Artificial intelligence offers Africa a chance to tackle key challenges and drive economic growth. But to fully capitalize on AI, significant investments are needed.
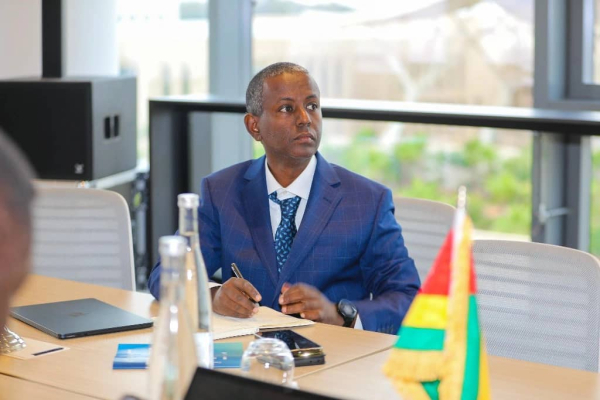
Djibouti plans to become a regional hub for artificial intelligence (AI) innovation, according to Houssein Ahmed Assoweh (photo), the country's representative at the ICESCO regional workshop for the development of the Islamic World Charter on AI.
In an interview with the Djiboutian News Agency ADI, Houssein Ahmed Assoweh said: "We will continue to invest in AI education and training to strengthen national skills. Additionally, we plan to launch several pilot projects in identified priority areas. The goal is to position Djibouti as an AI innovation hub in the Horn of Africa. I am convinced that Djibouti has an important role to play in the global AI ecosystem.”
According to the AI expert, Djibouti is developing its national AI strategy, focusing on improving living conditions in a challenging environmental context. The strategy includes the application of AI in critical areas such as smart agriculture, healthcare, logistics and transportation, as well as education. These efforts are part of "Vision 2035," the Djiboutian government's development strategy aimed at equipping the country with world-class digital infrastructure.
By investing in AI, Djibouti aims to become a key player in technological innovation in Africa. AI could notably enable significant advances in smart agriculture, optimizing crop yields despite the country's climate challenges. In healthcare, AI could facilitate more accurate diagnoses and increased access to care, particularly in remote areas.
According to PwC's "Annual Global CEO Survey," AI could contribute up to $15.7 trillion to the global economy by 2030, with $1.2 trillion potentially generated in Africa. This contribution could represent a 5.6% increase in the continent's GDP over that period, highlighting the enormous potential of AI to boost Africa's economic growth if properly harnessed.
Samira Njoya
In many African nations governance is riddled with a lack of transparency, which is critical for building public trust and ensuring that development initiatives are implemented effectively. The introduction of digital platforms streamlines public administration to increase transparency in government activities, addressing public concerns about unfulfilled promises and resource management.
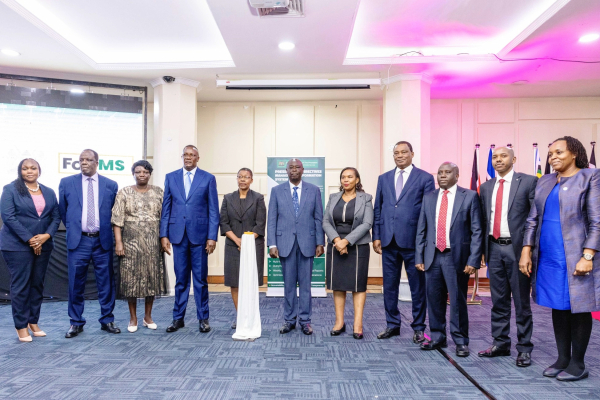
The Kenyan government launched, yesterday September 2, two innovative digital platforms, aimed at enhancing transparency and efficiency in public administration. The platforms, the Presidential Directives Management Information System (PDMIS) and the Foreign Travel Management Information System (FOTIMS), were officially introduced at the Kenyatta International Convention Centre by Deputy President Rigathi Gachagua and Dr. Margaret Ndung’u, the newly appointed Cabinet Secretary for Information, Communications, and the Digital Economy (MICDE).
“The Presidential Directives Management Information System (PDMIS) and Foreign Travel Information Management System (FOTIMS) are a huge milestone in our quest to deal with obscurity in decisions undertaken as raised by Kenyans recently,” said Rigathi Gachagua in a tweet shared the same day.
This system tracks and manages directives from President William Ruto, ensuring efficient and transparent implementation. It is accessible only to high-level officials, centralizing all directives and eliminating the need for paper copies.
FOTIMS digitizes the approval process for foreign travel by senior officials, ensuring justifications are made and resources are used wisely. Access is limited to authorized personnel, enhancing oversight.
The launch of PDMIS and FOTIMS represents a key step in Kenya's digital transformation, aiming to set higher standards for accountability and efficiency in public administration.
This move aligns with the Kenyan government’s efforts to improve digital governance. In the 2022 UN E-Government Index ranking, which assesses the digital government landscape of UN member countries, the country rose from 116th to 113th out of 193 countries, reflecting its ongoing commitment to enhancing its digital government capabilities. Introducing these new digital platforms further underscores Kenya's progress in public administration, as they are likely to contribute to continued improvements in transparency, efficiency, and overall governance.
Hikmatu Bilali
A financial expert with a focus on economic policy, he aims to expand financial access in Africa. His vision is for Service Cops to become a leader in technological innovation across Sub-Saharan Africa and Asia.
Ugandan entrepreneur Joseph Kiiza (photo) is the co-founder and executive chairman of Service Cops, a fintech startup focused on business process outsourcing (BPO).
Founded in 2012, Service Cops aims to optimize business processes, increase revenue, and reduce costs for its clients. The company seeks to become a global leader in fintech and BPO. It developed several fintech solutions, including SchoolPay, a universal digital platform that simplifies school fee payments and school management. This solution allows parents and guardians to easily pay fees, while school administrators can efficiently manage their tasks. Another solution is Vantage, a credit account management platform.
The company also designed other technological solutions, such as School Suite software, which facilitates the management of educational institutions. This software enables teachers, administrators, and students to digitize daily educational processes.
In 2023, Service Cops formed a strategic partnership with Awash Bank, a private Ethiopian bank, in the framework of its expansion. Under that partnership, it initially offers digital loans to Awash Bank’s clients before gradually extending the service to non-bank users.
“Our long-term growth plan is to have a significant presence in all emerging economies in Africa and Asia, targeting key economic blocs such as the East African Community (EAC), the Southern African Development Community (SADC), the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS), and the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN),” Kiiza stated.
In addition to his role at Service Cops, Joseph Kiiza is the CEO of Edge Micro Insurance, an insurance company in Uganda. He also serves on the board of Nepserv Consults, a Ugandan financial institution.
The entrepreneur holds two master's degrees from Makerere University in Uganda, one in finance and another in economic policy and planning, both obtained in May 2024.
Melchior Koba
He wants to revolutionize global health, entrepreneurship, and leadership. His career in healthcare has garnered numerous prestigious awards.
Kenyan entrepreneur Stephen Ogweno is the co-founder and CEO of Lifesten Health, a digital health startup based in Rwanda. Lifesten Health enables users to set specific health goals, track their vital signs, and receive rewards for their progress.
Founded by Ogweno and Peace Ndoli, Lifesten Health focuses on medical technologies and aims to educate and raise awareness about lifestyle-related diseases while promoting healthier living habits through technological advancements. Their digital health platform offers web and mobile solutions to help users better manage their nutrition, well-being, health, and mindfulness. By leveraging artificial intelligence and behavioral learning, the platform helps users understand their health status and receive expert advice to improve it, with a special emphasis on mental well-being.
Ogweno is also the founder and CEO of the Stowelink Foundation, an organization established in 2015 that develops innovative community health projects focused on people, prioritizing non-communicable diseases, health technologies, research, and advocacy. Additionally, he serves as the director of the World Obesity Foundation, an organization dedicated to combating obesity, and is a member of the Board of Governors for NCD Child, a multi-stakeholder coalition advocating for the rights and needs of children, adolescents, and young people affected by non-communicable diseases.
Ogweno holds a bachelor's degree in population health from Kenyatta University in Kenya, obtained in 2019, and a master's degree in public health from the University of Manchester in England, earned in 2023. His commitment to digital health innovation and public health has been recognized multiple times. In 2020, he was named one of Africa's 100 most influential young leaders, and in 2021, he was honored as one of Kenya's Youth of the Year as part of the Top 35 Under 35 National Awards. In 2022, he was awarded the Kenyan Quality Health Care Award for Health Innovation of the Year.
Melchior Koba
African nations are increasingly forming partnerships to accelerate their digital progress. New initiatives are emerging rapidly, building momentum towards a digitally transformed continent.
A Sierra Leonean delegation visited Guinea last week to discuss the implementation of a fiber optic interconnection project between the two countries. The project aims to enhance internet connectivity and resilience in both nations.
According to Mohamed Kourouma, general manager of Guinea's National Backbone Management and Operations Company, the project is crucial as Guinea currently relies on a single submarine cable for international internet connectivity.
The working visit follows discussions initiated in early August between Guinea's Minister of Posts, Telecommunications, and Digital Economy, Rose Pola Pricemou, and her Sierra Leonean counterpart, Salima Manorma Bah. During the talks, they announced an ambitious project aimed at ensuring a permanent and reliable Internet supply in both countries.
The discussions among the various parties laid the groundwork for the signing of a framework agreement, which is expected to be signed after review by the competent authorities of both nations. This agreement will define the technical modalities for implementing this strategic partnership.
The partnership is seen as a way to significantly improve the quality and scope of connectivity services while reducing associated costs. Moreover, strengthening Internet access and sharing expertise will help accelerate the achievement of the two countries' shared ambitions for digital transformation, while also promoting digital inclusion for their respective populations.
Samira Njoya
Designed to expand credit access for African immigrants, it enables money transfers to approximately 20 African countries.
Kredete is a fintech solution developed by a Nigerian startup designed specifically for African immigrants in North America. The platform enables users to send money to over 20 African countries and establish a credit score.
Built on blockchain technology, Kredete ensures that all financial transactions are secure and efficient. For money transfers, the platform uses stablecoins, significantly reducing transfer fees. Launched in 2023 by Adeola Adedewe, Kredete secured $2.25 million in funding last August to enhance its technology and expand into new African markets.
According to Adedewe, "Kredete is more than just a remittance service; it’s a gateway to financial inclusion for African immigrants in the diaspora.”
“[...] Our goal is to empower our users to build a secure financial future, no matter where they are migrating into," he added.
Kredete is available as a mobile app on iOS and Android, with over 100,000 downloads on the Play Store. After downloading, users can create an account and access the platform. Users can then fund their multi-currency digital wallet to make various financial transactions.
On the mobile platform, users can transfer funds between digital wallets, send money to mobile money accounts in supported African countries, or make bank transfers. Each transaction contributes to building the user's credit score. Kredete updates user data with every transaction. Additionally, the startup offers a referral program that rewards users with up to $20 for each person they refer.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
Cocoa is a vital export for many African nations, yet production challenges limit the sector's potential. Leveraging technology can address these issues, leading to improved market access and higher prices for African cocoa.
Cameroon's cocoa sector has unveiled plans to launch a digital platform that will provide georeferencing data for cocoa plantations across the country. The Cocoa and Coffee Interprofessional Council (CICC) formalized this initiative with an agreement signed on August 28. Supported by key industry players such as Atlantic Cocoa Corporation, Neo Industries, Ofi Cam, Sic Cacaos, Telcar Cocoa, and the Cocoa and Coffee Subsectors Development Fund, the platform aims to ensure that all cocoa beans produced in Cameroon can be accurately traced to their origin.
CICC Executive President Apollinaire Ngwe emphasized the significance of this initiative, stating, “This marks a significant step forward in technological integration and inter-professional collaboration. The system will provide operators with immediate access to precise and up-to-date data, facilitating more efficient supply chain management.”
Georeferencing involves assigning precise geographical coordinates to cocoa plantations, enabling each location to be uniquely identified. This data-sharing system will centralize important information such as farmers’ locations, farm details, productivity, and sales, allowing cocoa exporters to quickly access coordinates for producers' farms.
This initiative is driven by the need to meet EU legislation set to take effect by the end of the year, which will prohibit the entry of goods produced on deforested or degraded land into the European market. The platform will be instrumental in maintaining Cameroon’s access to this crucial market where in 2020 the country exported 65% of the cocoa it produced, according to data from the EU sustainable cocoa program.
Cameroon is one of Africa’s top cocoa producers globally. WorldAtlas ranks the country as one of the top six cocoa-producing countries producing over 290,000 tons annually. The new platform will guarantee the international standard quality of its production.
Hikmatu Bilali
Malaria remains one of Africa’s most pressing public health issues, accounting for over 90% of global malaria cases and deaths. Leveraging AI to enhance prevention, detection, and treatment can drastically reduce the disease’s burden, saving lives and improving health outcomes.
The University of Zambia (UNZA) and the Convergence Research Centre for Insect Vectors (CRCIV) of South Korea have signed an agreement to advance malaria research using artificial intelligence (AI). The partnership, signed on August 30, will establish a Research Center of Excellence at UNZA’s School of Engineering, focusing on preventing malaria outbreaks through AI technology.
For UNZA Acting Vice Chancellor, Professor Bornface Namangala, the partnership marks the beginning of a transformative effort to tackle malaria, a leading cause of death in Zambia.
SMART Zambia National Coordinator, Percy Chinyama, praised the collaboration, noting that the center could serve as a learning platform and help institutionalize AI in Zambia.
The initiative will leverage cutting-edge AI technology to identify mosquito species and combat malaria. An AI-powered system will be deployed to collect and accurately classify mosquito species, enhancing the precision of malaria prevention efforts. This project has garnered strong support from the government.
According to the U.S. President’s Malaria Initiative (PMI), which aids sub-Saharan African countries in controlling and eliminating malaria, Zambia remains highly endemic, with the entire population at risk. In 2022, the National Malaria Elimination Centre (NMEC) reported over 8.4 million cases, an incidence rate of 428 per 1,000 people annually, and 1,337 malaria-related deaths, equating to 8 deaths per 100,000 people.
This initiative aligns with Zambia’s National Malaria Monitoring and Evaluation (M&E) Plan 2022-2026, which outlines a framework for tracking malaria program indicators, data sources, analysis, information flow, reporting, and feedback for informed decision-making. It directly supports the plan’s goal of improving data-driven decision-making and achieving better health outcomes.
Hikmatu Bilali
The Bank of Uganda has granted Tanzanian fintech NALA an International Money Transfer Operator (IMTO) license, the fintech announced on August 29. This allows NALA to expand its operations in Uganda by integrating directly with mobile money services, offering users a seamless way to transfer funds into local mobile wallets and enhancing the efficiency and security of cross-border payments.
NALA facilitates money transfers from the UK, US, and EU to several African countries, including Uganda. It has collaborated closely with the Bank of Uganda to meet regulatory requirements, contributing to an increase in foreign exchange supply, which is vital for economic growth.
As an IT project manager and application developer, he has implemented various technological solutions across different sectors in Côte d'Ivoire. One of his most well-known products is a telemedicine application.
Anicet Amani (photo) is an Ivorian computer scientist and entrepreneur, and the founder and CEO of Skan Technologies, which specializes in software development and technological innovation.
Founded in 2011, Skan Technologies has developed several technological solutions across Africa. Its flagship product, SkanMed, is a telemedicine application that allows users to find a doctor and receive consultations remotely via video calls. After the consultation, the doctor can prescribe medication and/or recommend tests. SkanMed also enables users to order home healthcare services.
Another notable product from the startup is SkanTicket, an electronic ticketing application. This free solution allows users to create custom events, offer tickets or invitations online, promote their events, and manage access control on the day of the event.
Skan Technologies has also initiated other projects, such as SkanPhoto and SkanNpay. SkanPhoto is a photo sales application that, using facial recognition, allows anyone photographed at an event to automatically find their pictures. SkanNpay is a mobile payment app that facilitates payments via QR code.
Amani holds a master's degree in electronics, electrotechnics, automation, and computer science, obtained in 2009 from Félix Houphouët-Boigny University in Côte d'Ivoire. He began his career in 2010 at SA TIERI (Engineering, Studies, and Industrial Realizations) as an automation engineer, where he developed simulator systems. In 2012, he joined the software company VEONE Technologies as a Java project manager. From 2013 to 2019, he served as a solutions integration engineer at MTN in Côte d'Ivoire.
Melchior Koba
More...
The Mauritian government has rolled out several ambitious programs to boost the country's digital transformation. Early results are promising, with modern infrastructure and digital public services becoming a reality.
Mauritius launched its Mobil ID, a digital identity card, on Thursday, marking a significant milestone in its digital transition.
The event, presided over by Technology Minister Deepak Balgobin, also showcased the Mobile Wallet Application (MWA), the tool through which the digital ID can be obtained.
Balgobin said the Mobil ID is more than a technological innovation; it represents a decisive government commitment to modernizing the nation. "Mauritius stands out as the first African country to adopt a digital identity card that meets international ISO standards. This technological advancement positions our country at the forefront, reinforcing our role as a leader in this new digital era," he stated.
The Mobil ID is the result of a collaboration between Thales and Harel Mallac Technologies. It is a key component of the "Digital Mauritius 2030" strategy, which aims to make digitalization one of the main pillars of the Mauritian economy. This ambitious strategy includes significant investments in digital infrastructure, digital skills training, and transforming public administration into a fully digital model. Supporting this initiative, Mauritius Telecom (MT) expanded its 5G network nationwide as early as June.
According to DataReportal figures published at the beginning of 2024, Mauritius had approximately 982,500 Internet users out of a population of 1.3 million, reflecting the population's growing embrace of the digital age.
The Mobil ID stands out for its advanced features, allowing citizens to report a change of address or declare the loss of their physical identity card. It also facilitates the electronic signing of official documents. To ensure user security, the Mobil ID incorporates two verification systems and dual authentication, providing effective protection against identity theft.
Samira Njoya
He has over 12 years of experience in software engineering, data science, artificial intelligence, and business development. With his latest venture, he aims to make cutting-edge AI technologies more accessible to businesses.
Idris Babatunde Olayemi (photo), a trained computer scientist and Nigerian entrepreneur, is the co-founder and CEO of InovaAI, a company specializing in artificial intelligence.
Founded in 2023, InovaAI provides AI-driven solutions to address complex challenges across the continent. The company offers an AI marketplace that allows businesses to access solutions via APIs (application programming interfaces) without requiring technical expertise. InovaAI also helps machine learning and AI engineers monetize their models.
InovaAI's mission is to make AI technology accessible to everyone in Africa. Among its flagship products is BetaBird, a solution designed to optimize the health and productivity of poultry. Through this application, farmers can detect poultry diseases early, assess egg quality, and significantly enhance their farming experience.
In addition to his role at InovaAI, Olayemi is the founder and CEO of Babtech Computers, a tech company established in 2020. Babtech Computers offers IT education services, software development, and training programs aimed at international-level businesses.
Olayemi also serves as the technical lead at Connetmi Live Market, an online commerce platform that allows sellers to interact directly with their customers and prospects.
Before venturing into entrepreneurship, Olayemi worked as a software developer in several Nigerian companies from 2013 to 2018. He later joined Diamond Bank as a data specialist. In 2019, he was appointed as a data scientist at The Emel Group, a wholesale trading company.
Melchior Koba
Amazon has been expanding its presence in Africa for years. As the company celebrates its 20th anniversary on the continent, it is setting ambitious goals to achieve by 2029.
Amazon.com Inc's cloud computing unit, Amazon Web Services (AWS), plans to invest an additional $1.7 billion in Africa by 2029 to expand its cloud and artificial intelligence services, the company said on Thursday. The investment was announced at the AWS Summit 2024 in Johannesburg.
"The AWS community in Sub-Saharan Africa is thriving," said Chris Erasmus, AWS Managing Director for South Africa. "We have thousands of AWS customers in Sub-Saharan Africa today, and we see this as an incredibly strategic growth area for us. [...] We have over 6,000 partners helping us build and deliver our business value."
The investment is part of Amazon's celebration of its 20th anniversary in Africa. In 2020, the company followed Google by launching data centers on the continent. In October 2024, it launched its online retail service in South Africa, the second African country where it has introduced this service, following Egypt.
Amazon's investment will also focus on generative AI, highlighting Amazon Bedrock, its platform that enables businesses to create and develop generative AI applications.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
Nairobi, Africa’s Silicon Savannah, will host the AfricArena Nairobi Summit during Africa Climate Tech Week from September 3-4, 2024.
We’re heading to Kenya! 🇰🇪 Excited to announce the AfricArena Nairobi Summit from Sept 1-4, focusing on Climate Tech in Africa! 🌍
— AfricArena (@AFRICARENA) July 15, 2024
This summit will bring together investors, startups, and policymakers to advance Climate Tech in Africa.
🔗https://t.co/rGN8PJAEki🌱#ClimateTech pic.twitter.com/3MJeD6RMAc
The event will highlight over 20 top climate tech and green economy startups, showcasing innovations and reinforcing Nairobi’s role as a key driver in Africa’s tech and investment scene.
The summit will feature startups like Aquarech, RHEA Soil Health, and iShamba Limited, along with 6 Korean startups expanding into Africa.