Telecom (150)
Some 2.6 billion people still have no access to the Internet across the globe. In remote areas, where conventional networks seem limited, satellites are positioning themselves as a reliable alternative.
On Friday, October 6, American e-commerce giant Amazon launched the first two satellites of its 3,236-satellite constellation. Dubbed "Project Kuiper", the satellites will orbit lower around the Earth to provide high-speed, low-latency satellite Internet services like Elon Musk’s Starlink.
Project Kuiper aims to bridge the digital divide by providing fast, affordable broadband to communities unserved or underserved by traditional communications technologies. To achieve this, Jeff Bezos's company intends to invest $10 billion.
"Our goal with Project Kuiper is not just to connect unserved and underserved communities, but also to delight them with the quality, reliability, and value of their service. [...] From day one, every technology and business decision we’ve made has centered on what will deliver the best experience for different customers around the world, and our range of customer terminals reflects those choices," explained Rajeev Badyal, Amazon’s vice president of technology for Project Kuiper, last March.
Amazon, which is still lagging in terms of satellite deployment, ultimately wants to compete with Starlink in the satellite internet segment. For that purpose, it plans to launch more than 1,500 satellites before 2026 to retain its operating license granted in 2020 by the US Federal Communications Commission. Meanwhile, Starlink already has over two million active users worldwide with plans to conquer the African market. This year, it intended to enter 23 African markets but currently, it has effectively launched in six owing to various legislations.
It is worth noting that the costs of Starlink’s equipment are pretty high for the average African. Earlier this month, the company decided to reduce the cost of its equipment by 21% in Nigeria, from 378,000 naira (around $487) to 299,000 naira. Last September, Kenyan President William Ruto also asked Starlink to reduce the price of its services. The equipment costs 89,000 Kenyan shillings (approx. $595), with a delivery charge of 3,100 shillings. In Zambia, the equipment costs 10,774 kwachas (around $505).
Will Amazon’s equipment be more affordable for Africans?
Amazon wants to offer three antenna models for its customers. The firm revealed that the production cost of the standard model is around $400, which implies that the standard selling price will be higher than this amount. Truly, equipment is a one-off expense but, at this rate whether it is higher than that practiced by Starlink in African markets or not it remains high. What's more, after reducing its prices in Nigeria, Elon Musk's firm will probably continue this pricing policy in other markets to standardize its offerings across the continent.
As a reminder, the number of people covered by fixed broadband in Africa remains below 10%. This is the lowest level in the world. With conventional networks’ failure in this area, satellite Internet remains the most attractive alternative for remote and underserved areas to access broadband Internet.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
The sheer volume of high-speed telecom infrastructure deployed in Africa since 2010 has made the continent a market with high financial potential for many international tech groups. But these investments appear to be underexploited.
Over the past ten years, the number of people covered by fixed broadband in Africa has remained below 10%, despite the considerable financial investments made during this period. In its "Global Connectivity Report 2022", the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) reports that in 2021, only seven out of every hundred households were covered by the service, compared with 82% for mobile. This is the lowest level worldwide and has not changed since. In Europe, the coverage rate is 96%, compared with 88% and 86% respectively in the Asia-Pacific and Americas.
In terms of subscriptions, only 1% of consumers had subscribed to the service on the continent by 2021. This was also the lowest level worldwide. In Europe, the figure was 35%, compared with 23% and 17% in the Americas and Asia-Pacific respectively, according to the ITU.
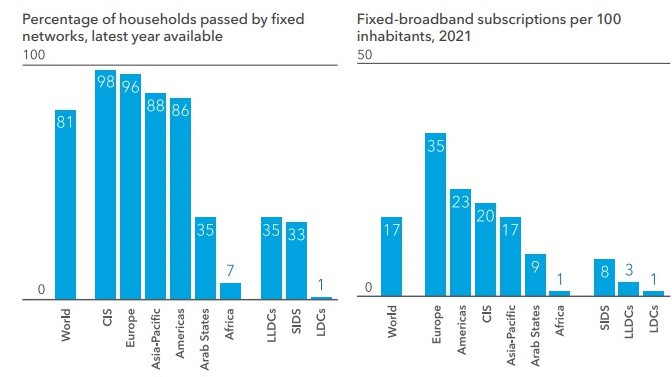
Worldwide fixed broadband coverage (Source: ITU, 2021)
According to the ITU, the lag in fixed broadband is explained by consumer preference in terms of usage. They opt for mobile, which is more flexible and less expensive. For telecom operators, the choice is explained by investment costs. "Fixed broadband networks are very costly to deploy, maintain, and upgrade, depending on the geography and extent of the territory to be covered," says the ITU. At 17.9% of monthly gross national income per capita, fixed broadband access costs in Africa are the most expensive in the world. Meanwhile, the ITU recommends less than 2%.
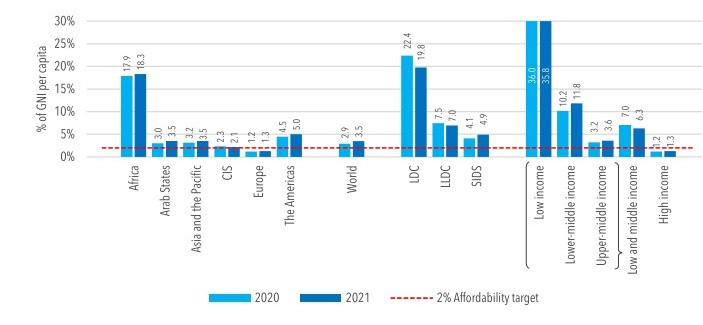
Fixed broadband access costs in 2021 (Source: ITU)
Since 2020, Africa has recorded the fastest annual growth rate in Internet transmission capacity in the world, according to the report "The State of Broadband 2023 Digital Connectivity: A Transformative Opportunity" by the United Nations Broadband Commission. The continent is already home to more than 25 submarine fiber optic systems and is covered by almost 1.2 million km of terrestrial fiber optics. But only 25% of the population lives within 10 km of a fiber optic network.
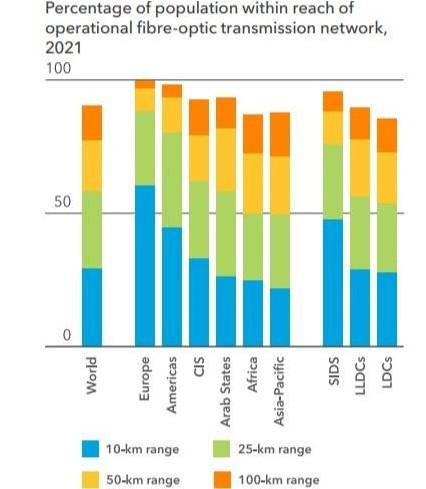
Percentage of population near a fiber optic network (Source: ITU)Worldwide, only 2.3 billion people (29%) were living within 10 kilometers of a fiber optic network in 2021. In Europe, over 60% of the population lives within 10 kilometers of a fiber-optic network, nearly 47% in the Americas, and 22% in the Asia-Pacific region.
“Although more people use mobile networks than fixed networks to connect to the Internet, the latter remains important. For example,fixed-broadband networks generally have a higher data capacity than mobile networks, and download limits are higher than similarly priced mobile-broadband plans. They are faster and are more reliable than 3G or 4G networks, making them more suited for high-bandwidth activities such as games and video calls," explains the Union.
Broadband internet is more strategic for small and medium-sized businesses. In its survey "The State of Broadband: Accelerating Broadband for New Realities September 2022," the Broadband Commission for Sustainable Development conducted a survey of informal businesses in nine African countries, revealing low levels of ICT use. "Internet use for business purposes was 7% on average, ranging from 24% in South Africa to 1% in Rwanda. Computer ownership is also low: over 90% of businesses surveyed in Ghana, Kenya, Mozambique, Nigeria, Rwanda, Tanzania, and Uganda said they did not have one," the survey shows
While a one-person micro-business may find that a smartphone with wireless access is sufficient to carry out its activities, particularly for online sales on social media, many businesses still feel that they don't need Internet access or a computer. Yet, fixed broadband can improve operational and commercial activities, as the Covid-19 crisis demonstrated.
In the report "Economic impact of broadband in LDCs, LLDCs, and SIDS: An empirical study, 2019", the ITU estimates that a 10% increase in fixed broadband penetration would increase gross domestic product per capita by 2.0 to 2.3%.
Muriel Edjo
Incumbent operator Telecom Egypt is gradually moving towards its goal of becoming the leading connectivity services provider in the region. As part of its strategy, the company is teaming up with like-minded international partners.
Egyptian telecom operator Telecom Egypt and 4iG, a Hungarian IT service management company, signed a memorandum of understanding in Cairo on Wednesday, October 4, to link Egypt and Albania via a high-capacity fiber optic submarine cable.
The cable to be built will be a new traffic entry to Europe via Albania and will add a new multiple route to Egyptian-European traffic. "With an open access model and multiple branching units, the system is set up to be a new European cable entry point with a different transit passage compared to the already existing Mediterranean routes to the main internet Point of Presence (PoP) such as the ones in Frankfurt in addition to numerous potential Points of Presence in Eastern Europe," said 4iG in a press release.
For Budapest-based 4iG, the new agreement represents a gateway to “enter as a new player in the market for intercontinental data transmission infrastructure between Europe and Asia, and Europe and East Africa.” Meanwhile, Telecom Egypt indicates that the initiative is part of its strategy to diversify transit options in the Mediterranean basin by means of multiple, high-capacity submarine cables linking Egypt and Europe.
According to Amr Talaat, Egypt's Minister of Communications and Information Technology (MCIT), the country is already connected to 14 international submarine cables, and work is underway to establish five new cables. In addition, Telecom Egypt is the partner of choice for the deployment of submarine cables for over 160 companies worldwide.
Ultimately, the new submarine cable will, among other things, facilitate connectivity in the countries concerned and create new opportunities for cooperation with partners in many countries.
Samira Njoya
The test is carried out in preparation for a service rollout in 2024.
American satellite service provider Starlink has rolled out its services in Tunisia for a three-month trial period. This was announced, on Monday, October 2, by the Ministry of Communication Technologies during a workshop organized to discuss the present and future situation of satellite internet in Tunisia.
The test will be carried out in three cities, namely Tunis, Ariana, and Gabes. It aims, among other things, to help discover satellite Internet technologies and compare them with traditional methods currently available in Tunisia, such as internet services offered by telecom operators, fiber optics, or subsea cables. It will also offer the opportunity to review the legal and regulatory framework surrounding the marketing of the services as well as the business model.
Tunisia, like most countries on the continent, is looking for alternatives to connect the majority of the population, in this case those in landlocked and/or remote areas, through its national strategy for the development of digital infrastructure and technical solutions. This pilot phase follows Tunisian ICT Minister Nizar Ben Néji's visit to the United States in July. During his visit, the government official signed a partnership agreement with the American firm to enable his ministry, the national spectrum agency, the Telecommunications Research and Studies Center, and the telecoms regulator to draw up licenses for the provision of satellite Internet services.
According to its roll-out schedule published earlier this year, Tunisia is not due to receive Starlink’s internet services in 2024. The pilot phase launched this month (the first month of the fourth quarter of the year), confirms this schedule.
Let’s note that according to DataReportal, in Tunisia, Internet penetration rate was 66.7% in 2022.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
Telecom operators are increasingly investing in fifth-generation Internet. In Sierra Leone, French telecom giant Orange is entering this segment, adding to the list of countries where it has already launched 5G.
Last week, Orange Sierra Leone announced the launch of the pilot phase of fifth-generation mobile Internet, to offer subscribers higher connection speeds, improved connectivity, and low latency. This pilot phase will take place solely in the business district of Freetown, the country's capital.
"This launch is indeed an important milestone for Sierra Leone. I am delighted that Orange Sierra Leone is taking the lead in setting the baseline technology standard for 5G by deploying this state-of-the-art pilot phase on our network, in line with the company's vision to become a leading mobile Internet service provider in Sierra Leone," said Sekou Drame, Chairman and CEO of Sonatel, the parent company of Orange Sierra Leone.
During an audience with Sonatel’s delegation, Julius Maada Bio (photo, center), President of Sierra Leone, praised the initiative. Internet is a key point in Sierra Leonne’s 2019-2029 National Innovation and Digitalization Strategy. In that context, the 5G test is in line with authorities’ ambition to boost access to the Internet.
Let’s note that Orange is multiplying its investments in 5G technology on the continent. Among other countries, the telecom company has carried out 5G commercial tests in Botswana, Tunisia, DRC, Côte d’Ivoire, and Senegal. Last week, it inaugurated a 5G lab in Madagascar, to enable local tech players to discover this technology, demonstrate use cases, and test its impacts on their products and services.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
Thanks to the regional fiber loop it is building by interconnecting with its neighbors, Tanzania aims to form a large regional loop that will enable it to offer its population high-quality, affordable, and ultra-high-speed connectivity.
Tanzania will connect Uganda to its National Fibre Optic Cable network named National ICT Broadband Backbone (NICTBB). This is one of the terms of a memorandum of understanding signed between Tanzania Telecommunications Corporation (TTCL) and the National Information Technology Authority Uganda (NITA-U) on Friday, September 29, to strengthen the ICT cooperation between the two countries.
The 15-year agreement will be implemented by NITA-U and TTCL, costing $28.8 million.
"ICT connections with Uganda will create another connection opportunity with other countries. The government will continue investing in infrastructure management to increase productivity,” said Nape Nnauye, Tanzania's ICT Minister, adding that the agreement offers an important opportunity to establish a connection between the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) and South Sudan in the coming months.
This ICT partnership between Tanzania and Uganda is the result of Tanzanian President Samia Suluhu Hassan's visit to Uganda in May 2022. During that visit, she agreed with her Ugandan counterpart Yoweri Museveni to integrate the two countries' ICT backbones for improved internet services.
According to Chris Baryomunsi, Uganda's Minister of ICT and National Orientation, the MoU will transform people's lives by providing them with opportunities. It will also stimulate economic growth in both countries through the use of ICT.
Tanzania's fiber optic link with Uganda will follow that currently underway with Malawi. Earlier this month, Tanzania signed an agreement with Malawian authorities to extend its national fiber optic infrastructure to the border town of Kasumulo. Once the interconnection is complete, Uganda will join the list of countries with which Tanzania shares an interconnection. These include Burundi, Kenya, Mozambique, and Rwanda.
Samira Njoya
French telecommunications group Orange is stepping up its investments to facilitate digital transformation in its operating countries. The lab inaugurated is its third in Africa and the 19th worldwide.
Orange, a French telecoms group operating in 16 African countries, inaugurated its 5G lab in Antananarivo, Madagascar, last Thursday, September 28. The lab was inaugurated during a trade fair organized to showcase the 5G internet speed. It enables various players in the technology sector to discover 5G, demonstrate its use cases, and assess the potential of 5G in their products and services.
"This fair marks the launch in Madagascar of an Orange 5G Lab, which is based at the Orange Digital Center Madagascar premises in Ankorondrano. The Orange 5G Lab Madagascar program aims to help digital and economic players better understand the opportunities, value, and usefulness of 5G," Orange indicates in a press release.
5G offers higher upload and download speeds and more consistent connections, revolutionizing the technology sector in many ways. With its labs and similar investments, Orange is increasingly establishing itself as a key player in the acceleration of digital transformation in Europe, Asia, and Africa. The Antananarivo-based Orange 5G Lab is the third it inaugurated in Africa. In June and September 2022, it respectively inaugurated Orange 5G Labs in Dakar (Senegal) and Abidjan (Côte d'Ivoire).
Adoni Conrad Quenum
With the ongoing digital transformation, investments are pouring into Africa to guarantee quality internet connection for populations. Over the past three years, new telecoms infrastructures have been commissioned for this purpose.
Demand for high-speed Internet services in Africa has been rising since 2020. This need is currently having a direct impact on the continent's transmission capacity, which has recorded the fastest compound annual growth rate (CAGR) in the world over the past three years, indicates the Broadband Commission of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), in its report "The State of Broadband 2023 Digital Connectivity: A Transformative Opportunity."
Between 2020 and 2023, a dozen new submarine cable systems were commissioned on the continent, boosting total available bandwidth by more than 70 terabits. In addition to cables such as the South Atlantic Inter Link, Orval, METISS, DARE1, EllaLink, Maroc Telecom West Africa, Equiano, 2Africa, etc., thousands of kilometers of terrestrial fiber optic cable have also been deployed by suppliers such as Liquid Telecom. Added to this are the data capacities of national and international satellite communication systems such as Eutelsat, YahClick, Intelsat, Starlink, OneWeb, etc.
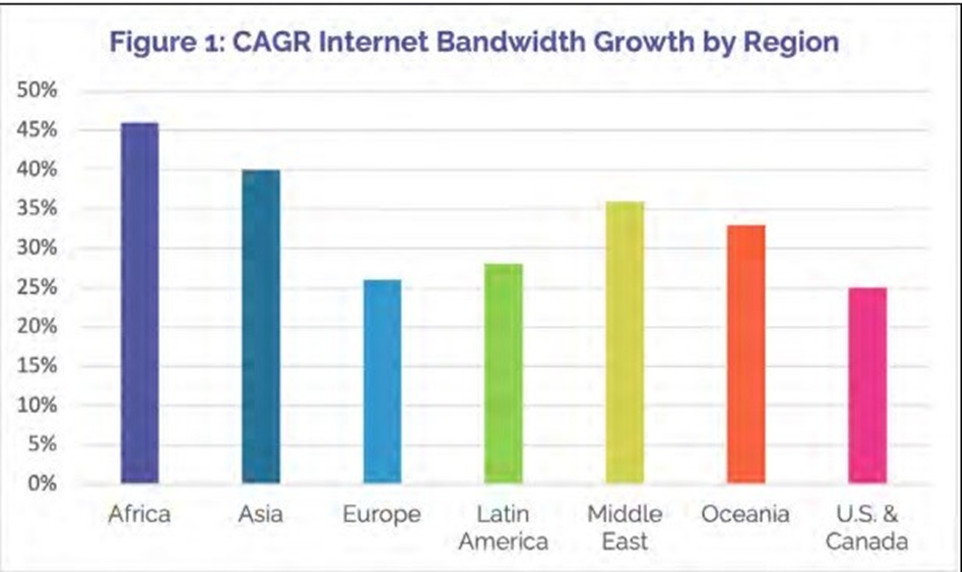
Source: Broadband Commission
In its June 2020 Mobility Report, tech company Ericsson reported that in sub-Saharan Africa, home to more than half the African population, monthly internet trafic per smartphone was 1.9 gigabytes in 2019. By June 2022, this monthly traffic had climbed to 4.7 gigabytes. Ericsson estimates that this growth in demand volume will reach 19 GB by 2028, for individual consumers alone. However, the rapid annual growth in high-speed transmission capacity does not always benefit all African populations, even though 83% of them are covered by a telecoms network (49% by 4G and almost 30% by 3G), according to the ITU. The Internet access rate is only 33% (87% in Europe, 81% in the USA, 61% in Asia-Pacific), despite the significant potential for high-speed connectivity. A number of obstacles are still holding back the full exploitation of the various Internet investments made by governments and service providers. These include the high cost of entry-level broadband services. They are still well above the threshold set by the Broadband Commission: less than 2% of monthly gross national income per capita.
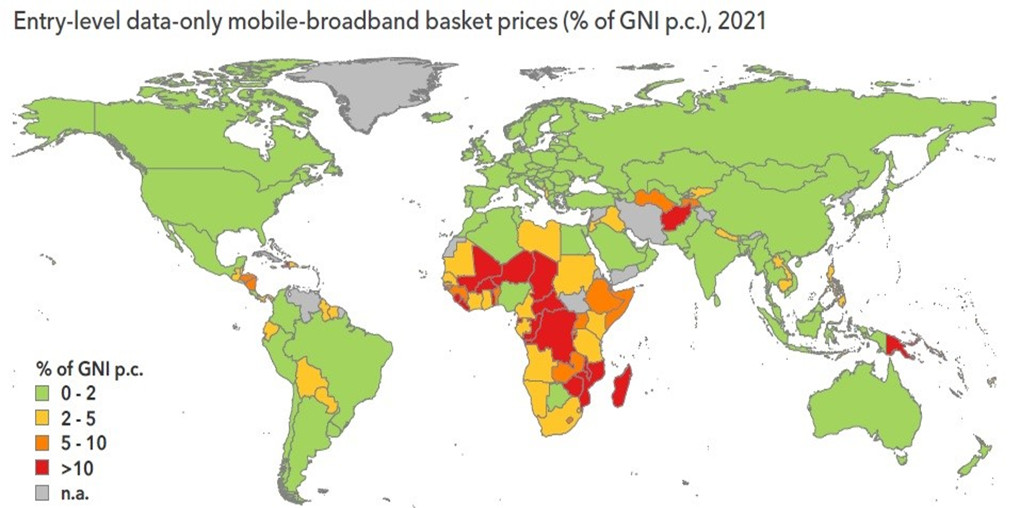 Source: UIT
Source: UIT
The cost of internet-enabled phones is another obstacle. In its study "To Luxury To Lifeline. Reducing the cost of mobile devices to reach universal internet access" covering 70 countries worldwide, the Alliance for Affordable Internet (A4AI) drew up a heat map revealing the markets where the price of a smartphone is most affordable. Access to computers is also expensive. Only 1% of the African population is connected to fixed broadband at home (35% in Europe, 23% in the USA, 17% in Asia-Pacific), out of the nearly 2.5 million km of fiber optic cable already deployed on the continent.
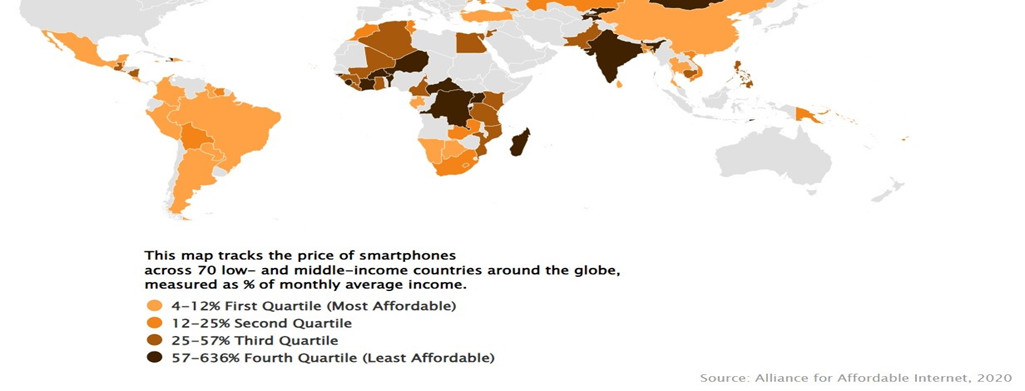 Source: Alliance for Affordable Internet
Source: Alliance for Affordable Internet
According to the ITU, the Internet is currently an undisputable catalyst for economic and social development. The UN agency states that improving mobile and fixed broadband penetration rates by 10% would add 2.5% and 1.5 respectively to gross domestic products (GDP).
