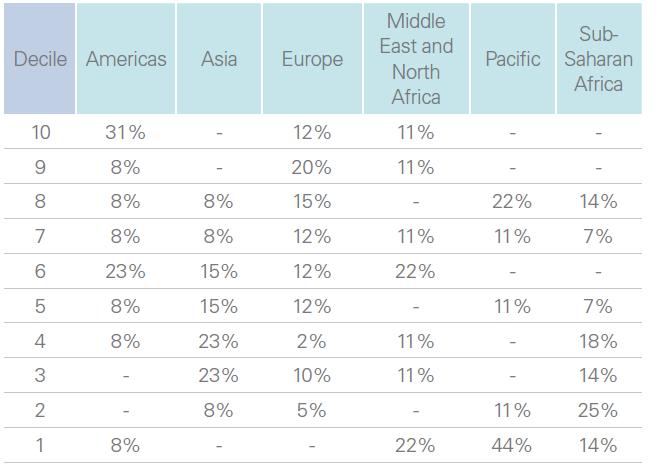
Distribution of parliaments by region for each decile ranking
At the bottom of the index, parliaments in countries like Djibouti, Lesotho, Madagascar, and the Central African Republic scored an average of 1 out of 10, reflecting significant gaps in digital adoption.
To address these gaps, the report recommends that institutions and governments develop clear strategic visions and comprehensive digital strategies; allocate adequate financial, human, and technological resources; establish robust governance frameworks; invest in capacity building; prioritize citizen participation; and strengthen inter-parliamentary collaboration.
Additionally, generative artificial intelligence is highlighted as a strategic lever to accelerate parliamentary digital transformation, offering the potential to deliver valuable insights and enhance the accessibility of parliamentary processes.
Samira Njoya
Lire aussi: