To bolster economic integration across Africa, governments are focusing on establishing a free trade area. This involves the execution of projects designed to streamline trade and cross-border transactions.
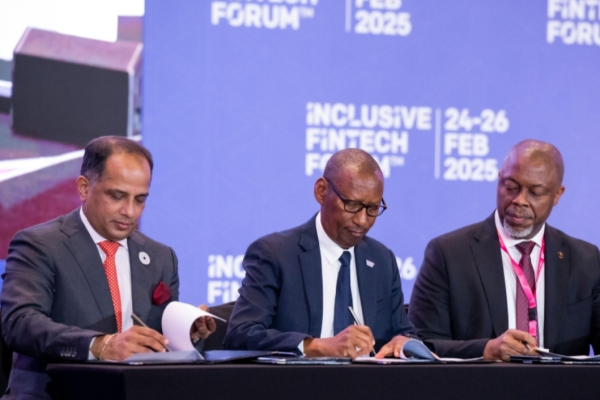
The Global Finance & Technology Network (GFTN), an organization founded by the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS), has partnered with the central banks of Ghana and Rwanda to launch Africa’s Next-Gen Digital Payment Infrastructure project, also known as "Project 54." The initiative aims to deploy a next-generation digital payment infrastructure, enabling instant, secure, and low-cost cross-border transactions across Africa. The project was unveiled on Tuesday, Feb. 25, at the Inclusive Fintech Forum (IFF) in Kigali.
"As stewards of the financial system, we must remain steadfast in our mission to break down barriers, empower businesses, and create inclusive opportunities for all. Through initiatives like this, we are shaping the future of Africa’s financial landscape," said John Rwangombwa, Governor of the National Bank of Rwanda.
The project aligns with the establishment of the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA), which seeks to create a single market across the continent. However, high transaction costs and slow fund transfers remain significant obstacles. According to a report by the Institute for Security Studies, remittances to Africa reached approximately $100 billion in 2022. Of this amount, $19.4 billion was transferred within Africa, underscoring the importance of intra-continental financial flows.
Project 54 aims, among other things, to facilitate money transfers between African countries. The initiative is built around three key pillars: a reliable identity infrastructure ensuring secure, verifiable, and universal digital identities to enable seamless financial transactions; an interoperable payment system creating a standardized infrastructure for real-time cross-border transactions within Africa’s financial ecosystem; and a passporting framework for fintech licenses, allowing licensed companies in one of the two participating countries to operate in the other with simplified regulatory requirements. An agreement has already been signed between Ghana and Rwanda to this effect.
In the coming months, project leaders will finalize the roadmap, harmonize regulatory approaches, and launch pilot deployments ahead of large-scale adoption. A tailored pricing model will be introduced to accommodate transactions of varying values, ensuring the system’s financial sustainability. Additionally, regulators, financial institutions, fintech companies, and investors will collaborate to co-create a sustainable digital payment ecosystem.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
Digital transformation is a key priority for the Congolese government, which intends to bolster the nation's telecommunications infrastructure to support its objectives.
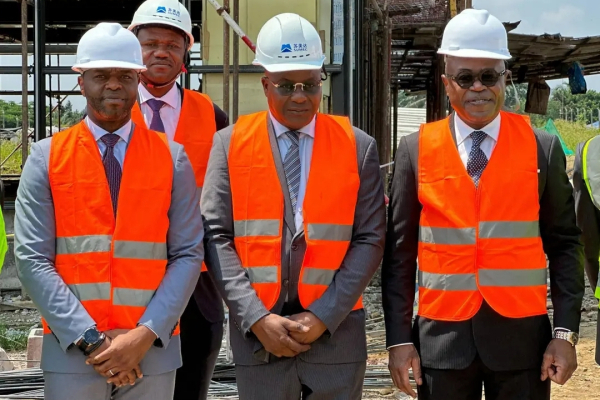
The Republic of Congo's new national data center is expected to be inaugurated next November, according to the government. Construction of the facility, which began in early 2024, is already 80% complete.
Léon Juste Ibombo, Minister of Posts, Telecommunications, and the Digital Economy, announced this on Thursday, Feb. 28, during a site visit. He was accompanied by Solomane Koné, Deputy Director General for Central Africa at the African Development Bank (AfDB), which is financing the project with a $13 million investment.
The specific features and technical details of the data center have not been disclosed to the public. However, it is known that it will be housed in a three-story expandable building with a basement. The facility will include dedicated rooms for servers, monitoring, and supervision, as well as meeting and conference spaces. Separate areas will be reserved for power supply and cooling equipment to ensure the data center operates efficiently.
As the Congolese government seeks to accelerate its digital transformation and make it a pillar of socioeconomic development, the data center’s commissioning could help strengthen the country’s national telecommunications infrastructure. In 2024, the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UNDESA) gave Congo a telecommunications infrastructure index score of 0.2776 out of 1, part of the E-Government Development Index (EGDI). The country ranked 166th out of 193 globally, with its score falling below the averages for Central Africa (0.3354), Africa (0.4247), and the world (0.6382).
The facility is also expected to contribute to Congo’s digital sovereignty, according to officials. “All data generated in Congo must be stored somewhere. Currently, this data is stored abroad, which is why many of our domain names end in ‘.fr’ or ‘.com’ instead of ‘.cg.’ From now on, we will be able to host all public data within the data center, as well as data from telecommunications operators, banks, insurance companies, and other private firms that wish to store their information here—including backups of their primary storage sites,” said Michel Ngakala, Coordinator of the Central African Backbone (CAB) project, during the launch of construction in 2024.
By Isaac K. Kassouwi,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
This groundbreaking solution aims to revolutionize cardiovascular disease management in Africa by providing continuous monitoring and easier access to healthcare professionals.
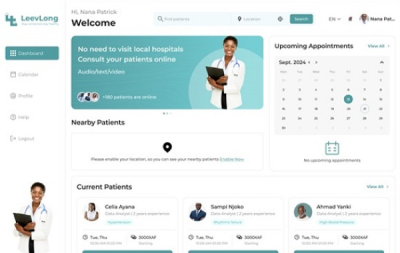
LeevLong, a medical telemonitoring solution developed by a Cameroonian startup, aims to improve the quality of life for patients, particularly those with cardiovascular diseases.
Launched in 2024, the service, led by Haoua Dally, combines connected devices with mobile and web applications to provide real-time monitoring of vital signs and facilitate communication between patients and healthcare professionals. The system includes three wearable supports—a bracelet, an armband, and a tank top—paired with a connected device that continuously collects vital signs such as blood pressure, heart rate, and body temperature. Data is transmitted via Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or GSM, and alerts are triggered if critical thresholds are exceeded.
On the patient side, the mobile application allows users to monitor their vital signs in real-time, receive notifications and recommendations in case of anomalies, access medical assistance via teleconsultations and forums, and schedule medication intake and medical appointments.
For healthcare professionals, the web and mobile platforms provide real-time access to patients’ health data, enable teleconsultations based on availability, suggest interventions in case of abnormal vital signs, and facilitate communication through forums and a dedicated messaging system.
To access LeevLong’s services, users must first purchase the kit and subscribe to a plan. The basic subscription includes real-time data visualization, access to a discussion forum, and a history of recorded parameters. The standard plan adds anomaly alerts and teleconsultation options, while the premium package offers all these benefits along with a virtual assistant and medication and appointment scheduling features.
In February, LeevLong secured third place at the Orange Summer Challenge, an international competition by Orange promoting responsible entrepreneurship in Africa and the Middle East. Alongside support from Orange, the solution will also receive backing from Nokia, which has pledged 40,000 euros (approximately $41,630) to fund project pre-incubation and incubation.
By Adoni Conrad Quenum,
Editing by Feriol Bewa
Niger, like many African nations, is pursuing digital technology as a key driver of development. The government's roadmap prioritizes modernizing administration, strengthening infrastructure, and expanding access to digital services.
Niger will adopt a national policy for the development of its digital sector next month, the government said last Wednesday. Speaking on Radio Télévision du Niger (RTN), Minister of Communication, Posts, and Digital Economy Sidi Mohamed Raliou said the policy aims to structure and accelerate the country’s digital transformation, making digital technology a driver of growth and modernization.
The national policy will encompass all sectors and government administrations, he explained. The objective is to digitize public services, gradually eliminating paper documents and optimizing service management. The policy will be supported by connectivity infrastructure, including fiber optic deployment to interconnect different regions.
The initiative is part of a broader set of strategic projects designed to strengthen Niger’s digital sector. These projects include the launch of three satellites for communications, remote sensing, and airspace surveillance, as well as the construction of a national data center to secure and centralize digital data.
Additionally, the government plans to establish a National Cybersecurity Agency to oversee IT system protection, combat cyber threats, and raise public awareness about cybersecurity best practices. Efforts are underway to improve nationwide internet access, particularly in rural areas.
The policy aligns with Niger’s ambition to modernize digital services and attract investment in the telecommunications sector. In 2024, the country scored 0.1578 out of 1 on the Telecom Infrastructure Index (TII), significantly below the African average of 0.4534, according to the United Nations. In terms of e-governance, Niger ranked 187th out of 193 countries with an index score of 0.2116. These figures highlight the significant efforts needed to enhance the country’s digital transformation.
Once adopted, the national digital policy is expected to transform Niger’s digital ecosystem by strengthening infrastructure, expanding access to online services, and improving cybersecurity. The development of broadband and the expansion of internet coverage will foster greater digital inclusion, enabling citizens and businesses to benefit from modern tools.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
The Moroccan government has prioritized digital technology as a cornerstone of the country's socioeconomic development. In addition to investing in infrastructure, the administration is committed to equipping the population with the necessary digital skills to achieve these goals.
Morocco will open a new school specializing in programming and coding in the Fès-Meknès region, the government said Friday. An agreement to establish the "YouCode Fès" school was signed under the leadership of Amal El Fallah Seghrouchni, Minister Delegate in charge of Digital Transition and Administrative Reform.
"Under this agreement, the ‘YouCode Fès’ school will offer a two-year training program in information technology and digital fields. Each cohort will welcome 80 students, contributing to the expansion of employment opportunities in the digital sector within the region and improving young people’s employability in tech-related professions," the ministry said in a Facebook announcement.
The initiative aligns with Morocco’s Digital Maroc 2030 strategy, which aims to develop a high-quality talent pool in the digital sector. The government's long-term goal is to enhance its outsourcing and digital export hub. By 2030, the country aims to increase employment in the sector to 270,000 jobs, up from 130,000 in 2022. Rabat is also targeting digital export revenues of 40 billion Algerian dinars ($296.13 million) by 2030, compared to 15.8 billion dinars in 2022.
According to the World Bank, nearly 230 million jobs in Sub-Saharan Africa will require digital skills by 2030. While Morocco is not part of this region, the trend highlights the critical role of digital training in Africa’s technological transformation.
The timeline for the new school’s launch has not been announced. Similar programs may be expanded to other regions. YouCode already operates campuses in Safi and Youssoufia (Marrakech-Safi region) and in Nador (Oriental region).
By Isaac K. Kassouwi,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
Egyptian Fintech Fawry announced on February 26 that it has invested 80 million EGP (1,579,200 US Dollar) in three leading Egyptian tech firms—Dirac Systems, Virtual CFO, and Code Zone. The new investment is part of the fintech’s strategy to expand its business solutions ‘Fawry Business’ and drive digital transformation in Egypt,
The EGX-listed company has acquired 51% of Dirac Systems, 56.6% of Virtual CFO, and 51% of Code Zone, strengthening its role as a one-stop provider of ERP, financial management, and digital payment solutions for businesses.
This investment aligns with Fawry’s vision to accelerate Egypt’s fintech and business technology sectors, equipping companies with cutting-edge digital solutions to enhance growth in an increasingly cashless and digital economy.
In Rwanda, JaliKoi positions itself as a super-app, combining convenience, financial benefits, and growth opportunities for businesses and individuals.
JaliKoi is an application developed by the Rwandan fintech Jali Finance. Launched on Monday, February 24, 2025, on the sidelines of the second edition of the Inclusive Fintech Forum (IFF), it aims to transform the financial experience for individuals and businesses by offering a comprehensive range of integrated services. The Kigali-based startup is led by Félix Nkundimana.
"Each company offers its own digital platform, forcing consumers to use multiple channels to access services. What we have done is centralize all digital services provided by different companies so that they are accessible through a single platform, JaliKoi," said Frank Mugisha, Chief Technology Officer at Jali Finance.
The JaliKoi app, available on iOS and Android, allows individuals to access financing for items such as motorcycles or vehicles, with affordable interest rates and flexible repayment terms. Users receive a percentage of their spending as cashback on each transaction, which they can use to pay bills or make new purchases.
The app also facilitates payment of utility bills, including mobile top-ups, electricity, and TV subscriptions, with cashback rewards. For businesses, the platform offers cashback-based loyalty programs, socially driven sales campaigns, and an e-commerce marketplace to sell products online.
"Fintech brings agility and innovation, while financial institutions provide trust and scale. Together, they can unlock new opportunities for growth and inclusion," said Félix Nkundimana.
The company said potential challenges to growth include raising user awareness, ensuring a smooth and secure experience, and competition. Partnerships with telecom operators and banks could strengthen its market position.
By Adoni Conrad Quenum,
Editing by Feriol Bewa
Microsoft said Friday it will discontinue Skype in May 2025, ending the live communication software that helped popularize Voice over IP (VoIP). The decision is part of the company's strategic shift toward Microsoft Teams, a collaboration platform designed to streamline free communication services and meet users' evolving needs.
"With Teams, users have access to many of the same core features they use in Skype, such as one-on-one calls and group calls, messaging, and file sharing," said Jeff Teper, Microsoft's President of Collaborative Apps and Platforms. "Additionally, Teams offers enhanced features like hosting meetings, managing calendars, and building and joining communities for free."
Launched in 2017 as the successor to Skype for Business, Microsoft Teams gained widespread adoption during the COVID-19 crisis, particularly during lockdowns in 2020 and 2021. Microsoft said "In the past two years, the number of minutes spent in meetings by consumer users of Teams has grown four times, reflecting the value Teams bring to everyday communication and collaboration."
To minimize disruption for Skype users, Microsoft has implemented transition measures, including options to export data. Skype was created in 2003 by Swedish entrepreneur Niklas Zennström and Danish entrepreneur Janus Friis, and was acquired by Microsoft in 2011 for $8.5 billion.
Muriel Edjo
Niger is looking to digital transformation as a key driver for its socioeconomic growth. To achieve this, the government is committed to modernizing and strengthening its national telecommunications infrastructure.
Construction of Niger's national data center has reached 13% completion and is on track for completion by September 30. The nine billion CFA Francs (approximately $14.3 million) project, was discussed last week by the Minister of Communication, Posts, and Digital Economy, Sidi Mohamed Raliou, during a televised address reviewing his ministry’s work.
While the minister did not disclose specific details about the facility's capacity and technical features, he confirmed the data center will be Tier 3, based on Uptime Institute standards. This classification ensures multiple power and cooling pathways, minimizing downtime to 1.6 hours per year. The facility will store and secure public data in Niger.
The data center is expected to strengthen Niger's digital infrastructure, a key step in the country's digital transformation efforts.
According to the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UNDESA), Niger scores 0.1578 out of 1 on the telecom infrastructure index, a component of the E-Government Development Index (EGDI). Niger's overall EGDI score is 0.2116, ranking 187th out of 193 countries. This is below the averages for West Africa (0.3957), Africa (0.4247), and the global average (0.6382).
In addition to the data center, Niger must expand telecom coverage and increase adoption of digital technologies. The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) estimates 3G and 4G networks cover 24% and 17.5% of the population, respectively, compared to 92% for 2G. DataReportal figures show Niger had 4.69 million internet subscribers at the beginning of 2024, with a penetration rate of 16.9%. Mobile phone penetration was 59.4%.
By Isaac K. Kassouwi,
Editing by Feriol Bewa
With the acceleration of digital transformation in Africa, cooperation between countries is becoming crucial. It facilitates access to technology, optimizes resources, and fosters innovation.
The Bank of Ghana (BoG) and the National Bank of Rwanda (NBR) signed a memorandum of understanding on Tuesday, February 25, during the Inclusive Fintech Forum recently held in Rwanda. The agreement establishes a "license passporting" framework, allowing fintech companies that comply with regulations to operate freely in both countries, facilitating their expansion while reducing regulatory barriers.
"The signing of this memorandum of understanding reaffirms our commitment to the broader idea of an integrated African market. It holds the prospect of enhancing the livelihoods of our citizens and creates opportunities for an environment that encourages fintech innovation and investment, ultimately benefiting our economies, particularly micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs)," said Johnson Asiama, former Deputy Governor of the Bank of Ghana.
This partnership aligns with a broader strategy to strengthen Africa’s fintech ecosystem and promote regional economic integration. Rwanda, which aims to attract 300 fintech firms by 2029, create 7,500 direct jobs, and secure $200 million in investments, recently launched a National Fintech Strategy and a national digital payment system. Ghana, a key player in financial technology, continues to enhance its payment infrastructure and support innovative initiatives.
By facilitating the integration of digital financial services, this agreement plays a vital role in advancing the vision of the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) and accelerating the continent’s digital transformation. As Africa’s fintech sector experiences rapid growth, the continent has the potential to emerge as a global fintech hub—provided it can overcome challenges related to digitization and financial inclusion.
In 2024, African fintech startups raised $1.034 billion, accounting for 47% of all funding secured by startups across the continent, up from 42% in 2023, according to Africa: The Big Deal.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
More...
Launched by two Nigerians, the solution is part of various AI-enabled tools that aim to make education more accessible, interactive, and effective for all.
uLearn is a digital platform developed by the Nigerian startup EqualizAI. It enables users, particularly teachers, to generate lesson plans, notes, and quizzes in English and local languages. The startup, based in Lagos (Nigeria) and Washington, was founded in 2024 by Olubayo Adekanmbi and Ife Adebara.
"uLearn is designed to help teachers with their everyday tasks and workload from planning lesson notes to creating assessments so they can spend more time on what matters most - teaching and engaging their students. We understand that each classroom is as unique as its students. uLearn is your teaching assistant that creates content and resources tailored to your teaching style and the students’ learning needs," the startup explains.
After creating an account, teachers can develop educational content, including videos, interactive quizzes, and written materials, which students can then access to enhance their learning. Notably, uLearn can generate content in African languages, in addition to English.
Olubayo Adekanmbi said, "Our mission is to ensure that AI speaks our languages, understands our contexts, and addresses our unique challenges. This is not just about technology; it’s about empowerment and inclusion."
The platform also provides personalized tracking through analytical tools, enabling learners to measure progress and identify areas for improvement. The startup's flexible model is designed to accommodate professionals seeking to upskill without geographical or time constraints.
uLearn offers both free and premium subscription plans. The free version provides access to essential features, while the premium plan unlocks the full content library, advanced interactive tools, and personalized recommendations based on user profiles.
By Adoni Conrad Quenum,
Editing by Feriol Bewa
Digital transformation is a priority for Tanzanian authorities to drive socio-economic development. Achieving these goals requires expanding public access to digital services.
The Tanzanian government aims to support the development of its local ICT equipment industry, including phones, computers, and tablets, Nkundwe Mwasaga, Director General of the ICT Commission (ICTC), announced during a visit last week to the Tanztech Electronics Limited factory in Arusha. These efforts could improve public access to devices essential for digital services.
According to the GSMA, limited access to smartphones is a major barrier to mobile internet adoption worldwide. The organization estimates that in 2023, 40 million Tanzanians were not connected to mobile internet, while the country's population stood at 67.4 million, according to the World Bank. Official statistics indicate that by the end of December 2024, Tanzania had 47.85 million mobile internet users. However, this figure represents the number of SIM cards used to access the service, meaning some individuals may own multiple SIMs.
"President [Samia Suluhu] directed us to find investors who will establish factories to produce various ICT products here in Tanzania so that we can work together to drive the digital economy agenda," said Mwasaga. He added that ICTC will work with investors to ensure that locally manufactured products are both competitive and affordable for the population.
To achieve these goals, the government must address key challenges facing the local ICT equipment industry. Gurveer Hans, CEO of Tanztech Electronics Limited, highlighted the need to reduce tax burdens across the production and distribution chain in Tanzania. "We import raw materials from our partners in China, but we are burdened with heavy taxes, which make locally made products costly for consumers,” he explained.
By Isaac K. Kassouwi
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
The GSMA Innovation Fund, supported by the UK Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office (FCDO), is providing grants to small and growing enterprises (SGEs) using AI and mobile technology to address socio-economic and climate challenges in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs).
The fund is open to for-profit enterprises with up to 250 employees. Eligibale businesses must be based in Africa, South Asia, Southeast Asia, or the Pacific.
Successful enterprises will receive grants ranging from £100,000 to £250,000 for projects lasting 15 to 18 months. They will also gain tailored venture-building support, partnerships with mobile network operators, and increased visibility through GSMA platforms and events.
The deadline for pitch submissions is 19 March 2025.
As digital connectivity expands across Africa and globally, ICT skills are in high demand. Recognizing this trend, Morocco is implementing strategic programs to prepare its youth for careers in the digital sector.
Samsung Electronics Maghreb Arab, the Moroccan subsidiary of South Korean tech giant Samsung, and Morocco’s Ministry of National Education, Preschool, and Sports signed an amendment to their partnership agreement on Wednesday, February 26, to enhance digital education in Morocco. The initiative aims to support educational development and equip younger generations with the skills to tackle future technological challenges.
"Samsung is committed to supporting education and innovation in Morocco, and we are delighted to strengthen our partnership with the Ministry of National Education. By integrating artificial intelligence into the Samsung Innovation Campus and launching the NationBy integrating artificial intelligence into the Samsung Innovation Campus and launching the National Hackathon, we want to offer young Moroccans opportunities to explore and develop their skills in future technological fields," said Hee Young Hong, President of Samsung Electronics Maghreb Arab.
This initiative builds on a collaboration established last year to strengthen digital education in Morocco through the Samsung Innovation Campus program. The program offers ICT training to young people seeking employment in the rapidly evolving tech sector. To date, it has trained 780 teachers, and 1,273 participants have taken part in nationwide Python programming courses.
For the Moroccan government, this initiative aligns with the Morocco Digital Strategy 2030, launched last September. The strategy aims to train 100,000 young people per year in digital careers, with a goal of creating 240,000 jobs in the digital sector by 2030 to meet the growing demand for tech skills.
According to a new report by the Brookings Institution, titled "Foresight Africa 2025-2030," an estimated 230 million jobs in sub-Saharan Africa will require digital skills by 2030. The report also anticipates up to 650 million digital training opportunities, representing a potential market of $130 billion. This trend underscores the importance of initiatives like Samsung’s, which aim to equip young Moroccans with the skills to become future leaders and innovators.
This renewed collaboration between Samsung and the Ministry of Education presents a promising opportunity for digital education in Morocco. By enhancing teachers' capabilities and providing students with essential tools to excel, this initiative could contribute to both local community development and the global digital economy.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji