Digital technologies are crucial for driving economic growth, innovation, job creation, and social inclusion. However, Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) grapples with significant challenges in digital development, such as underdeveloped infrastructure and costly connectivity. Entry into the African telecom market with 5G infrastructure is pivotal for African development, promising to enhance digital inclusion, spur economic growth, reduce costs for local telecom operators, and hasten technological progress.
Reliance Industries Ltd (RIL) is set to enter the African telecom market by providing 5G shared network infrastructure through its subsidiary Radisys, in collaboration with Next-Gen Infrastructure Co. (NGIC), backed by the Ghanaian government. Radisys announced this on May 27.
"By bringing Fixed Wireless Access alongside 4G and 5G cellular services to help drive economic growth and digital inclusion, Radisys looks forward to helping Ascend and NGIC build a disruptive and affordable shared broadband infrastructure across Ghana," said Arun Bhikshesvaran, CEO of Radisys.
Radisys, owned by RIL's unit Jio Platforms Ltd (JPL), along with Tech Mahindra and Nokia, will collaborate with NGIC to develop 4G and 5G networks across Africa, starting with Ghana. NGIC plans to invest $200 million in this initiative over the next three years, offering the networks as shared resources to local mobile operators to cut costs. With partnerships already established with AT Ghana and Telecel Ghana, NGIC aims to replicate India's low-cost, high-speed data model, providing affordable and efficient digital services across the continent.
This investment aligns with the strategy outlined in August 2023 by Owusu-Ekuful, Ghana’s Minister for Communication and Digitisation, during the 12th African Peering and Interconnection Forum (AfPIF). She disclosed the government's decision not to issue a 5G license, which would require significant investment from telecom operators. Instead, the government plans to establish a neutral shared infrastructure company to provide the necessary networks to operators.
Andrew Dabalen, the World Bank's Chief Economist for Africa, emphasized that increasing mobile internet usage could create jobs and spur economic recovery. A 2023 World Bank report (Digital Transformation Drives Development in Africa) revealed that extreme poverty decreased by around 7% in Nigeria and Tanzania, and labor force participation increased by up to 8% after three or more years of internet coverage. Addressing these gaps is crucial for fully harnessing digital technologies' potential in SSA.
Hikmatu Bilali
E-health is rapidly transforming Africa's healthcare landscape. By leveraging information and communication technologies, e-health solutions are making it easier for patients to connect with healthcare professionals, while also increasing the accessibility and availability of medical expertise across the continent.
Beesiha is an e-health solution developed by an Algerian startup. It allows users to book medical appointments with just a few clicks via its web and mobile platforms. The startup, based in the Said Hamdine district of Algiers, was founded in 2019 by Said Admane and Amine Babou.
The mobile application is available on both iOS and Android, where it has already been downloaded over 10,000 times, according to Play Store statistics. After downloading the app, users can register using their Facebook account or by providing information such as their name, surname, and phone number. Once registered, they can log in and access the various services offered by the startup.
Using a search bar where the user can enter the medical specialty, medical facility, or city they are looking for, Beesiha provides the most relevant results. Users can book appointments for free based on the availability of the selected doctor. It is also possible to book an appointment for a third party, such as a friend or family member.
To ensure patients don't miss consultations, Beesiha sends frequent appointment reminders. For added convenience, the platform offers remote consultations, with patients benefiting from a digital medical record storing test results, prescriptions, and consultation history – all under their complete control.
For doctors, Beesiha offers a digital agenda, allowing them to schedule their working hours as they see fit. The platform includes most medical specialties, making it easier to adopt the solution. Since its launch, Beesiha boasts more than 800 healthcare professionals available on its web and mobile platforms and over 215,000 appointments booked.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
The COVID-19 crisis significantly impacted the postal sector, and the subsequent surge in digitalization has further disrupted the market, forcing postal services to contend with innovative competitors. This challenge is particularly acute in Africa, where postal services must adapt and reinvent themselves to remain relevant.
Equatoguinean investors, represented by INVERFIN, met with Gabon's Minister of Communication and Media, Laurence Ndong, on Thursday, May 23rd, to discuss potential investments in the country's postal and telecommunication sectors.
The investors signaled their interest in supporting Gabon's postal service (La Poste SA) in its digital transformation initiatives. The discussions also explored backing an economic group formed by La Poste SA, Télédiffusion Gabon (TDG), and Universal Services for expanding telecom network coverage in underserved areas.
According to a Facebook post by Minister Ndong, INVERFIN expressed willingness to "fully finance La Poste SA's digital projects" across the tri-border zone (Gabon, Equatorial Guinea, Cameroon) and beyond. The investment seeks a return based on a memorandum of understanding (MoU) currently under legal review by La Poste SA and the Ministry.
This financial support aligns with Gabon's Digital Plan and the Universal Postal Union's (UPU) directives, emphasizing the need for La Poste SA to adapt and capitalize on e-commerce, e-government, and digitalized financial services. The UPU's 2023 Integrated Index for Postal Development (2IPD) ranks Gabon's postal development as "weak" with a score of two out of ten.
“INVERFIN representatives are expected to return to Libreville in a few weeks for the final signing of the memorandum of understanding,” Minister Ndong's post informs.
The Organization of Information and Communication Technologies Professionals in Senegal (OPTIC) recently announced the 7th edition of the International Fair for Professionals of the Digital Economy (SIPEN). This event is scheduled to take place on June 27-28 in Dakar. The event will focus on the theme "Accelerating Digitalization: A Powerful Lever for the Competitiveness of the Senegalese and African Economy."
Informal sector traders across Africa are often excluded from the traditional financial system. Recognizing this issue, tech entrepreneurs have developed innovative solutions to offer alternatives to conventional financial institutions.
Proboutik is a fintech solution developed by Senegalese startup ProXalys to transform the way informal sector traders manage their financial operations. Launched in 2021 by Thierno Sacko and Abdoulaye Faye, Proboutik enables local merchants to digitize their financial transactions, bringing them into the fold of modern financial systems.
In January 2024, ProXalys raised $500,000 to support the growth of Proboutik. The mobile application, available on both iOS and Android, has already been downloaded over 10,000 times from Playstore. Users can register with their phone numbers and access various financial management services. These include cash flow management, customer portfolio management, real-time tracking of receivables and payables, automated payment reminders via SMS, and the generation of account statements and reports.
"The application records all your deferred payment transactions, ensuring transparent traceability and better management of your business operations," explains the startup. Additionally, Proboutik offers financing to users based on the credits they have extended to their customers. This feature aims to facilitate business growth and prevent financial strain for traders.
Proboutik provides two subscription options: a monthly plan priced at 990 CFA Francs (approximately $1.63) and an annual plan at 10,000 CFA Francs. On May 23, Proboutik was selected, along with 19 other African fintechs, for the second cohort of Visa's acceleration program.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
As part of its initiatives in Africa, Google is significantly increasing its investments in digital infrastructure. The goal is to harness the opportunities presented by the internet economy, contributing to a prosperous and sustainable digital future for the continent.
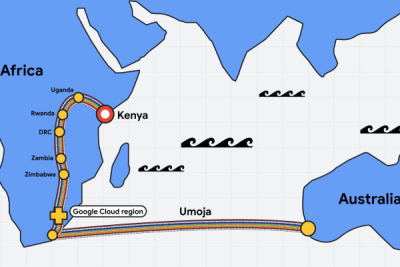
Google on Thursday announced the Umoja fiber optic cable project, aiming to significantly enhance the reach and reliability of digital connectivity across Africa. This initiative aligns with Google's broader Africa Connect strategy, following the successful deployment of the Equiano cable connecting Africa to Europe.
The Umoja network leverages a partnership with Liquid Intelligent Technologies to establish a terrestrial segment connecting Kenya, Uganda, Rwanda, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Zambia, Zimbabwe, and South Africa. From South Africa, a subsea connection will traverse the Indian Ocean to link directly with Australia.
Google's investment in Umoja comes at a critical juncture. Recurrent outages in existing subsea cables serving Africa have resulted in widespread internet disruptions. The most recent incident occurred on May 12th, when failures in the SEACOM and EASSY systems caused disruptions in several East and Southern African countries. Similar issues arose in March, affecting numerous cables – WACS, MainOne, ACE, SAT3, Seacom/TGN, AAE1, and EIG – impacting internet access across a dozen West, Central, and Southern African nations.
"This initiative is crucial in ensuring the redundancy and resilience of our region’s connectivity to the rest of the world, especially in light of recent disruptions caused by cuts to sub-sea cables," stated Kenyan President William Ruto. "By strengthening our digital backbone, we are not only improving reliability but also paving the way for increased digital inclusion, innovation, and economic opportunities for our people and businesses."
Isaac K. Kassouwi
A communications graduate with experience in Moroccan industry, she identified a gap in communication between healthcare providers and patients. To address this challenge, she and her team developed a mobile application aimed at streamlining these interactions.
Sabrine Zahroubane (pictured), a Moroccan marketing and communication specialist, is the co-founder and CEO of SehaLink, a healthtech company aiming to streamline communication between doctors, patients, and laboratories.
Zahroubane, who holds a master's degree in marketing from ESCA School of Management in Casablanca (2016), co-founded the company (originally Ta7alil.ma) in 2020 with Maryem Renaja. Rebranded as SehaLink in May 2024, the company seeks to address challenges patients face in retrieving test results and managing appointments.
The SehaLink app offers several features, including online appointment scheduling with healthcare professionals, digitization and archiving of medical records, receipt of test results and reports, and management of blood donation requests.
SehaLink's innovative approach has earned them a spot among startups exhibiting at GITEX Africa, taking place May 29-31, 2024, in Marrakech.
In addition to her role at SehaLink, Sabrine Zahroubane is an associate director at Digital & Creativity, a digital communication agency she founded in 2017 with Maryem Renaja. She also chairs the Lueur d’espoir Casablanca association, which works in humanitarian and medical fields.
Zahroubane's professional journey began in September 2016 as a project manager at Bonzai Agency, a brand design and maintenance company. In September 2017, she transitioned to advertising manager at Klem, a Moroccan communications firm.
Melchior Koba
After earning her engineering degree and accumulating three years of experience in research and development, Marwa Moula decided to dedicate herself to entrepreneurship. In 2020, she founded her first company to revolutionize the e-commerce industry in Africa.
Marwa Moula (pictured) is a Tunisian DevOps engineer, digital marketing specialist, and entrepreneur. She is the co-founder and CEO of IleyCom, a social marketplace offering products crafted by entrepreneurs primarily based in Africa.
Founded in 2020, IleyCom provides African artisans with an omnichannel platform to sell their handmade creations, including traditional Berber clothing and culinary specialties. Its mission is to "reinvent fair e-commerce to create a more fulfilling and sustainable world, and we are committed to using the power of business to strengthen communities."
In addition to its marketplace, IleyCom runs an incubation program for young social entrepreneurs, helping them develop impactful projects and showcase their products.
Since Wednesday, May 22, 2024, Marwa Moula has been representing her startup at the VivaTech conference, which concludes on Saturday, May 25.
Apart from her work at IleyCom, Marwa Moula has served as the president of the association "La Tunisie De Demain" since 2020. This organization promotes the establishment of a social and solidarity-based economy (ESS) in Tunisia.
Marwa Moula graduated from the National Institute of Applied Sciences in Lyon, earning a master's degree in mechanical engineering in 2016, followed by a Ph.D. in materials science in 2020. In 2021, she obtained a DevOps engineering degree from Ib Cegos, a subsidiary of the Cegos Group, specializing in IT professional training.
Before venturing into entrepreneurship, Marwa gained extensive experience in France. In 2014, she was a computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) engineer at STELIA Aerospace, a manufacturer of components for the aerospace industry. In 2015, she joined LaMCoS, a mechanical laboratory, as a numerical simulation engineer. In 2021, she became a research and development engineer at the University of Lille.
Melchior Koba
Limited access to financing remains a critical hurdle for startups, especially in Africa and the Middle East. Bolstering these startups fosters innovation, creates jobs, and energizes the regional digital economy.
Orange Ventures, the investment arm of telecoms giant Orange Group, and Digital Africa, a pan-African initiative supporting early-stage businesses, joined forces on Thursday to co-invest in startups across the Orange Digital Centers (ODC) network in Africa and the Middle East.
The partnership, announced on the sidelines of the Vivatech technology fair in Paris, underscores both organizations' commitment to fostering innovation and growth within the region's burgeoning digital economy.
"Orange Digital Centers are true catalysts for innovation, where ideas take shape and dreams become reality," said Asma Ennaifer (pictured left), Executive Director of CSR, Communication, and the Orange Digital Center program for Orange Africa and the Middle East . "By joining forces with Orange Ventures and Digital Africa, we're giving African startups the means to thrive and make their mark in a rapidly expanding digital world."
This initiative builds upon a strategic agreement signed between Orange and Digital Africa in June 2023 to streamline financing and support for ODC network startups. Under the new collaboration, the partners can leverage Fuzé, an investment scheme implemented by Digital Africa, to potentially double the funding offered to individual startups through joint application review and co-investment.
This enhanced partnership marks a significant step towards bolstering support for African entrepreneurs within the ODC network. In its first year, the previous collaboration provided funding of up to €50,000 to five startups through the Fuzé program. With Orange Ventures now on board, the initiative is expected to empower a growing number of African entrepreneurs from the early stages of their ventures by offering comprehensive financial and strategic backing.
Samira Njoya
Investing in digital infrastructure is a significant step for African development as it is crucial in enhancing government efficiency, improving data management, and fostering economic growth. By integrating advanced technology, Nigeria sets a precedent for other African nations to modernize their operations, support digital transformation, and boost overall development.
Nigeria will launch a state-of-the-art data center with a storage capacity of 1.4 petabytes before May 29, 2024, to house critical national information, including citizens' bio-data. The Minister of Interior Dr. Olubunmi Tunji-Ojo announced this during a meeting with the National Union of Nigerian Associations in Italy (NUNAI) on May 20, a statement from the Interior Ministry dated the same day revealed.
Dr. Olubunmi Tunji-Ojo emphasized that adopting advanced technology would enhance efficiency and accountability across national operations, the statement read.
In its 2019 publication titled “Nigeria Digital Economy Diagnostic: A Plan for Building Nigeria’s Inclusive Digital Future,” the World Bank assessed that “Nigeria is capturing only a fraction of its digital economic potential and will need to make strategic investments to develop a dynamic, transformative digital economy.” In line with this, in 2015, the Nigeria Communications Commission proposed transitioning the economy into a digital economy through investments in digital infrastructure.
The launch of this data center directly addresses this assessment, marking a strategic investment in Nigeria's digital infrastructure. This move is expected to unlock more of Nigeria's digital economic potential, promoting an inclusive and robust digital economy.
Hikmatu Bilali
More...
A technology expert, he has over 15 years of experience working with international firms. Since 2016, he is dedicated to facilitating access to energy for all Africans.
Abdala Dissa, a Burkinabe national, is a telecommunications expert and entrepreneur. He is one of the co-founders and the CEO of AliothSystem, a start-up focused on renewable energy and energy efficiency design and innovation.
Founded in 2016, AliothSystem established a domestic solar system (SHS) assembly unit to promote access to solar energy and advance renewable energy in Africa. Through a Pay-as-you-go system, the start-up enables users to pay according to their consumption, thereby helping rural inhabitants quickly access clean, affordable, and reliable energy.
AliothSystem's products are marketed under the brand "téréBox" in Burkina Faso. To date, the company has deployed over 3,500 domestic solar systems on behalf of the Ministry of Energy and the Burkinabe Rural Electrification Agency (ABER) over the past two years. The company aims to install one million SHS units by 2030.
Since May 13, 2024, the company has been participating in the third season of Orange Fab, organized by Orange Digital Center. Represented by its CEO, AliothSystem is attending the VivaTech conference in Paris, which has been ongoing since Wednesday, May 22, 2024.
Abdala Dissa holds an engineering degree in telecommunications and networks, earned in 2009 from Télécom Saint-Etienne. His professional career began in 2008 at N-SOFT, a technology company, where he served as a technical support engineer and project manager for the Europe, Middle East, and Africa region.
In 2012, he became a senior core network engineer at the telecommunications and technology company SFR. The following year, he joined Ericsson as a senior core network engineer. In 2014, he moved to Hub One, a digital technology operator, where he worked as a senior core network operations engineer and then as a core network VoIP/ToIP architect from 2017 to 2020.
Melchior Koba
In September 2023, Kenyan President William Ruto visited Silicon Valley to meet with several tech company leaders. Since then, many of these companies have announced investments in this East African country.
Microsoft and G42, a United Arab Emirates-based firm specializing in artificial intelligence and cloud computing, have announced plans to invest $1 billion in Kenya's digital sector. The announcement was made through a press release issued by Microsoft on Wednesday, May 22.
The investment will be directed towards the construction of a data center in Olkaria, which will be powered entirely by renewable geothermal energy. G42 and its partners will oversee the development of this infrastructure to utilize Microsoft Azure in a new cloud region in East Africa. The data center is projected to be operational within 24 months after the signing of definitive agreements, scheduled to take place on Friday, May 24, in Washington, D.C.
“A letter of intent formalizing the relationship will be signed on Friday as part of Kenyan President William Ruto’s state visit to the United States of America, the first state visit to Washington, D.C., by a sitting African head of state in nearly two decades. The letter of intent will be signed between Microsoft, G42 and Kenya’s Ministry of Information, Communications and the Digital Economy, and was crafted with the assistance of the governments of the United States and the United Arab Emirates,” the statement read.
This initiative builds upon a memorandum of understanding signed between Kenya and Microsoft last September, focusing on integrating the cloud services of the Redmond-based company to enhance public service delivery through a cloud-first approach. Kenya aims to position itself as the digital hub of the region, attracting investments from various tech giants. In addition to Microsoft, Oracle is preparing to establish its second data center in Africa in Nairobi.
The investment will also involve the development of four key pillars in collaboration with local stakeholders. These pillars include creating AI models in local languages and related research, establishing an innovation lab in East Africa, providing extensive digital skills training in AI, investing in international and local connectivity, and working with the Kenyan government to promote cloud services across East Africa.
Despite having a promising startup ecosystem, Kenya currently ranks 19th with a score of 54.2 out of 100 in the 2023 ICT Development Index for African countries, as reported in the "Measuring Digital Development: The ICT Development Index 2023" by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).
Adoni Conrad Quenum
The horticultural sector in Ethiopia is experiencing remarkable growth. To achieve even impressive results, various digital initiatives are being implemented.
On Tuesday, May 21, the Ethiopian Horticulture Producer Exporters Association (EHPEA) and Trade Mark Africa, an African trade assistance organization, signed a partnership agreement in Addis Ababa. This initiative aims to develop comprehensive online learning and knowledge management systems in Ethiopia's horticulture sector.
Tewodros Zewdie (photo, center), Executive Director of EHPEA, highlighted the importance of this partnership, emphasizing that the project will help maintain competitiveness in the country's dynamic horticulture sector. "Through this project, we are investing not just in technology but in the future of Ethiopia’s horticulture sector. Our partnership with TradeMark Africa will enable us to equip our members with the necessary resources to thrive in an increasingly digital marketplace," he stated.
The partnership will benefit from a €139,000 grant from the European Union, provided through the French Development Agency (AFD). This financial support will facilitate the implementation of the learning platform, offering access to valuable resources, training materials, and interactive modules to enhance skills and knowledge sharing in horticultural production and export practices.
This collaboration is part of a broader program focusing on the Ethiopia-Djibouti corridor. It comes at a time when the Ethiopian horticulture sector has seen significant growth in recent years, becoming a fundamental pillar of the national economy. According to official data, the sector contributes 86% to the agricultural GDP.
A web developer, he is passionate about creating innovative solutions to address his clients' problems. He has already developed dozens of digital projects.
Mamadou Dieye, a Senegalese web developer, IT consultant, and entrepreneur, has founded Peelo, a startup specializing in creating chatbots for e-commerce and financial institutions. These chatbots are designed to boost online sales and automate customer support, revolutionizing commerce and communication with smart, no-code WhatsApp chatbots that make interactions with a broader audience easier.
Peelo's chatbots enable e-merchants and financial institutions to efficiently respond to customer messages and comments, thereby increasing conversion rates and collecting data to personalize the user experience. On May 21, 2024, Mamadou Dieye presented Peelo at the Orange Fab Demo event in France, and since May 22, he has been participating in the VivaTech expo, organized by the Les Echos-Le Parisien group.
In addition to Peelo, Mamadou Dieye is also the founder of Mojay.pro, a startup he founded in 2022 to assist established companies and startups in their digital transformation process by offering technology solutions tailored to their daily challenges. Through Mojay.pro, he has successfully completed over 50 projects.
Mamadou Dieye graduated from the University of Dakar’s Polytechnic School and began his career in 2016 as a programmer analyst at Agence 3W, a digital agency providing innovative communication solutions. In 2019, he joined the Impact Hub Dakar incubator as a business developer, and in 2021, he became a web development instructor at Go My Code, a startup that trains people in digital skills.
Melchior Koba