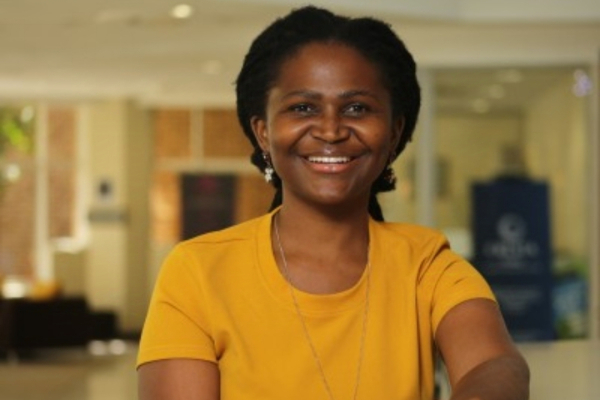
A qualified lawyer, she is actively committed to empowering young people in Africa through education. To date, she has trained thousands of young individuals and has received numerous accolades in recognition of her significant impact on youth.
Lusanda Magwape (photo) is an entrepreneur based in Botswana. She is the founder and CEO of Dream Factory Foundation, an organization that supports young people, whether schooled or not, in achieving their ambitions.
Founded in 2011, Dream Factory Foundation works with schools and rural communities to empower youth to realize their boldest dreams. Its mission is to empower young people through education, equipping them with skills and creating meaningful opportunities to help them become active citizens leading purpose-driven lives.
The organization designs and implements programs tailored to the socio-economic needs of young people while enabling them to contribute constructively to society. It places particular emphasis on digital skills training, notably participating in Africa Code Week, an annual event introducing millions of young people to digital tools.
To date, Dream Factory Foundation has trained 50,000 youth in digital skills, impacted more than 140,000 individuals through its various programs, and helped 320 young people access concrete economic opportunities. The organization's vision is to positively impact one billion young people worldwide by 2030.
In addition, Lusanda Magwape serves as CEO of 50-50 Farmers App, a digital platform dedicated to small-scale farmers in Botswana. The platform aims to boost agricultural yields by providing agronomic advice, specialized training, and easier access to markets. She is also a digital skills and entrepreneurship trainer and coach with UpSkill Digital, an agency specializing in designing learning programs.
Lusanda Magwape holds a Master’s degree in Commercial Law, earned in 2010 from the University of Cape Town. Her remarkable career has earned her numerous awards and distinctions. In 2017, she was named one of the 100 Most Inspiring Social Entrepreneurs in the World by Social Enablers and was a finalist in the Fairlady Santam Women of the Future Awards in 2019.
By Melchior Koba,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
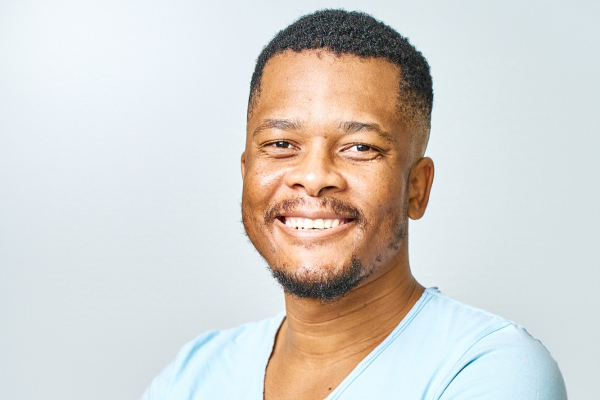
He is a dedicated investor in Africa's growing tech ecosystem. Leveraging his expertise, he actively supports technology companies in South Africa.
Phiwa Nkambule (photo) is a tech entrepreneur, investor, and software engineer from eSwatini. He is the co-founder and CEO of Riovic Capital Group, a South Africa-based tech investment company.
Founded in 2015, Riovic Capital Group is committed to driving innovation and growth in Africa through its three main programs: a research and development program, a venture capital program, and a private equity program.
The research and development program, called Riovic Co-Build, invests in groundbreaking projects. It supports innovative ideas and promising talents capable of transforming industries and improving lives.
The venture capital program, Cybatar Seed Fund, targets early-stage tech companies with high growth potential. It provides them with funding, mentorship, and strategic advice to help them grow and disrupt traditional industries.
The private equity program, Riovic Exit Acceleration Capital Fund, focuses on mature companies with strong growth potential. By collaborating with management teams, this program aims to optimize operations, implement innovative strategies, and maximize value creation.
Before founding Riovic Capital Group, Phiwa Nkambule created Cybatar in 2014, a venture capital platform dedicated to helping tech founders launch their first product and attract initial customers. He also serves as Managing Director of IPOXCap AI, a company specializing in research and development of advanced artificial intelligence solutions tailored to specific industry needs.
Phiwa Nkambule holds a Bachelor of Laws degree from the University of Pretoria, obtained in 2012. In 2018, he served as Chief Technology Officer for Youth Employment Service (YES) South Africa, a social initiative aiming to create job opportunities for one million young South Africans.
In 2019, he joined the Royal Science and Technology Park, a public enterprise in eSwatini, as a non-executive director, supporting the design and patenting of inventions. Between August and November 2024, he also worked as an expert advisor for ALX Ventures, a tech training provider.
Phiwa Nkambule has been recognized for his impact and leadership. In 2018, he was listed among Forbes Africa’s 30 Under 30 most promising entrepreneurs in the technology category. He was also named on Destiny Man’s Power of 40, which celebrates 40 influential young leaders under the age of 40.
By Melchior Koba,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
Digital transformation of healthcare systems is becoming crucial for improving the quality and efficiency of care. Innovative technologies are modernizing data management and optimizing patient services.
Canadian multinational YULCOM Technologies has been selected to implement an information and patient file tracking system in five hospitals in Togo. This project, carried out in collaboration with the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis, and Malaria, aims to digitize hospital processes to enhance the efficiency and transparency of medical care.
"The digitization of hospitals is essential to improving healthcare coverage in all countries. This project will allow us to contribute to digitizing the patient journey and establishing digital health records in Togo," said Youmani Jérôme Lankoandé, CEO of YULCOM Technologies.
The hospital information system (HIS) developed by YULCOM will include key features such as managing admissions, diagnoses, treatments, and prescriptions, as well as tracking patients after discharge. It will also incorporate advanced tools like decision-making algorithms, interactive dashboards, and integration with the DHIS2 platform, an open-source health information management system, to improve health data monitoring.
This initiative is part of a continent-wide movement to digitally transform Africa's healthcare infrastructure in response to the growing demand for modernization and efficiency in medical data management. Togo, which recently launched the construction of a National Digital Health Center, places this project at the core of its national public health strategy.
The global digital health market’s growth potential further highlights the significance of such initiatives. According to Fortune Business Insights, this market, valued at $234.5 billion in 2023, is expected to reach $559.52 billion by 2027, underscoring the increasing global interest in healthcare digitization.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
The fintech sector is experiencing rapid growth across Africa, unlocking new economic and technological opportunities. Rwanda aims to capitalize on this momentum to position its economy as a key hub for financial innovation on the continent.
On Thursday, November 28, Rwanda unveiled a five-year national fintech strategy designed to foster a conducive ecosystem for financial innovation and position the country as a regional financial hub.
“This strategy is not just a policy document but also a commitment to positioning Rwanda as a leading financial technology hub in Africa. In 2014, we had only three registered fintech companies; today, we boast over 75 active fintech players serving more than three million users across the country,” said Paula Ingabire (photo), Rwanda’s Minister of ICT and Innovation.
Over the years, Rwanda has invested heavily in ICT to modernize its economy and expand access to financial services. This new strategy builds on these efforts, yielding significant results. Official data show that financial inclusion rates have risen from 93% in 2020 to 96% in 2023. These achievements reflect the country’s firm commitment to transforming itself into a model digital economy in Africa.
The strategy sets ambitious targets: hosting 300 fintech companies by 2029, creating 7,500 direct jobs, and attracting $200 million in investments. The government also aims to achieve an 80% adoption rate of fintech services, rank among the top 30 countries in the global fintech index, and become Africa’s foremost technological and financial hub.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
Digital transformation has become a critical factor in modernizing healthcare systems worldwide, unlocking unprecedented opportunities to enhance care. International collaborations are driving this transition, introducing innovative solutions tailored to local needs.
Libya’s Deputy Prime Minister and Health Minister, Ramadan Abou Janah (photo, right), and his Russian counterpart, Mikhail Murashko (photo, center), formalized a cooperation agreement on Monday, December 2, to strengthen bilateral ties in the healthcare sector. The initiative centers on integrating digital technologies to modernize Libya’s healthcare system.
According to a statement from the Russian Embassy in Libya, the agreement includes expanded collaboration in organizing and managing healthcare systems, short-term professional training, and implementing digital technologies in healthcare. The partnership also involves joint activities such as the exchange of expertise, statistical and analytical data, hosting medical conferences, and fostering partnerships between medical, educational, and scientific organizations in both countries.
Russia, currently the largest digital healthcare market in the treatment and care segment according to Statista, is well-positioned to support Libya’s digital transformation. The sector is experiencing strong growth, with market projections estimating a volume of €3.7 billion by 2029. This expertise makes Russia an ideal partner in Libya’s efforts to overhaul its healthcare system.
For Libya, the agreement reflects the government’s commitment to revitalize a healthcare system severely disrupted by years of conflict. By leveraging information and communication technologies (ICT), Libya aims to enhance access to and quality of care. Russia’s pioneering work in telemedicine offers innovative solutions that could enable effective remote healthcare delivery in Libya.
Through the integration of digital technologies, Libya seeks to streamline healthcare management, improve medical staff training, and modernize its healthcare infrastructure. This collaboration marks a significant step toward achieving those goals while addressing the country’s pressing healthcare challenges.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
In an effort to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and traffic congestion, two tech entrepreneurs have developed a tailored solution to streamline urban and intercity travel.
Enakl, a digital platform developed by a Moroccan startup, connects travelers heading to the same destination with semi-collective transport providers, such as minibuses. The initiative aims to reduce traffic congestion and carbon emissions. Founded in 2022 by Samir Bennani and Charles Pommarede, the Casablanca-based company also operates an office in Paris.
On Tuesday, December 3, the startup announced it had successfully raised $1.4 million in a funding round. The funding will be used to develop intelligent collective transport solutions for daily commutes within and beyond Morocco.
“This funding allows us to deepen our impact in Casablanca, expand our reach, and accelerate the development of our technology, leveraging AI to optimize routes, enhance commuter experiences, and drive sustainable urban mobility solutions,” the co-founders told Disrupt Africa.
Enakl offers a mobile app, available on iOS and Android, which has already been downloaded over 1,000 times, according to Play Store data. After downloading, users create an account by providing their personal details. They can then plan a ride or trip in just a few clicks by entering their starting point, destination, and desired arrival time.
Based on this information, Enakl suggests the best option for a seamless journey. Users receive details about their transportation—typically a minibus—including the time and pickup point, located within walking distance of their specified location.
Currently managing more than 15,000 reservations per month, Enakl plans to expand into other Moroccan cities before venturing into additional markets across the African continent.
By Adoni Conrad Quenum,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
He is an environmental scientist with over 12 years of experience in teaching and research. He leverages technology to support scientists in their research efforts.
Babajide Milton Macaulay (photo) is a Nigerian tech entrepreneur and the co-founder and CEO of Wadi Africa, a startup dedicated to connecting African researchers with the resources and opportunities they need to advance their work.
Founded in 2022, Wadi Africa provides an online platform designed to support research on the continent. The platform grants researchers access to a wide range of tools, including equipment, information, a collaborative community, training programs, funding opportunities, and a robust support network. The company’s mission is to accelerate scientific and technological progress in Africa, fostering meaningful development across various sectors.
Before launching Wadi Africa, Macaulay founded iLLUMANIA in 2018, an online consulting platform specializing in postgraduate educational services. As its CEO, he focused on building human capacity in emerging economies. He is also a board member of Scholarly, a platform that helps users advance academically and professionally.
Macaulay serves on the board of Boys Without Borders NG, an organization dedicated to advocacy, outreach, and the reorientation of young men in Nigeria. Additionally, he is the training and scholarship director for Africa at the Women For Equality, Inclusion and Sustainability Foundation (WEISF), which promotes the well-being of women, girls, and children across the continent.
Macaulay holds a bachelor’s degree in biology from the Federal University of Technology Akure (2010). He earned a master’s degree in sustainable environmental management from the University of Greenwich in England (2013) and completed a PhD in environmental geochemistry and geomicrobiology at the University of Manchester in 2019.
His professional journey began in 2009 as a scientific intern at the Wazobia Medical Laboratory and Blood Bank. More recently, from 2023 to 2024, he worked as a career coach for Zeed Worldwide, a U.S.-based virtual training and coaching academy aimed at nurturing and guiding young professionals.
By Melchior Koba,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
Passport fraud remains a challenge globally, with fraudulent documents enabling illegal immigration, identity theft, and terrorism. Adopting Chip-embedded passports significantly improves security, making it difficult for criminals to forge or alter documents.
Ghana’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Regional Integration has announced the transition from biometric passports to advanced chip-embedded travel documents. This initiative, unveiled on December 2, reflects Ghana’s dedication to enhancing security, improving efficiency, and aligning with international standards for travel documentation.
Sector Minister Shirley Ayorkor Botchwey hailed the initiative as a significant milestone in Ghana’s digital transformation, emphasizing that the country, as the “gateway to Africa,” must lead in adopting advanced security technologies.
The new passports will feature embedded microprocessors to store biometric and photo data, enhancing security measures and preventing fraud. This upgrade aligns Ghana with International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) regulations and global standards for biometric identification.
The chip-embedded passports will include enhanced anti-fraud measures, such as latent and patent security indicators, and integrate an online system to streamline application and delivery processes. Infrastructure improvements will also be made at Passport Application Centres and Ghanaian Missions abroad to support the new system.
The project, initiated in 2016, is being executed through a Build, Operate, and Transfer (BOT) agreement with Biometric Travel Solutions Limited, a Ghanaian firm. This rollout aims to accelerate passport issuance and combat illegal activities like extortion by intermediaries, commonly known as “Goro boys.” Through these measures, Ghana seeks to modernize its travel documentation and ensure compliance with global best practices.
Ghana has shown steady progress in digital transformation, with a focus on integrating technology into public services. The new passports align with this strategy, complementing existing efforts to modernize government processes.
As of December 2024, the Ghanaian passport ranks 142nd globally on the VisaGuide Passport Index. It allows visa-free travel to 46 countries, requires an eVisa for 19, and mandates visas for 140 destinations.
Hikmatu Bilali
Manufacturing is critical to economic transformation in Africa. However, Africa’s share of global manufacturing output remains far below its potential. The ManuTech Hub aims to leverage startups to address challenges such as low productivity, limited technology adoption, and skills gaps that hinder industrial growth.
The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and Ethiopia’s Ministry of Industry have unveiled the Timbuktoo ManuTech Hub. The initiative, announced November 23 in a UNDP press release, is designed to support African startups with funding, mentorship, and advanced technical resources. Set to open in early 2025, the hub will be based in Addis Ababa and serve as a platform for innovation in the manufacturing sector through technology and strategic partnerships.
According to the release, “ManuTech aligns with Ethiopia’s goal of becoming a leading light manufacturing hub in Africa, an ambition reflected in the country’s investments in establishing multiple industrial parks.”
Ethiopia has long aspired to become a manufacturing hub in Africa. In the 2010s, the government adopted the Growth and Transformation Plans (GTPs) to accelerate industrialization, focusing on textile and apparel manufacturing. This led to the development of Hawassa Industrial Park, Africa’s largest eco-friendly park, which attracted brands like PVH Corp. However, they faced numerous challenges which led to underperformance.
The ManuTech Hub represents a new phase in Ethiopia’s industrial strategy, focusing on tech-driven manufacturing to overcome past challenges. By fostering startups, the hub provides a pathway for Ethiopia to diversify its economy and integrate into global value chains.
The hub will provide a three-month hybrid accelerator program for selected startups, offering training, mentorship, technology access, and guidance to align their solutions with Africa’s manufacturing needs. In addition to technical support, participating startups will also receive seed grants to scale their innovations. The Ministry of Industry will supply the physical space for the hub, reinforcing Ethiopia’s commitment to becoming a manufacturing leader on the continent.
Applications for the first cohort are now open and can be submitted through the UNDP website until December 25, 2024. Startups from across Africa will be selected bi-annually, with the first cohort set to launch upon the hub’s completion.
By fostering innovation and nurturing a new generation of entrepreneurs, the hub seeks to bridge the skills gap, enhance manufacturing efficiency, and accelerate Ethiopia’s industrial growth. As a collaborative effort between UNDP and the Ethiopian government, the hub has the potential to drive transformative change not only in Ethiopia but across Africa’s manufacturing landscape.
Hikmatu Bilali
Paystack has partnered with Vendy, a marketplace that helps merchants create customizable WhatsApp Shops, to simplify mobile commerce and streamline sales directly on WhatsApp, techcabal reports.
Buyers can browse catalogs, place orders, and pay without needing additional apps or sign-ups. Merchants can choose from over 60 shop templates tailored to their needs, ensuring a personalized and efficient setup.
This collaboration marks a major step in advancing mobile commerce in Africa, leveraging WhatsApp’s popularity to create seamless and trusted buying experiences while helping businesses grow.
More...
Africa’s domestic payment card scheme Verve International has announced its cards are now accepted on AliExpress, one of the world’s largest online retail platforms.
This collaboration marks a significant step in Verve’s global expansion efforts, providing millions of cardholders access to AliExpress’s extensive product offerings.
By adding their Verve card details during checkout, cardholders can pay in local currency for a wide range of products.
She is a recognized expert in developing technological solutions in Africa. As a serial entrepreneur, she founded three startups in Ghana and Kenya.
Safari Mugendi (photo) is a Kenyan tech entrepreneur. She is the co-founder and CEO of Disheey, a startup leveraging technology and data to help restaurants operate more efficiently.
Founded in 2023, Disheey aims to transform restaurant management. The startup offers an innovative app that simplifies operations and increases revenue. This solution includes kitchen order management, real-time reconciliation for greater transparency, and advanced analytics for informed decision-making.
Through data collection, Disheey helps restaurants better understand customer preferences, identify the most popular dishes, and resolve bottlenecks in their services. This information is used to optimize menus, operational processes, and promotions, improving efficiency and profitability. Additionally, the platform facilitates sourcing fresh ingredients directly from farmers.
Before founding Disheey, Safari Mugendi co-founded Eduzuka Education in 2020, a learning center in Kenya. In 2021, she launched Vazeey in Ghana, a startup specializing in the online sale of second-hand products.
The Kenyan entrepreneur holds a degree in Management Information Systems from Ashesi University. In 2023, she completed a digital marketing course at HubSpot Academy, an online learning provider.
Her professional career began in 2019 as a relationship officer at Equity Bank Ltd. In 2021, she worked as a program manager at Yecham Property Consult, a Ghanaian consulting firm specializing in real estate solutions for investors.
In 2022, Safari Mugendi interned in marketing at Global Mamas, a Ghanaian nonprofit dedicated to empowering women. Most recently, between February and August 2024, she worked as a sales advisor at Odoo, a software company based in Kenya.
By Melchior Koba,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
The Ghanaian government has made digital technology a cornerstone of its socioeconomic development strategy. The administration plans to launch a $5 million fund to support technological innovation across the country.
Ursula Owusu-Ekuful (photo, center), Ghana’s Minister of Communications and Digitalisation, officially unveiled the country’s new Digital Economy Policy and Strategy last week. This roadmap aims to harness digital technologies to spur economic growth, improve public services, and ensure equitable access to digital resources.
The strategy focuses on five key pillars: entrepreneurship, digital skills, digital government, universal access, and emerging technologies.
According to the minister, the policy is designed to enhance and accelerate Ghana’s ongoing digital transformation efforts. Ghana currently ranks 108th globally on the 2024 E-Government Development Index (EGDI) by the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UNDESA), with a score of 0.6316 out of 1. While this places the country above the averages for West Africa (0.3957) and the African continent (0.4247), it remains slightly below the global average of 0.6382.
In the ICT Development Index, Ghana scores 66.2 out of 100, according to the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), which also recognizes Ghana as a global leader in cybersecurity practices.
“By aligning digital efforts with job creation and GDP growth, the policy aims to ensure that technology becomes a powerful engine for inclusive development, reducing poverty and enhancing prosperity for all Ghanaians,” the Ministry of Communications and Digitalisation stated in a news release.
A joint study by the International Finance Corporation (IFC) and Google forecasts that Africa’s digital economy will be worth at least $712 billion by 2050, representing approximately 8.5% of the continent’s GDP. In Ghana, data from the Ghana Statistical Service (GSS) reveals that the ICT sector contributed GHS 21 billion ($1.36 billion) to GDP in 2022, accounting for about 4% of the economy. This marks a significant increase compared to its contribution of GHS 4.4 billion in 2016.
By Isaac K. Kassouwi,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
The integration of digital technologies is gradually transforming traffic management, providing innovative solutions to streamline traffic flow and enhance safety. In Africa, these initiatives are gaining momentum, reflecting a commitment by countries to modernize their transportation infrastructure.
On Friday, November 29, Senegal’s Minister of Infrastructure, Land, and Air Transport, Malick Ndiaye (photo, right), met with Terry HE (photo, left), President of Huawei Northern Africa (North, West, and Central Africa). Their discussions focused on the implementation of a road traffic digitization project aimed at improving traffic flow and enhancing road safety across the country.
During the meeting, several adjustments were agreed upon to maximize the project’s impact. A comprehensive coverage plan for the Dakar region was finalized, including the strategic deployment of digital systems for optimal coverage. The number of traffic radars will be doubled, with a particular focus on high-risk interurban areas prone to accidents. Additionally, the project will include the training and immersion of 10 Senegalese engineers tasked with independently managing the digital platforms and infrastructure introduced through the initiative.
This visit follows Huawei’s recent presentation of its intelligent and connected transport system to Senegalese government officials, specifically designed for Dakar. The project aligns seamlessly with Senegal’s ongoing digital transformation strategy, which aims to modernize infrastructure while integrating innovative technological solutions to address urban and national mobility challenges.
Scheduled for rollout next year, the project aspires to significantly improve traffic fluidity, reduce accidents, and enhance the enforcement of traffic regulations. Moreover, the training of Senegalese engineers will bolster the nation’s technological capabilities, ensuring the project’s sustainability while fostering local expertise in strategic digital sectors.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji