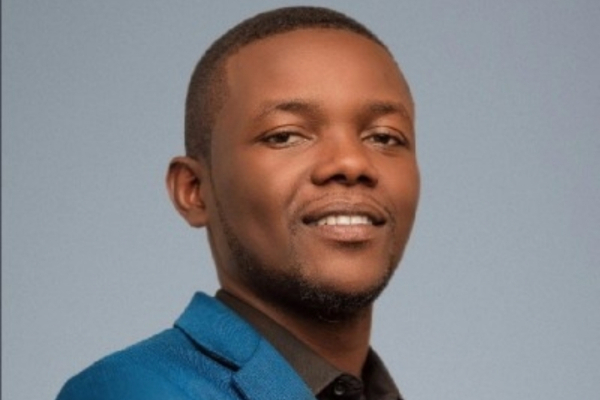
A professional IT specialist, he leverages his technology skills to address the challenges faced by African populations. As the head of a tech company, he has developed several technological solutions.
Nsadi Mbiapa (photo) is a computer scientist and entrepreneur from the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). He is the co-founder and CEO of Faithful, a startup specializing in the development of IT solutions.
Founded in 2020, Faithful's mission is to solve problems faced by African populations through technology. The company assists its clients in creating web and mobile applications, developing software, and managing systems and networks. It also offers services such as data analysis, IT maintenance, and consulting. Innovatively, the startup has developed several solutions to meet societal needs.
One of Faithful's key developments is Newmed, a software that handles registration and card generation for the entrance exam to the Faculty of Medicine at the University of Kinshasa. The startup also designed Lata, a social network dedicated to fashion, and Smart Couture App, an application for managing orders, finished products, and deliveries for tailors.
In addition to his role at Faithful, Nsadi Mbiapa co-founded and became the CEO of Express App in 2021. This mobile application, which operates without an internet connection, provides mobile money, mobile banking, and other financial services in the DRC and Central Africa.
Also in 2021, he co-founded Masolo, a free instant messaging app in the DRC that ensures the confidentiality of communications. Masolo offers features such as instant messaging, voice and video calls, and file transfers.
Nsadi Mbiapa holds a master's degree in computer engineering from the University of Kinshasa, obtained in 2023. During his studies, he served as the head of the IT department at Convipat, an NGO promoting agriculture. He also worked as an IT consultant for RATALBI Pisciculture, a fish production center in Kinshasa.
Between 2019 and 2020, he was the deputy project manager for a University of Kinshasa initiative aimed at creating a potable water system for the residents of Dwale, in the Bateke Plateau of the DRC.
Melchior Koba
Founded by three tech entrepreneurs, the solution digitizes insurance brokerage services, making it easier for people to find the right insurance policy
Amenli is a digital solution created by an Egyptian startup that helps users find the most suitable insurance policies tailored to their needs. Founded in 2020 in Cairo by Adham Nauman, Omar Ezz El Din, and Shady El Tohfa, the startup aims to protect individuals and businesses from unexpected costs and incidents. In October 2023, Amenli secured $1 million in funding to support its growth.
Commenting on the funding round, Shady El Tohfa said, "The backing of these prominent investors, who all possess extensive experience in the tech and insurance sectors regionally and globally, has reinforced our belief in the strength of our vision and in moving forward with our plans for Amenli’s expansion and growth."
The solution offers a mobile app available on both iOS and Android, which has been downloaded over a thousand times, according to Play Store data. Users can create an account to access Amenli's services, which include a variety of insurance policies such as health, car, home, and business insurance.
With just a few clicks on the web or mobile platform, users can obtain quotes or subscribe to policies that meet their needs. Amenli claims the insurance policies provided are the best options available from partner insurance companies. Additionally, Amenli manages claims with insurance companies on behalf of its clients.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
Founded by two tech entrepreneurs, it aims to simplify the shopping experience for students.
Chao, a Nigerian startup founded in 2022 by Gift Akobundu and Melvin Senne-Aya, enables users, particularly students, to order food, groceries, and medications for delivery directly to their university campus.
The startup was born out of the founders' observation that there was no efficient way for students to order meals from nearby stores, as no food delivery platform operated in the area. Akobundu, a software engineer, began engaging with restaurant owners to better understand their business operations and explore potential solutions.
“It was not possible to efficiently order meals from stores because no food delivery platform operated within campus environs. I began talking with restaurants to gain deeper insights into their individual business operations, understanding what it would take to solve the problem as a software engineer – not just for users, but also for the stores,” Akobundu told Disrupt Africa.
Chao's solution features a mobile app available on both iOS and Android platforms. Users can create an account and access partner restaurants, grocery stores, and pharmacies. They can then place orders for cooked meals, groceries, or medications to be delivered to their location.
After launching its beta service, Chao decided to expand its offerings beyond prepared meals to meet the diverse needs of its target market.
The startup currently boasts over 3,000 users and serves two campuses: Babcock University and the University of Port Harcourt. Chao aims to expand to other communities within the next 24 months.
In 2023, Chao was recognized for its achievements, winning the eCommerce award at the Wema Bank Hackathon and Grand Summit. In 2024, the startup further solidified its success by winning at Markhack 3.0, organized by Eko Innovation Centre and GDM Group. This accolade earned Chao $1,000 in Amazon credits, a $50,000 seed investment from Eko Innovation Centre, and a three-month acceleration program valued at $10,000.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
With over 10 years of experience in business management, engineering, and project execution, he offers a comprehensive business management application that enables users to focus entirely on their strategy and business growth.
Paul Kimani (photo), a Kenyan electronics engineer and entrepreneur, is the co-founder and CEO of Workpay, a startup focused on making payroll, benefits, and human resource management solutions accessible and affordable for businesses across Africa.
Founded in 2019 by Paul Kimani and Jackson Kibigo, Workpay offers a comprehensive solution for managing human resources, payroll, and employee benefits, designed for fast-growing companies. The platform allows businesses to focus on their strategy and growth instead of repetitive administrative tasks.
The Workpay app provides companies with online services and real-time team management from a smartphone. It features precise time-tracking, facilitates the recruitment of top talent across the continent, delivers real-time expense insights, and enables performance management.
Paul Kimani holds a bachelor's degree in electronic and electrical engineering, obtained in 2013 from the University of Nairobi, Kenya. His professional career began in 2007 at Equity Bank Ltd, where he worked as a relationship officer.
In 2010, he joined software development company MTL Systems as a web and mobile application developer. In 2014, he became the commercial director at Coolpoint HVAC Engineers Ltd, a Kenyan company specializing in air conditioning, heating, refrigeration, and ventilation services. The following year, he joined Afrisoft Africa Ltd, an IT company, as executive director, a position he held until 2018.
Melchior Koba
Lucky, an Egyptian fintech startup, has secured a US$3 million in a funding round led by Lorax Capital Partners, KEM, DisrupTech Ventures, and other existing investors.
The newly raised funds will be strategically allocated to expand Lucky's credit services, reinforcing its position as a leading consumer credit fintech in Egypt.
Lucky offers financial flexibility and increased spending power through its lending schemes, discounts, and cashbacks.
Agriculture is a strategic economic sector that generates wealth and employment in Africa. However, a number of countries are still struggling to organize it effectively. Digital technology can help to overcome this weakness
The Federal Ministry of Agriculture and Food Security has inaugurated a Technical Working Group (TWG) focused on developing a seamless database to accurately identify Nigerian farmers, a press release by the Federal Ministry of Information and National Orientation dated August 17 revealed. The initiative, led by Permanent Secretary Mr. Temitope Fashedemi, aims to improve the distribution of agricultural inputs and support to farmers across the country.
During the inauguration ceremony, held recently at the Ministry’s Conference Room in Abuja, Fashedemi emphasized the importance of this initiative in shaping the future of Nigeria's agricultural sector. He noted that a reliable database would enable the Ministry to more effectively deliver services and resources to the farmers who need them most.
To achieve this goal, the Ministry plans to collaborate with the National Identity Management Commission (NIMC), which will play a crucial role in creating a robust database. The Permanent Secretary highlighted that this collaboration would help ensure the accuracy and completeness of the data collected, thereby enhancing the Ministry's ability to implement agricultural programs efficiently.
The TWG, comprising members from the technical departments of the Ministry and NIMC, has been tasked with developing effective modalities for collaboration between the Ministry and NIMC. The group's Terms of Reference (TOR) include creating a comprehensive work plan with clear timelines and roles, designing data collection tools to capture essential farmer information such as identification details, farm size, and crop types, and identifying training programs for field officers and data collectors to ensure data accuracy, the release further stated.
The database will help assess financial credibility for connecting farmers to microfinance and subsidy programs, facilitating access to credit and aid.
According to the latest data from the World Bank, agriculture, forestry, and fishing contributed approximately 22.72% to Nigeria’s GDP in 2023. This underscores the importance of the government's initiative to develop a comprehensive database of farmers. With agriculture being such a vital part of the economy, accurate data collection will enable a more targeted and effective distribution of resources, ultimately enhancing productivity and supporting economic growth.
Hikmatu Bilali
Over the past five years, Nigeria has experienced significant adoption of crypto assets, coinciding with successive declines in the value of the naira. The government, viewing these assets as contributing to the depreciation of the local currency, has decided to regulate the sector to restore order.
The Nigerian government is set to regulate the cryptocurrency industry by September 2024. Zacch Adedeji, Executive Chairman of the Federal Inland Revenue Service (FIRS), announced this during the FIRS 2024 Stakeholders Engagement with the Senate and House of Representatives Committees on Finance on August 17.
The proposed legislation will address the regulation of cryptocurrency transactions, an area currently lacking legal oversight in Nigeria. "While we cannot ignore cryptocurrency as there is currently no law in Nigeria regulating it, there is a need for legislation to govern this type of transaction," he stated.
In parallel, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) is encouraging virtual asset service providers to join its Accelerated Regulatory Incubation Programme (ARIP) to expedite their registration and compliance with the upcoming Digital Assets Rules.
Nigeria is currently Africa’s largest cryptocurrency market and one of the leading markets worldwide. According to New York-based research firm Chainalysis, the country ranked second in the 2023 Global Crypto Adoption Index that measures crypto adoption across the globe. The widespread adoption highlights the need for a legal framework that can both harness the economic potential of cryptocurrencies and address associated risks, ensuring that the sector contributes positively to Nigeria's economic development.
Hikmatu Bilali
African countries are rapidly digitizing their administrative services. To maximize the benefits for their citizens, they need reliable identification systems.
TECH5, a contactless biometrics solution provider, announced on Thursday, August 15, that it has partnered with the Mauritanian government and local integrator SmartMS to launch the pilot phase of a digital identification solution in Mauritania. Funded by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), this project aims to modernize the country's digital identity infrastructure.
"We are proud to be part of this project contributing to the technological transformation of the country. Mauritania looks to be on track to become one of the first countries to adopt fully digital national ID biometrically linked to its holder," said Ameya Bhagwat, TECH5 Chief Revenue Officer.
For this pilot phase, a software solution was developed to facilitate the digital integration and verification of citizens. Tested by over 70 people, this solution adheres to NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) standards for identity verification and incorporates biometric verification via OpenID Connect flows. This enables password-free access to the Mauritanian e-government portal. Users are verified by the application through a selfie, which is then compared to their digital identity derived from their passport or ID card.
The successful completion of the pilot project led to the recent launch of the "Houwiyeti" application, an innovative solution that combines functionality and security, leveraging open-source and digital technologies. This initiative is fully aligned with the Mauritanian government's and its partners' goals of promoting an inclusive and rights-respecting digital transformation. It also reflects a broader trend in Africa, where biometrics is playing an increasingly crucial role.
According to the "Biometrics - Global Market Trajectory & Analytics 2020" report published by the American research firm Global Industry Analysts, the biometrics market in Africa and the Middle East is expected to grow at an annual rate of 21%, while the global biometrics industry could reach $82 billion by 2027. This trend underscores the growing importance of biometric technologies in global digital development and their potential to transform governance systems and public services.
