To bolster economic integration across Africa, governments are focusing on establishing a free trade area. This involves the execution of projects designed to streamline trade and cross-border transactions.
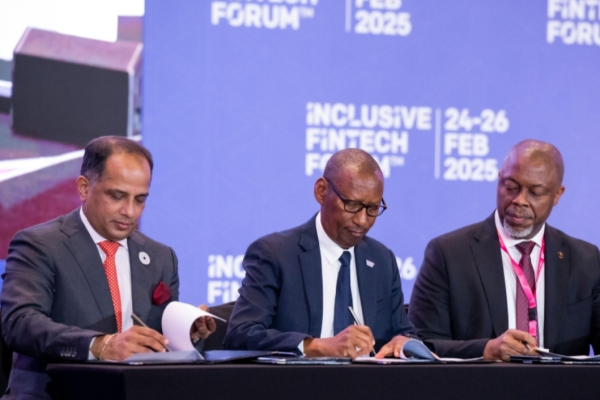
The Global Finance & Technology Network (GFTN), an organization founded by the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS), has partnered with the central banks of Ghana and Rwanda to launch Africa’s Next-Gen Digital Payment Infrastructure project, also known as "Project 54." The initiative aims to deploy a next-generation digital payment infrastructure, enabling instant, secure, and low-cost cross-border transactions across Africa. The project was unveiled on Tuesday, Feb. 25, at the Inclusive Fintech Forum (IFF) in Kigali.
"As stewards of the financial system, we must remain steadfast in our mission to break down barriers, empower businesses, and create inclusive opportunities for all. Through initiatives like this, we are shaping the future of Africa’s financial landscape," said John Rwangombwa, Governor of the National Bank of Rwanda.
The project aligns with the establishment of the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA), which seeks to create a single market across the continent. However, high transaction costs and slow fund transfers remain significant obstacles. According to a report by the Institute for Security Studies, remittances to Africa reached approximately $100 billion in 2022. Of this amount, $19.4 billion was transferred within Africa, underscoring the importance of intra-continental financial flows.
Project 54 aims, among other things, to facilitate money transfers between African countries. The initiative is built around three key pillars: a reliable identity infrastructure ensuring secure, verifiable, and universal digital identities to enable seamless financial transactions; an interoperable payment system creating a standardized infrastructure for real-time cross-border transactions within Africa’s financial ecosystem; and a passporting framework for fintech licenses, allowing licensed companies in one of the two participating countries to operate in the other with simplified regulatory requirements. An agreement has already been signed between Ghana and Rwanda to this effect.
In the coming months, project leaders will finalize the roadmap, harmonize regulatory approaches, and launch pilot deployments ahead of large-scale adoption. A tailored pricing model will be introduced to accommodate transactions of varying values, ensuring the system’s financial sustainability. Additionally, regulators, financial institutions, fintech companies, and investors will collaborate to co-create a sustainable digital payment ecosystem.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji