News (1790)
Since the beginning of the year, investment vehicles have been forming across the continent to fund the startup ecosystem. Several companies have joined forces to launch a new initiative in this direction.
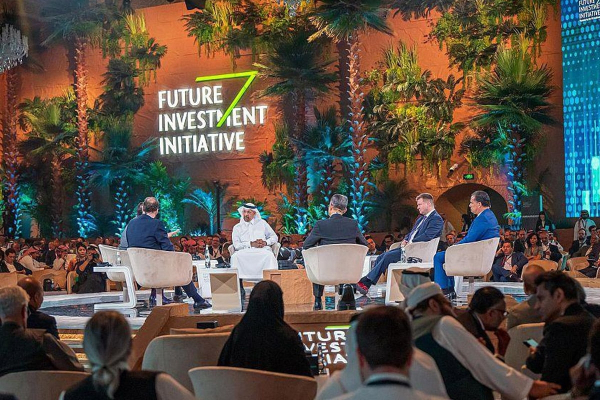
Mara Group, a conglomerate founded by British entrepreneur Ashish Thakkar, has announced the creation of a $250 million investment vehicle to support African startups. The agreement was signed on the sidelines of the 2024 Future Investment Initiative, held last week in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Mara Group has partnered with Startupbootcamp, a technology accelerator, and India-based investment firm Blend Financial Services to execute this project. The new fund will target growth-stage startups and pre-IPO financing, with a focus on South Africa, Nigeria, Kenya, Côte d'Ivoire, and Egypt.
Besides Côte d'Ivoire, the other four target countries represent Africa’s most attractive startup ecosystems in terms of funding. According to Partech Africa data, startups in the "Big Four"—South Africa, Nigeria, Kenya, and Egypt—drew nearly 79% of the continent’s total venture capital funding in 2023, amounting to $1.79 billion. In 2022, these countries captured 72% of funding, totaling $3.5 billion. Startups in Côte d'Ivoire raised $33 million in 2022 and $21 million in 2023, making it the only Francophone country included in the initiative.
This move comes amid a tightening of capital in Africa’s tech ecosystem since 2023, a year marked by a sharp decline in startup fundraising. According to Africa: The Big Deal, African startups have raised $1.7 billion so far this year, a 32% drop from the same period in 2023.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
Egypt’s startup ecosystem is set for growth, driven by rising investor interest, government-led digital transformation, and a growing talent pool. By tackling funding and regulatory challenges, Egypt is on course to become a major tech hub in Africa and the MENA region, boosting economic diversification and digital innovation.
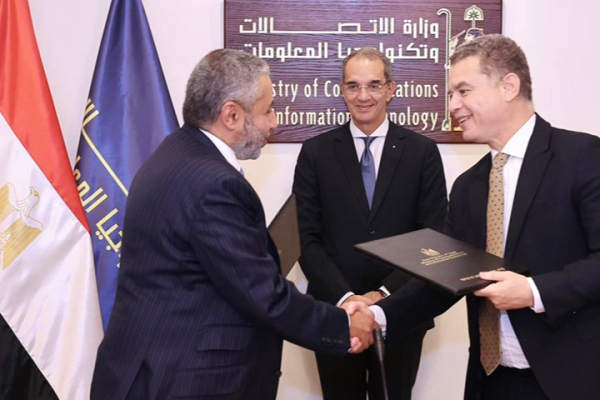
The Minister of Communications and Information Technology, Amr Talaat, attended the launch of "Invest IT," an innovative program to enhance investment readiness for tech startups. The program was organized on November 4, in a collaborative effort between the Technology Innovation and Entrepreneurship Center (TIEC), part of the Information Technology Industry Development Agency (ITIDA), and Flat6Labs, a leading venture capital firm in the MENA region.
Minister Talaat reaffirmed the government’s dedication to creating a conducive environment for startups and entrepreneurs. He outlined several ongoing initiatives focused on skill development, attracting international incubators, facilitating investor access, and establishing Creativa Innovation Hubs across Egypt to nurture innovative talent.
In addition, Talaat emphasized efforts to streamline startup registration processes, enhance post-establishment support, and invest in digital infrastructure to enable startups to thrive.
Ahmed Elzaher, CEO of ITIDA, expressed excitement over partnering with Flat6Labs, highlighting the agency's commitment to supporting startups from ideation to scaling internationally.
Egypt's startup ecosystem is a top performer in the MENA region, ranking third in attracting venture funding. In 2023, Egyptian startups secured $503 million in funding, a decline from the $810 million raised in 2022, according to Lucidity Insights.
The drop in funding for Egypt's startup ecosystem in 2023 highlights potential challenges in sustaining investment momentum amid shifting economic conditions. While Egypt remains a leading startup hub in the MENA region, the decline may indicate heightened caution from investors due to global economic uncertainties, regional competition, or evolving funding priorities. This shift emphasizes the need for robust support mechanisms, like government-backed programs and strategic partnerships, to help startups weather funding fluctuations.
Invest IT is designed to support ICT-enabled startups at the seed and pre-series A stages across Egypt’s governorates. The program aims to equip startups with the skills and resources needed to secure investment deals, providing a structured path to help them navigate the complexities of funding and growth.
The program will run over six to eight weeks, supporting 12 startups as they develop investment strategies and refine their pitches to investors. Upon completion, participants will have opportunities to connect with potential investors, with ongoing support from the program team.
With this support, Invest IT is poised to accelerate the growth of Egyptian tech startups by fostering a robust ecosystem that prepares them for sustainable growth and successful investment outcomes.
Hikmatu Bilali
As cities continue to grow at a rapid pace, smart mobility solutions are emerging as crucial tools to improve traffic safety and efficiency. These interconnected systems optimize road networks and help address the challenges posed by urbanization.
Dakar’s roadways are set to receive a smart, connected transportation system developed by Huawei, as part of a partnership between Senegal and China. The innovative system was presented on Wednesday, November 6, by the Chinese tech firm to members of the Senegalese government.
“This nationwide project, with a significant digital component, exemplifies the need for coordinated digital initiatives by the State of Senegal. This collaborative approach is part of a broader effort to foster unified digital governance,” said Alioune Sall, Senegal’s Minister of Communication, Telecommunications, and Digital Economy.
The project will equip Dakar with smart technologies aimed at optimizing traffic flow and enhancing road safety. Key elements include a video surveillance system to detect and penalize traffic violations; variable message signs (VMS) to provide real-time information to drivers; and an advanced urban control center to monitor traffic. Additionally, checkpoints will be installed to identify speeding and other risky behaviors, contributing to safer and smoother traffic management in the capital.
This initiative aligns with Senegal’s vision for secure infrastructure and the development of smart, safe cities, as outlined in the "Senegal 2050" National Transformation Agenda.
Dakar, with a population of over 4 million, according to the 2023 national census, faces growing transport challenges, including congestion, pollution, and road safety concerns. A study by the Executive Council of Urban Transport in Dakar (CETUD), shared by its Director General Thierno Birahim Aw, highlights that these issues lead to economic losses of nearly 900 billion CFA francs ($1.4 billion) annually, around 6% of Senegal’s GDP.
Once deployed, the new smart transport system is expected to significantly improve traffic safety and management. Real-time video monitoring will detect traffic violations, increase penalty revenues, and promote better discipline among road users. In case of incidents, the high-tech control center will enable swift intervention and better coordination with emergency services, bolstering response times and overall traffic efficiency.
Samira Njoya
As global trade rapidly shifts towards digital ecosystems, international collaborations in this area are becoming essential to drive innovation and broaden digital inclusion.
South Africa and India are set to deepen their collaboration in the digital sector. On Tuesday, November 5, a strategic meeting was held between India’s High Commissioner to South Africa, Shri Prabhat Kumar (photo, left), and South African Minister of Communications and Digital Technologies, Solomon Solly Malatsi (photo, right), to enhance bilateral partnerships in digital technology and connectivity. Key focus areas included IT, digital payment platforms, and cybersecurity. “It’s essential to equip officials with digital skills so that South Africa can thrive alongside global tech leaders,” stated Malatsi.
This meeting builds on a memorandum of understanding between the two countries, emphasizing strategic goals such as expanding broadband connectivity and strengthening cybersecurity. A review of the progress in this partnership is scheduled for early 2025, ahead of the G20 summit in South Africa, to realign priorities and tailor strategies to future needs.
India, with its robust experience in digital development, offers valuable expertise. In digital payments, for instance, its Unified Payments Interface (UPI), launched in 2016, recorded over 100 billion transactions in 2023 alone. In cybersecurity, India has made strides, recently establishing a 5,000-member cyber commando unit to protect critical infrastructure and respond to cyber incidents.
For India, this collaboration opens up significant opportunities to expand its technological and economic influence in Africa. The partnership also positions India as a key tech ally in global digital development, meeting Africa’s growing demand for digital services and connectivity at a crucial moment in the continent's digital transformation.
Samira Njoya
Chadian citizens frequently complain about poor telecom services, particularly internet quality. The latest major outage occurred on October 15 and lasted about 24 hours.
Boukar Michel (photo), Chad’s Minister of Communications, Digital Economy, and Digitalization of Administration, has announced a series of projects aimed at modernizing the national telecom network and reducing consumer costs. He addressed the National Transitional Council on November 5, following the adoption of a law amending Article 13 of the Regulatory Authority for Electronic Communications and Postal Services (ARCEP).
A New Mobile Operator to Enter the Market
One of the key initiatives includes the upcoming launch of Salam, a subsidiary of the state-owned operator Sotel, which will end the current duopoly of Airtel and Moov Africa. In Q3 2024, Moov Africa Chad, a subsidiary of Maroc Telecom Group, reported 6.7 million subscribers and held a 55% market share as of September 2023, making it the market leader.
The entry of Salam is expected to increase competition, ultimately benefiting Chadian consumers seeking better quality services at more affordable prices.
Additionally, the government aims to sell 60% of its stake in Sotel to a private investor to bring in the technical and financial resources needed to revitalize the operator and make it more competitive against Airtel and Moov Africa. Sotel’s fixed and mobile subscriber base has declined over the past seven years, reaching only 23,907 in 2020, according to ARCEP.
Improved Telecom Infrastructure
Michel also announced plans to deploy 200 telecom sites with 3G and 4G capabilities to improve nationwide coverage. According to the International Telecommunication Union's (ITU) DataHub, 3G and 4G networks covered 68% and 36% of the population in 2022, respectively. While 2G coverage reached 86.8%, 5G is yet to be deployed in Chad.
This infrastructure upgrade aims to improve service quality amidst a recent decline in telecom availability. The latest significant outage on October 15 lasted approximately 24 hours, and just ten days later, Airtel Chad experienced a service disruption affecting voice, SMS, and internet for several hours.
These infrastructure investments align with the government’s strategy to strengthen the digital network, particularly through the Trans-Saharan Fiber Optic Backbone project. This initiative will connect Chad with neighboring countries, providing indirect access to undersea cables via coastal nations such as Nigeria, Benin, and Algeria, each linked to multiple undersea cables. The project is expected to be completed by late 2024 or early 2025.
These expanded capacities should enhance internet quality in Chad, a landlocked nation currently reliant on Cameroon and Sudan for its international connectivity.
Starlink
The minister also revealed ongoing discussions with satellite internet provider Starlink. The government anticipates that SpaceX’s Starlink subsidiary will help drive down internet costs.
Starlink plans to begin commercial operations in Chad in 2025, pending regulatory approvals. Pricing details for Chad are not yet available. However, in Benin, where Starlink launched in November 2023, the monthly subscription costs 30,000 CFA francs (around $50), with a one-time terminal cost of 400,000 CFA francs.
Isaac K. Kassouwi
African nations are undergoing a profound digital transformation, with increasing numbers of people coming online, and economies and societies becoming more tech-dependent. This rapid digital growth is expanding opportunities for cybercriminals, making cybercrime one of the continent's most rapidly escalating threats.
The Nigeria Police Force apprehended on November 2, 2024, 130 suspects over alleged involvement in cybercrimes and activities that threaten national security. The suspects include 113 foreign nationals-predominantly Chinese and Malaysian - as well as 17 Nigerian collaborators.
Force Public Relations Officer, ACP Olumuyiwa Adejobi, confirmed that police are conducting “thorough investigations and scientific analysis” of evidence gathered from the suspects. “The suspects will be charged to court upon conclusion of our investigations,” he stated, pledging to provide further updates on the case’s progress.
This crackdown is crucial as cybercrime continues to escalate in Nigeria and across Africa, posing severe economic threats. The INTERPOL African Cyberthreat Assessment Report 2024 highlights that the continent lost over $4 billion annually to cybercrime in 2021. By 2023, Africa experienced a 23% year-on-year increase in average weekly cyberattacks per organization—the highest rate globally.
Furthermore, the Cybersecurity Experts Association of Nigeria (CSEAN) revealed in its National Cyberthreat Forecast 2024 that in 2023, Nigeria faced a sharp rise in ransomware attacks, marking it as the year's top cyber threat. This surge was fueled by ransomware-as-a-service, allowing even low-skilled individuals to launch complex attacks. Active groups like ALPHV, 0XXX Virus, DJVU, and the Cobalt Strike toolkit highlighted the attacks' diversity. Both public and private sectors suffered, incurring losses in the billions of Naira due to operational disruptions and costly recovery.
The operation was executed by the Nigeria Police Zone 7 Command in Abuja. Under the supervision of AIG Benneth Igweh and the National Cybercrimes Centre led by CP Ifeanyi Henry Uche, officers targeted a building in the Next Cash and Carry area of Jahi, Abuja, where suspects reportedly used computers and advanced equipment for cybercriminal activities.
This operation underscores the Nigeria Police Force's ongoing commitment to tackling cybercrime and enhancing national security amidst rising digital threats across the region.
Hikmatu Bilali
In response to rising traffic violations, several countries are turning to technology to enhance road safety. Video-based ticketing is emerging as a promising tool to improve compliance with traffic laws and deter risky driving behaviors.
Seychelles Vice President Ahmed Afif announced last week, the upcoming piloting of a digital road monitoring system based on video ticketing to enhance road safety in the country.
Speaking at a cabinet press briefing on October 31st, he explained: The system “will provide the government with a lot of information, as we have seen nowadays people are driving without a valid license in addition to other illegal activities happening on the roads.”
The said system will utilize public surveillance cameras to enforce traffic laws remotely. When a violation is detected, an image of the vehicle is captured, identifying its make and reading its license plate number. A traffic officer can then issue an electronic ticket remotely, which is sent to the driver via message. Targeted infractions include speeding, using a phone while driving, and not wearing a seatbelt.
The eight-week pilot project will be launched in the Roche Caïman district on Mahé Island. During this phase, authorities will assess and fine-tune the technology to fit local needs. The trial results will be critical, guiding future infrastructure planning and traffic law enforcement. If successful, the system may be permanently implemented in partnership with Australian technology firm Acusensus.
This initiative is part of the government’s strategy to combat dangerous driving behaviors. If adopted, it will target key causes of road insecurity, particularly in urban areas, and promote lasting changes in driver behavior. The system would also streamline and accelerate the processing of violations, reducing the burden on law enforcement and increasing the efficiency of traffic law enforcement.
Samira Njoya
Earlier last year, Algerian authorities launched the digitization of the national agricultural registry. They have completed the digitization goal ahead of schedule.
On Sunday, November 3, Mohamed Yazid Hambli, President of Algeria's National Chamber of Agriculture, announced the completion of the digitization of the National Agricultural Registry (RNA). The announcement was made during the opening ceremony of the second National Exhibition of Agricultural Equipment, Products, Livestock, Agribusiness, and Refrigeration in Mascara.
"The process of digitizing the National Agricultural Registry, initiated early last year and carried out by the National Chamber of Agriculture, is now fully complete. This initiative has allowed for the issuance of digital cards to farmers across all 58 wilayas," stated Mohamed Yazid Hambli (photo, center).
Under President Abdelmadjid Tebboune, Algeria has leveraged digital transformation as a driver of development since 2019, achieving substantial progress on various digital indicators. According to the International Telecommunication Union, Algeria reached a score of 80.9 on the ICT Development Index in 2024, up from 77.8 in 2023, marking a notable advancement in the tech sector.
However, the digitization of the RNA faces several challenges. Farmers and local agents require training to effectively use digital tools, while limited access to telecommunications networks in rural areas hinders connectivity. Robust measures are also essential to protect the privacy and security of farmers' sensitive data. These obstacles could reduce the initiative's effectiveness if not addressed.
If these challenges are overcome, the RNA digitization could transform agricultural resource management by enabling better monitoring of land, crops, and water resources. It would allow for more targeted subsidies and aid based on farmers' actual needs and improve transparency in production chains. By facilitating precise resource management and enhancing transparency in the agricultural sector, this initiative could support more sustainable and equitable agricultural development.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
As part of its digital economy development plan, Nigeria is placing a strong emphasis on securing strategic partnerships. Each state in the country is ramping up efforts to deliver high-quality digital services to its citizens.
On Wednesday, October 30, Benue State Governor Hyacinth Iormem Alia (photo, center) announced a strategic partnership with Chinese tech group Huawei to accelerate digital transformation across the region. This agreement aims to modernize Benue's infrastructure, boost its economy, and improve the quality of life for its residents.
“This partnership with Huawei will revolutionize our state's infrastructure, enhance security, improve education [and] healthcare, and create countless job opportunities for our people. We must be intentional about the development of our state, for ourselves [and] future generations,” the governor explained on X (formerly Twitter).
The initiative is part of a broader effort to establish Benue State as a digital hub in Nigeria. It follows a recent agreement with EVNT Technologies, a Saudi-based IT company, to transform Benue’s technological landscape.
The Huawei partnership is expected to bolster local digital initiatives, particularly the Benue Tech Skills program, which aims to create over 50,000 jobs by training young people in essential digital skills. The program includes training in coding, advanced data analysis, UI/UX design, digital marketing, and e-commerce—all critical skills for the global digital economy.
These efforts align with the goals set by Nigeria’s Federal Ministry of Communications, Innovation, and Digital Economy under its strategic plan, “Accelerating our Collective Prosperity through Technical Efficiency.” This plan seeks to raise the digital sector’s contribution to Nigeria’s GDP to 22% by 2027, positioning the country as a leader in digital economy and tech innovation in Africa.
Samira Njoya
After supporting the development of around twenty promising startups, global accelerator Techstars has announced its withdrawal from Nigeria, a country where the startup ecosystem is experiencing rapid growth.
Techstars, a global startup accelerator and venture capital firm, is ending its operations in Nigeria after two years. The decision follows the conclusion of its partnership with ARM Labs, the Nigerian innovation entity with which it launched the ARM Labs Lagos Techstars Accelerator program.
“Techstars’ partnership with ARM Labs has ended, and we will not proceed with a third ARM Labs Lagos Techstars Accelerator Program. The first two cohorts featured outstanding companies and founders, supported by a dedicated group of mentors.We remain optimistic about collaborating with the local startup community to maintain our presence in this vibrant innovation hub,” said Matthew Grossman, Techstars’ global Chief Brand and Communications Officer.
Techstars and ARM Labs partnered in December 2022 to create an accelerator program to support early-stage African startups. Over two cohorts, the program added 24 startups to the Techstars portfolio, each receiving up to $120,000 in funding.
Techstars’ exit from Nigeria comes as the accelerator adjusts its finances, recently cutting 17% of its global workforce. This move raises concerns about the impact on Nigeria’s startup ecosystem, particularly regarding access to crucial resources and support. However, startups already funded through the ARM Labs Lagos Techstars Accelerator will remain part of Techstars’ portfolio and continue to benefit from its global network.
Samira Njoya
More...
Dans plusieurs pays, le service postal occupe une place clé dans l’économie. Cependant, cette institution publique a progressivement perdu de son influence en raison d’un manque de vision stratégique. Aujourd’hui, grâce aux TIC, il devient possible de la réinventer pour répondre aux besoins actuels.
La Cameroon Postal Services (Campost), un opérateur public postal du Cameroun, a signé le vendredi 1er novembre un partenariat stratégique avec FindMe, une start-up camerounaise spécialisée dans l’identification et la géolocalisation. Cette collaboration vise à résoudre le problème de localisation au Cameroun, où une grande majorité de la population ne dispose pas d’une adresse postale officielle.
« Avec le boom de l'e-commerce, il est important pour le service postal de se réinventer afin de mieux satisfaire les clients, en répondant aux besoins de livraison jusqu’au dernier kilomètre et en optimisant nos services financiers grâce à une meilleure identification de nos clients bancaires, en conformité avec les exigences de KYC (Know your customer) », a déclaré Pierre Kaldadak (photo, à droite), directeur général de la Campost.
L'initiative s'inscrit dans la vision de modernisation et de transformation de la poste camerounaise. Elle fait suite à plusieurs mois de collaboration entre la Campost et la start-up FindMe, permettant l’implantation de cette solution au Cameroun depuis juillet 2024. Les premiers travaux ont également permis au gouvernement de créer des codes postaux couvrant l’ensemble du territoire national. Grâce au partenariat, chaque citoyen camerounais et chaque entreprise camerounaise peuvent désormais générer gratuitement une adresse postale en seulement deux minutes via l’application mobile de FindMe. Cette adresse fournit des informations précises, notamment le numéro d’occupation, le nom de la rue, le code postal et la ville.
Au Cameroun, ce système numérisé devrait notamment améliorer l'efficacité des services de secours et des forces de sécurité, accélérer le développement de l’e-commerce et des services postaux, et faciliter les opérations des services fiscaux et fonciers, contribuant ainsi au développement économique national. L’objectif plus large est de créer un référentiel national d’adressage sur lequel les services publics pourront s’appuyer pour déployer leurs diverses opérations.
Samira Njoya
Lire aussi:
Guinea is making strides in digitalizing its public administration, but there's still room for improvement. According to the United Nations, the country's digital governance score increased from 0.2955 in 2022 to 0.4006 in 2024. Despite this progress, Guinea remains behind and is working to accelerate its digital transformation.
The Guinean Ministry of Commerce, Industry, and Small and Medium Enterprises recently announced the upcoming launch of an administrative document management platform (PLAGED) on November 13. This platform aims to simplify administrative procedures for citizens, marking a significant step toward digital governance in Guinea.
This initiative follows Guinean Prime Minister Bah Oury’s recent call for a concerted push to improve the country's digital administration, where progress has lagged. Oury attributes this delay to limited familiarity with the rapid evolution of digital technologies. According to the United Nations' report "E-Government Survey 2024: Accelerating Digital Transformation for Sustainable Development," Guinea scored 0.4006 out of 1 on the E-Government Development Index (EGDI), ranking 29th on the continent. This is an improvement from a score of 0.2955 in 2022, reflecting gradual progress in online government services.
The report also noted Guinea’s Online Service Index score of 0.4808, which assesses the technical features of national websites as well as policies and strategies for online service delivery across general and sectoral levels.
Earlier this year, in April, Guinean authorities launched “e-Learning” and “e-Consulting” initiatives to modernize administrative processes with innovative training and management tools. The introduction of PLAGED aligns with these efforts, supporting the government’s digital strategy to improve service delivery and accelerate the adoption of digital tools across public administration.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
Social media plays a key role in election integrity by enabling citizens to report incidents, share information, and foster transparency. Civil society organizations have raised concerns that restrictions can harm both democracy and economic growth, underlining the long-term impacts on citizens’ rights and national development.
Mauritius's Information and Communication Technologies Authority (ICTA) has directed all internet service providers to block access to social media platforms from Friday November 1 through November 11. The announcement was made in a communique dated November 1, by the authority.
The restriction comes in response to “concerns regarding illegal postings that constitute a serious threat to national security and public safety," the communique reads.
This scenario in Mauritius is part of a broader trend in Africa, where several countries have implemented internet shutdowns or social media restrictions during elections or periods of civil unrest in recent years. For example, in Uganda’s 2021 election, social media was restricted, with authorities citing security concerns.
Between 2020 and 2023, at least 22 African countries enforced full or partial internet shutdowns, resulting in an estimated $3.9 billion in economic losses, according to consulting firm Africa Practice, which advises investors and development partners across the continent.
Hikmatu Bilali
Investing in digital skills accelerates regional tech development and prepares African nations for a digital future. This approach helps address critical challenges. Additionally, it tackles the region’s high youth unemployment, creating more opportunities for the next generation.
Nigeria announced a N2.8 billion ($1.7 million) commitment from Google to support the digital economy. The investment was led by Matt Brittin, Google’s President of EMEA Business & Operations. Announced on October 31 by the Minister of Communications, Innovation, and Digital Economy, this commitment aligns with Nigeria’s Strategic Blueprint for Digital Transformation.
The minister of Communications, Innovation, and Digital Economy commented on the move saying, “I appreciate the entire Google team for betting big on our technology ecosystem and their continued support. I look forward to building on our partnership, as we continue on our path of Digital Transformation in Nigeria.”
Such investments come as digital growth becomes increasingly essential. According to the National Bureau of Statistics, Nigeria's digital economy contributed 16.36% to the country’s GDP as of Q2 2024, just behind trade and Agriculture. This underscores the strategic importance of fostering technological innovation and skills to further boost economic resilience and global competitiveness.
The investment will fund initiatives to train 20,000 Nigerians in AI and Data Science, introduce 125,000 young students to AI fundamentals, support over 1,000 public officials in AI-driven governance, and empower 10 Nigerian AI startups with funding, tools, and mentorship.
Google's support aims to strengthen Nigeria's role in the global digital economy by promoting technical skills and fostering innovation nationwide. This effort is part of a broader $5.8 million investment to advance AI skilling programs across Sub-Saharan Africa.
Hikmatu Bilali