The implementation of this digital identity system in Mauritania represents a significant step toward the modernization and efficiency of public services. By providing secure and streamlined access to government services through a biometric-based mobile application, this system not only improves ease of access for citizens but also strengthens the security of digital transactions.
Samira Njoya
A tech entrepreneur with over 7 years of experience in software development, he has designed a digital security network aimed at protecting homes from attacks and break-ins.
Anatoli Kirigwajjo (photo) is a Ugandan computer scientist and entrepreneur, co-founder of Yunga Technologies, a company that develops community security devices for households. Founded in 2018, Yunga Technologies specializes in digital security technologies in Uganda. By leveraging the Internet of Things (IoT), the company designs tools aimed at preventing crime and enhancing community safety.
The Yunga system is a local digital emergency network that connects neighbors and links them to the police during emergencies. The device sends alert messages to other devices within the network, including the victim's coordinates and address, facilitating a swift community response. Notably, the system functions in areas without internet access, utilizing a long-range network with a 20 km radius. It can connect to both smartphones and basic phones via SMS.
Prior to founding Yunga, Kirigwajjo co-developed an application called E-liiso with two colleagues. This app captures a photograph of the eye and analyzes the image to detect conditions such as color blindness, myopia, hyperopia, and cataracts. He served as the Chief Technology Officer for the company behind this application, Sight for Everyone, from 2016 to 2017.
Kirigwajjo graduated from Makerere University, where he studied computer programming from 2011 to 2015. In 2023, he received the Engineering Innovation Award for Africa, presented by the Royal Academy of Engineering in the United Kingdom.
Melchior Koba
Committed to a greener future, Orange has set ambitious goals to reduce its environmental and climate impact across its 17 markets in Africa and the Middle East. Various initiatives are underway to achieve these objectives.
Orange Middle East and Africa (OMEA) has converted 10,000 telecom sites and about 20 data centers to solar energy, the company said on Friday, as part of its strategy to bolster infrastructure resilience and maintain profitability.
For Jean-Michel Canto, Chief Climate Officer of OMEA, "Solarization is now a standard configuration for new sites, with an 11% increase in the number of solar sites each year."
In Liberia, where the electrification rate is 12%, the company has solarized 77% of its sites. Jabateh Dweh Charles, Power Manager Operations at Orange Liberia, said this reduced their carbon footprint and fuel consumption by 25% in 2023 compared to 2022.
OMEA's 2023 Corporate Social Responsibility report showed a more than 70% increase in renewable energy use compared to 2022, bringing the share to 32.8% of total energy consumption.
The company prioritizes site solarization and collaborates with energy partners (ESCO – Energy Service Company). In 2022, Alioune Ndiaye, Chairman of OMEA's Board of Directors, noted that solar energy supply saves up to 55 million liters of fuel annually.
These investments align with OMEA's "Lead the Future" and "Net Zero Carbon" by 2040 plans. The company aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 30% by 2025 and 45% by 2030.
Dorothée Vignalou, Chief Financial Officer of OMEA, said, "We have always placed environmental and energy issues at the heart of our regional strategy. Recent crises have strengthened our determination to ensure sustainable management while addressing local community challenges."
More...
Many African populations lack access to traditional banking services. As a result, fintech solutions are growing in popularity across the continent. These solutions provide alternative ways to access financial services.
PaySika, a fintech startup based in Douala, Cameroon, provides users with access to online financial services through a smartphone app.
Founded in 2020 by Roger Nengwe Ntafam and Stezen Bisselou, it aims to create affordable, seamless, and transparent banking experiences, with a focus on simplifying online payments.
The mobile app, available on iOS and Android platforms, has garnered over 50,000 downloads on the Play Store. Through that app, users can create an account within minutes to access various services.
PaySika offers virtual and physical cards, allowing users to receive payments from PayPal, trading platforms, online betting, royalties from YouTube, Facebook, Instagram, TikTok, and many others.
The service enables purchases at local and international stores, ATM withdrawals worldwide, and card management features such as blocking, unblocking, deleting, or setting spending limits.
It charges 1% on online payments and ATM withdrawals, and 2% for international transactions and mobile money withdrawals. However, it does not charge for alerts, monthly management fees, or card maintenance.
The minimum recharge amount is XOF100 ($0.16), with a minimum withdrawal of XOF600.
In August 2024, PaySika was named among the twelve finalists in the Ecobank Fintech Challenge.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
After his studies in France and the United States, he embarked on an entrepreneurial journey to simplify life for African populations. He offers the Senegalese diaspora living in Europe a digital solution to send money to their loved ones back home.
Lamine Tall (photo) is a Senegalese computer scientist and tech entrepreneur. He is the founder and CEO of Cauri Money, a fintech company that enables the African diaspora to send money to their home countries. Founded in 2019, Cauri Money began its operations in January 2020, with a mission to facilitate money transfers from Senegalese expatriates to their families back home. The startup offers "a digital platform designed for African diasporas, aggregating alternative solutions to traditional money transfers at unbeatable prices."
SInce its creation, the platform’s stated ambition is to symplify money transfers from Europe to Senegal, while integrating Senegalese values and ensuring total security. Users can transfers between $0.17 and $10,000 fee-free with the platform ensuring optimal transparency for every transaction.
In addition to Cauri Money, Lamine Tall co-founded Samaritanz Technologies in 2017, a company that develops a social network to facilitate the collection and redistribution of food donations by non-governmental organizations (NGOs).
Lamine Tall holds a bachelor's degree in information technology from SKEMA Business School in France, as well as a master's degree in business information technology from Virginia Tech in the United States. In 2016, he also earned a master's degree in strategy from EDHEC Business School in France.
His professional career began in France in 2016, where he worked as a junior associate at CGI Business Consulting. In 2018, he joined EY as a consultant in digital business transformation, before becoming a fintech and financial services consultant at Deloitte in 2019.
On August 3, 2024, his startup, Cauri Money received a $25,000 investment from artist Pharrell Williams as part of the Black Ambition program.
Melchior Koba
Lack of internet access can be addressed by making mobile phones affordable in African countries. This is crucial for ensuring that all citizens, regardless of their socio-economic status, can participate in the digital economy
The Malawi Communications Regulatory Authority (MACRA) plans to launch a local smart device assembly program aimed at producing affordable mobile phones to bridge the significant digital divide in the country, Director General of MACRA Daud Suleman revealed on August 14. This was during the 3rd session of the National Youths Conversations hosted by the National Youth Council of Malawi (NYCOM) as part of commemoration of the International Youth Day 2024.
The Director General emphasized the importance of a collaborative effort from various stakeholders to enhance digital service access across the nation. “We need a multi-sectoral approach for citizens to have access to digital services at a reasonable distance,” he stated.
According to the Alliance for Affordable Internet (A4AI), cell phones, particularly smartphones, are still inaccessible to low-income populations in Africa. This situation hinders the participation of most of Africa’s population in the digital economy. Without a phone, there is no way to connect to the Internet or use digital services. The price disparity between cell phones and average incomes also exacerbates digital inequalities. People who cannot afford these devices miss out on the benefits of digital technology, including access to information, financial services, online education, and economic opportunities.
While no specific launch date has been provided, the upcoming initiative is expected to address the disparity in digital access.
The initiative aligns with the Malawi 2063 (MW2063) agenda, which seeks to transform Malawi into a prosperous, self-sufficient, and industrialized 'upper-middle-income country' by 2063.
Hikmatu Bilali
Huawei South Africa is inviting tech-savvy women entrepreneurs to apply for its Huawei Women in Tech Digital Skill Training Program. This initiative, offered in partnership with the Department of Communications and Digital Technologies, focuses on enhancing skills in 5G, Cloud, and Artificial Intelligence (AI).
The program aims to empower women by providing advanced training in these critical technology areas. Interested applicants should be available to travel to the Huawei Office Park and Henley Business School Africa in Johannesburg between August 22 to August 28 for the training.