News (1790)
Tech startups globally serve as economic pillars. Despite their crucial role, funding obstacles hinder their growth, particularly in Africa. To address this, companies are increasingly seeking funds to propel startup progress, recognizing their pivotal contribution to national development.
Investment firm Aduna Capital announced the launch of a $20 million fund dedicated to revolutionizing the African tech startup ecosystem, on November 20.
According to the press release announcing the fund, it will mainly target the underserved market of Northern Nigeria, which is home to over 128 million people (according to a 2021 report by the National Bureau of Statistics). Citing a 2023 report from the Northern Founders Community (NFC), the release indicates: “Start-ups in sectors like edtech and agritech in this region [ed. note: Northern Nigeria] are already making over $1.2 million in bootstrapped revenue.” Therefore, Aduna Capital believes that “With proper funding and support, these start-ups have the potential to scale significantly, both within the continent and globally.”
Founded by entrepreneurs Surayyah Ahmad Sani (the co-founder of Ethco, a startup helping ethnic stores go digital, and the chairperson of the Northern Founders Community (NFC) and Sanusi Ismaila (founder of Colab, the largest innovation hub in Kaduna), Aduna Capital stands as both an investment firm and an ecosystem fostering innovation.
Sanusi Ismaila notes Aduna Capital's strategy extends beyond Northern Nigeria, with 25% of the fund for the rest of Nigeria and 25% for start-ups across Africa, fostering a diverse portfolio. Committed to diversity, Aduna Capital allocates 50% of investments to female-led start-ups.
The Capital's strategy targets super early and pre-seed stage investments, aiming for “a 5–10x return on investment, balancing profitable returns for its investors with meaningful investments,” he revealed.
Aduna Capital's $20 million fund signals a transformative step for African tech start-ups. With a strategic focus on underserved regions, diversity, and pan-African growth, the firm aims to make a lasting impact on the continent's entrepreneurial landscape.
Hikmatu Bilali
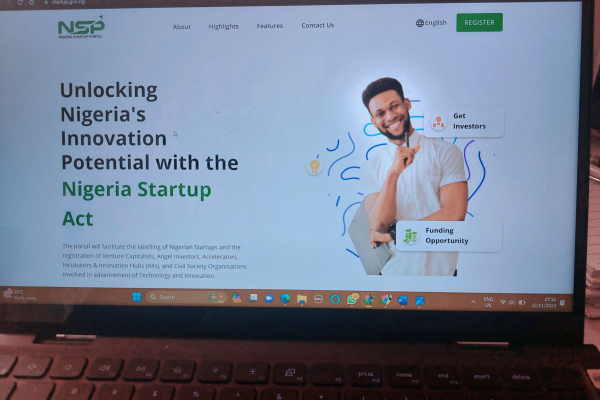
Nigeria, like several African countries, has promulgated its startup act to support the entrepreneurship ecosystem. However, the act is yet to be fully implemented.
On Tuesday, November 21, Bosun Tijani, Nigeria's Minister of Communications, Innovation and Digital Economy, announced the launch of the Start-up Support and Engagement Portal. It will help identify and aggregate Nigerian startups, venture capital firms, hubs, and innovation centers to facilitate the engagement and support of the various players in the ecosystem.
"The launch of the portal will allow us to initiate the process of setting up the startup consultative forums to select representatives to the National Council for Digital Innovation and Entrepreneurship to facilitate discourse and consensus among Nigerian ecosystem players," he said.
The establishment of the Startup Support and Engagement Portal builds upon the enactment of the Nigeria Startup Act in October 2022. This landmark legislation, championed by local tech ecosystem leaders and government authorities, has established a comprehensive framework for nurturing and supporting startups across the country. In April 2023, President Muhammadu Buhari further propelled the advancement of the tech sector by inaugurating the Nigerian National Council for Digital Innovation and Entrepreneurship (NCDIE), tasked with overseeing the implementation of the Startup Act.
To qualify for the "Startup" label, which unlocks a range of benefits under the Startup Act, startups must be in operation for less than 10 years and register on the Startup Support and Engagement Portal. These benefits include tax breaks, capacity-building programs, and access to grants, loans, and investment funds.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
Raxio Group entered the African data center market in 2019. Since then, the company has been stepping up investments to expand its geographical footprint on the continent.
On Tuesday, November 21, neutral data center builder and operator Raxio Group announced the official launch of a state-of-the-art data center in Ethiopia. The tier 3 infrastructure is located in the economic heart of Ethiopia, the country's capital, Addis Ababa.
According to Raxio Group, the new data center will accommodate up to 800 racks. In addition, it will offer "up to 3MW of IT power, providing a robust, fully-redundant environment for housing mission-critical IT infrastructure with 24/7 availability."
With the launch of the new data center, Raxio Group continues its African expansion strategy launched in 2019. This strategic move follows closely on the heels of the group's recent announcement securing $46 million in equity to fuel the expansion of its data center network across Africa. Recognizing the continent's surging demand for digital infrastructure, Raxio Group is committed to establishing ten to twelve data centers throughout Africa, providing businesses and individuals with the essential digital backbone they need to thrive.
Upon its completion, the data center is poised to play a pivotal role in expanding the ICT infrastructure network, ensuring that the transformative benefits of technology reach all corners of the country. This expansion will facilitate access to essential educational, social, and business resources, empowering individuals and communities to harness the power of technology for their advancement.
"We anticipate that this facility will be a catalyst for increased economic development in Ethiopia, supporting local businesses and government agencies, as well as attracting regional and international service and content providers into Ethiopia," said Bewket Taffere, General Manager of Raxio Data Centre in Ethiopia.
Samira Njoya
The coronavirus pandemic forced a change in consumer habits, affecting a wide range of sectors. To remain competitive, some of those sectors, including the creative industries adapted themselves, causing new revenue opportunities to emerge.
On Monday, November 20, Orange Middle East & Africa and Spotify announced a partnership to promote music, particularly African music. This collaboration, which enables Orange subscribers to enjoy free music on the Swedish streaming platform by subscribing to one of the telecom operator's mobile offers, is already effective in the Democratic Republic of Congo, Madagascar, and Mali. It will soon be effective for Orange subscribers in Guinea and eventually cover all of Orange’s 18 markets in Africa and the Middle East.
"As a multi-service operator on the continent, we want to provide our customers with easier access to the rich musical culture in Africa and the promotion of local talents. The deployment of this service in the countries where we are present will greatly facilitate access to an incomparable musical experience for all communities and thus contribute to the acceleration of digital inclusion on the continent," said Brelotte Ba (photo, right), Deputy CEO of Orange Middle East and Africa.
For Jocelyne Muhutu-Remy (photo, left), Managing Director for Spotify in Sub-Saharan Africa, the collaboration addresses a specific issue. “We are aware that data costs continue to be a hindrance for people who would like to stream music, that’s why we are actively working at Spotify SSA on partnerships like this one," she said.
The International Federation of the Phonographic Industry (IFPI) reports that streaming is currently the highest revenue-generating segment for the global music industry. In its "Global Music Report 2023", it reveals that starting from 2017, the growth in streaming revenues has accelerated to account for 67% of global music revenues in 2022. Specifically, streaming accounted for $17.5 billion out of the $26.2 billion in revenues generated by the music industry worldwide in 2022. Streaming also contributes to greater visibility for artists on the international scene.
Sub-Saharan Africa was the region with the fastest growth in recorded music revenues in 2022, at +34.7%. This growth was driven by a strong increase in revenues in South Africa, the region's largest market (+31.4%). Meanwhile, the Middle East and North Africa posted the world's third-highest revenue growth in 2022 (+23.8%, with 95.5% of that performance being driven by streaming).
Muriel Edjo
To achieve its digital ambition, Chad, like most African countries, needs a qualified workforce. For that purpose, the country is actively forging partnerships to secure a skilled workforce, ensuring that its youth gain access to essential digital skills.
Simplon Africa, a social enterprise that provides training in digital professions, and WenakLabs, a tech hub in Chad, signed a partnership agreement in N'Djamena on Thursday, November 16.
One of the goals of this collaboration is to give the Chadian youth access to high-quality training in digital professions, improving their employability.
"This partnership shows a strong dedication to developing digital skills in Chad. By working together and sharing our expertise, WenakLabs and Simplon Africa want to create top-notch training courses, giving learners exceptional learning opportunities," said the Chadian hub.
Under the agreement, Simplon Africa will create the teaching content and provide learners access to its online training platform. On the other hand, WenakLabs will give access to its resources and training materials to support both face-to-face and online learning.
This collaboration will result in the launch of a campus in the next few months, offering both paid online and face-to-face training courses to its main targets: students, entrepreneurs, and professionals.
This new collaboration follows a previous partnership that led to the Tech4Tchad program in 2021. Funded by France, Simplon, and several partners, including WenakLab, Tech4Tchad has trained 150 young people in the digital field so far.
Samira Njoya
Côte d’Ivoire, like several African countries, wants to set up a regulatory framework conducive to the development of innovative startups. The aim of this framework is to support local startups and spur the growth of the local tech ecosystem.
On Tuesday, November 14, the Ivorian Senate unanimously approved a law on the promotion of digital startups. Defended by the Minister for Digital Transition and Digitization, Ibrahim Kalil Konaté, before the Research, Science, Technology, and Environment Commission, it aims to define an incentive-based legal and institutional framework for the creation and development of young technology companies in Côte d'Ivoire.
"We have noticed that startups face some challenges as their models haven't been structured around proven business models that demonstrate market viability. Our goal is to provide support, incubate these startups, and help them realize their full growth potential," said Ibrahim Kalil Konaté.
The new law is part of the Ivorian government's efforts to encourage the emergence of digital startups in the country. Between 2020 and 2022, more than 2,847 digital entrepreneurs were supported by the Ivorian government, to the tune of more than 577 million CFA Francs ($960,000). Earlier this year, the executive also launched "Start-up Boost Capital", a 1 billion CFA Franc fund established to finance local startups.
Upon the President of the Republic's promulgation, this law will further fortify these initiatives. It is poised to catalyze the development of startups in their early stages, providing a dedicated framework for the support and governance of these enterprises. The overarching goal is to strengthen the entrepreneurial ecosystem, thereby accelerating socio-economic growth.
Samira Njoya
To bolster its digital transition program, Morocco requires a proficient workforce in digital professions. By ensuring the readiness of this workforce, the country wants to align the skills of its graduates with the dynamic requirements of the job market.
Morocco wants to triple the number of graduates in the digital sector within 4 years. To this end, an agreement was signed on Wednesday, November 15, by its Minister of Digital Transition and Administrative Reform, Ghita Mezzour (photo, right), the Minister for the Budget, Fouzi Lekjaa, and the Minister for Higher Education, Scientific Research and Innovation, Abdellatif Miraoui.
The agreement covers a program that equips graduates with digital specializations from Moroccan universities, spanning the period between 2023 and 2027. The objective is to elevate the number of graduates from the current 8,000 across various training cycles to 22,500 by 2027.
Notably, it provides for the launch of new digital training courses in 12 universities across the country. These courses will be broken down into 144 new fields of study, including data analysis, digital technologies, cybersecurity, program development, big data, and artificial intelligence (AI).
This interministerial project, which will take effect from the start of the next academic year, is part of the country's new digital strategy, which is currently being finalized. Dubbed "Maroc Digital 2030", it replaces the current strategy, which aims to make Morocco a benchmark digital and technology hub in Africa by 2025.
The new strategy places particular emphasis on talented, creative young people. It calls for the training of 45,000 digital talents per year, the introduction of 50,000 young people to digital professions, and the welcoming of 6,000 new foreign digital talents per year, among others.
Samira Njoya
The move is a strategic decision taken by Ghanaian authorities to help the University of Ghana’s students familiarize themselves with smart systems and cutting-edge technologies.
Ursula Owusu-Ekuful, Ghana's Minister of Communication and Digitalization, revealed on Tuesday, November 14, during the 75th annual New Year School Conference in Accra, the establishment of the Digital Youth Village at the University of Ghana. This initiative is designed to provide students with opportunities to engage with advanced technologies and intelligent systems.
"The Digital Youth Village for the New Year’s School is a project I am very excited about. The project would enable our students to have practical, hands-on learning about smart environments and smart offices alongside other cutting-edge technologies. Despite the challenges that have delayed the fruition of the project, I can confidently say that the Digital Youth Village for the New Year School and Conference of the University of Ghana will become a reality," said Ursula Owusu-Ekuful.
Ghana's authorities are actively advancing the nation's digital transformation by investing across various sectors to enhance the country's technology ecosystem. While not part of the continent's "Big Four" (Kenya, Nigeria, Egypt, South Africa), which collectively accounted for 67% of total startup fundraising in Africa during the third quarter of the year, as reported by TechCabal Insights in "The State of Tech in Africa Q3 2023," Ghana, under the leadership of Nana Akufo-Addo, is making significant strides. The United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UN DESA) "E-Government Survey 2022: The Future of Digital Government" positions Ghana as the seventh-ranked e-administration champion among sixteen leading nations on the continent. Additionally, earlier this year, Ghana joined the Digital Cooperation Organization, further underlining its commitment to digital progress.
During the November 14 event held under the theme Nurturing Resilience: Adopting Technology and Embracing Humanism for Sustainable Development," Minister Ursula also disclosed the various projects (both completed or underway) in the tech sector, including the Smart Community Project and The Rural Community Project.
"By embracing people-centered technology, Ghana will continue to strengthen its educational systems, healthcare services, and businesses and promote our own culture while empowering citizens to face the future with confidence and the requisite skills," added the Minister.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
The wave of digital transformation is sweeping across Africa, and Benin stands out as a commendable example. The country has initiated the digitization of a pivotal sector within its economy.
On Tuesday, November 14, Benin’s National Land Transport Agency (ANaTT) officially launched the Electronic Road Freight Management System (SYGFR). Financed to the tune of 290 million CFA Franc (around $479,480) by the Belgian Development Agency (Enabel), the platform provides sectoral stakeholders with an interface for real-time monitoring of road transport activities, freight transport especially.
Once completed, SYGFR will include three modules: freight supply management, statistics and dashboard management, and transport supply management. For the time being, authorities have launched the transport supply management module, which will among other things, facilitate the construction and maintenance of a database of professional drivers, the issuing of transport authorizations and transport cards, and registration of other freight players such as customs brokers and freight lessors.
In addition to facilitating the issuance of transport authorization and cards, the transport supply management module is expected to ease the issuance of consignment notes for freights from the Autonomous Port of Cotonou and other cargo hubs across the country.
"Effective organization is a prerequisite for the development of any sector. This [platform] is a stride forward and we need to embrace a collaborative thinking approach to meet ongoing challenges,” said Jacques Ayadji, who was representing Jose Didier Tonato, the Minister for the Living Environment and Transport in Charge of Sustainable Development.
Under President Patrice Talon, Benin has initiated the digitization of its services to become a tech hub in the West African region. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the process, and since then, more than a thousand services have been digitized. According to the United Nations e-government development index for 2022, Benin ranks 149th out of 193 countries, with a score of 0.4264, a leap of 8 places from 2020.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
In an era where digital technology is rapidly gaining global traction, the Chadian government is intensifying its endeavors to catch up in the sector. Numerous initiatives are in progress, and results are already perceptible.
Chad and Morocco will extend their bilateral cooperation in the field of information and communication technologies (ICT). To this end, a technical assistance memorandum of understanding has been signed between Chad's ICT development agency ADETIC, and Morocco’s telecom regulator ANRT.
The collaboration includes training for ADETIC engineers and exchanges of experience between the two agencies. The aim is to help Chad adapt and implement the Moroccan ICT model in favor of digital acceleration in the country, with a view to a prosperous digital economy.
The collaboration between the two regulatory agencies overseeing the telecommunications sector is a crucial component of the Chadian government's strategy to bridge the gap in the digital domain. This partnership materialized following a three-day mission by the ADETIC delegation to Morocco, during which they visited the host country’s digital development agency ADD and the ARNT.
"Most of the discussions focused on the Moroccan model for the digital transformation of public administration, the legal and regulatory framework, the management of ICT technical infrastructures, as well as domain name management and the provision of universal services," ADETIC wrote on Facebook.
This new partnership allows ADETIC to leverage the extensive expertise of ARNT, which boasts 25 years of experience in telecommunications sector regulation, approval of telecommunications equipment, administration of ".ma" domain names, and the management of electronic certification, among other areas.
Samira Njoya
More...
Technology advances offer unlimited job creation and development potential. To capitalize on those opportunities, fast-track technology adoption, and address the growing demand for skilled professionals in the evolving tech landscape on the continent, African countries are teaming up with international institutions.
The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and the Federal Government of Nigeria will collaborate to provide a significant boost to the country's tech sector. The Minister of Communications, Innovation and Digital Economy, Bosun Tijani announced the partnership on Tuesday, November 14 in a tweet.,
The partnership aims to offer 3,000 internship slots for participants in the Federal Government's tech initiative, 3MTT, which is designed to enhance skills and opportunities in the technology sector.
The 3,000 internship opportunities provided by the UNDP will catalyze individuals looking to gain hands-on experience in the dynamic field of technology. It not only offers a unique chance for personal and professional growth but also aligns with the broader goal of fostering a robust and competitive tech ecosystem in Nigeria.
The collaborative effort underscores the two parties’ commitment to bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application. By providing real-world exposure to aspiring tech professionals, this initiative is poised to make a tangible impact on the nation's tech landscape.
In a joint statement, representatives from both the UNDP and the Nigerian government expressed their enthusiasm for the partnership and its potential to drive positive change in the tech sector.
Hikmatu Bilali
In recent years, the African continent has witnessed a proliferation of startups. However, in numerous countries, authorities have not sufficiently supported their growth. Recognizing this gap, Kampala has decided to address the issue.
Uganda is planning to introduce a national policy for startups. The project, led by the Private Sector Foundation Uganda (PSFU), is supported by the Mastercard Foundation and coordinated by the Ugandan Ministry of Commerce, Industry, and Cooperatives. The aim of the policy is to govern interactions between the government, incubators, startups, and investors, with a view to promoting a culture of innovation and entrepreneurship in the country.
"Several multinationals come here and get several business facilitation privileges yet not so much is done for local start-ups. We believe that with this policy, Ugandan start-ups will have a chance to compete favorably on the market as it will not only establish what they need but also how to get support," said Keneth Twesigye, lead policy at Startup Uganda.
Uganda is actively enhancing its technological ecosystem. To qualify as a startup in the country, specific conditions must be fulfilled. These include maintaining a temporary management structure, allocating a portion of the budget to research and development, having majority ownership by Ugandans, and being locally incorporated in Uganda.
Let’s note that in Africa, the technology ecosystem is booming. African startups attract investors from all over the world, but for a variety of reasons, the largest share of funds is invested in Nigeria, South Africa, and Kenya. In the "Venture Capital Activity in Africa Q3 2023" report published by the African Private Equity and Venture Capital Association (AVCA), over $2.95 billion was invested in African startups in the first nine months of 2023.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
The South African government is stepping up initiatives to accelerate the adoption of broadband Internet as part of its digital transformation ambitions. It is supported in its efforts by a number of key international partners.
The International Finance Corporation (IFC) and South African investment bank Rand Merchant Bank (RMB) recently committed to investing a total of $49.2 million in the Eastern Cape fibre project piloted by Liquid Intelligent Technologies. Each of the two parties will invest 450 million rand ($24.6 million).
"Not only will this investment from RMB and IFC help fund the expansion of our fibre backbone network in the Eastern Cape, but it will also help us upskill more South Africans and create employment. We believe this collaboration sets a new benchmark for the financing and development of digital infrastructure in South Africa," said Hardy Pemhiwa (photo, center), Group Chief Executive Officer of Liquid Intelligent Technologies.
The funding granted to Liquid Intelligent is part of the three companies' collective commitment to advancing broadband connectivity in South Africa in general, and particularly in Eastern Cape, one of the country's least connected regions.
According to statistics quoted by Liquid, only 65% of households in the Eastern Cape have access to the Internet. What's more, only 5% of the province's households have Internet access from home, which is twice as low as the South African average, where 10% of the total population has Internet access from home.
Ultimately, the project will reduce the digital divide in the Eastern Cape and extend Internet access to underserved areas. The aim is to support the South African government's National Development Plan to achieve 100% broadband coverage in the country by 2030.
Samira Njoya
While presenting promising prospects and undeniable opportunities, technological advances can pose challenges in combating crimes, especially in Africa. This compels defense and security forces to improve their capabilities, notably those related to cybersecurity.
Last Monday (November 13), the Chinese Embassy handed a digital forensics laboratory to the Seychelles police’s cybercrime division. According to the Seychelles News Agency, the laboratory was handed out by Mu Jianfeng (photo, left), Chargé d'Affaires of the Chinese Embassy in Seychelles.
The laboratory is funded, to the tune of one million Yuan ($137,000), by the Chinese government. "The laboratory will be fully operational in the next few days, and its main functions include secure data extraction, storage media backup, rapid data acquisition, data analysis and authentication, and data recovery. It will be an effective tool for the Seychelles police and relevant authorities in digital data investigation and evidence collection," said Mr. Jianfeng.
The new laboratory comes at a time when the Seychelles government is stepping up measures in response to a growing rise in cybercrime in the country. In November 2021, a new law on cybercrime and other related offenses came into force in the country after being approved by the National Assembly.
In January 2023, discussions were also held between the Seychelles police force and an Interpol delegation to set up a unit to combat cybercrime.
Through this acquisition of technical equipment and the training of human resources to combat cybercrime, Seychelles will be able to secure its information systems, which are an indispensable component of digital transformation.
Samira Njoya