Muriel Edjo
In 2021, Starlink began negotiations to get the necessary authorizations to provide its satellite internet services in certain African countries. Pursuing the same objective, the company is partnering with African companies with converging ambitions.
Pan-African broadband connectivity provider Paratus announced on Friday, September 22 that it had signed an agreement to distribute Starlink's broadband Internet services on the African continent.
Under the terms of the agreement, Paratus will supply Starlink to customers across the continent as and when licenses are granted to Starlink in Africa. For the time being, Starlink will be available from Paratus in Mozambique, Kenya, Rwanda, and Nigeria, before being extended to other countries.
"This agreement aligns perfectly with our vision of transforming Africa through exceptional digital infrastructure and customer service. It means we can offer industry sectors – such as land and offshore energy, mining, hospitality, education, healthcare, agriculture, and more – the reliable and constant connectivity they need to flourish, no matter how remote they are," said Martin Cox, Paratus Group Chief Commercial Officer.
For Starlink, the new agreement is part of its expansion strategy to bring satellite broadband Internet services to every corner of the globe, including remote and landlocked areas hardly accessible for mobile operators' terrestrial networks.
In this way, the partnership between Paratus and Starlink should help to strengthen competition in the African Internet market and promote digital inclusion. According to a 2022 report by the International Telecommunications Union (ITU), in 2021, 33% of Africans used the Internet, compared with 63% for the global average. These figures have risen sharply in 2022 with the arrival of new telecom operators and the construction of new infrastructures in several countries.
Samira Njoya
Sattelite internet provider Starlink has expressed its interest in conquering the African market by 2024. To date, the company has launched operations in five countries and is looking to do the same in Chad, with plans to extend its reach to 23 African markets.
The Chadian Electronic Communications and Posts Regulatory Authority (ARCEP) has issued a warning to individuals illegally marketing and operating Starlink terminals in the country. In a press release published on social networks on Friday, September 22, the telecoms regulator warns offenders of the penalties provided for by law in the event of continuation of the aforementioned activities.
Providing unauthorized electronic communication services or maintaining the services despite legal orders to suspend it is punishable by one to five years imprisonment and fines ranging from XAF100 million ($162,500) to XAF200 million or one of the two penalties, the release informs quoting Article 113 of Law No. 014/PR/2014 on electronic communications.
ARCEP's release comes as the Starlink network is increasingly used in Chad. On social networks, users are approving the new services, which they say are bridging the digital divide in the country by providing Internet access to underserved communities at an affordable cost.
For the telecoms regulator, the problem lies in the license that Starlink would need to obtain before launching operations in the country. Two days earlier, ARCEP held a consultation meeting on Starlink's application to become a Satellite Internet Service Provider (ISP) in Chad. A response is expected in the next few days.
In Chad, the legal use of Starlink should stimulate the digital sector and offer a high-speed Internet connection to a population that constantly complains about the poor quality and high costs of the Internet in the country.
Samira Njoya
More...
The International Telecommunication Union considers broadband access to be an indicator of development. At a time when digitalization is accelerating in Africa, ensuring connectivity for the population is more than just an economic issue.
Repairs on the West African Cable System (WACS), South Africa Transit 3 (SAT3), and Africa Coast to Europe (ACE) submarine fiber optic cables, damaged in early August 2023, have been completed. The three high-speed telecoms infrastructures linking the west coast of Africa to Europe had been severed off the coast of the Democratic Republic of Congo following a rockfall in an underwater canyon. Repairs were carried out by the cable-laying vessel Léon Thévenin, which arrived in South Africa on August 21.
Openserve –the broadband Internet arm of South African telecoms group Telkom, which is also one of the members of the WACS and SAT3 cable consortium– confirmed the successful completion of the repairs on Wednesday, September 20.
“The completion of this work is good news for Internet users as this means that there is more available capacity and improved network resiliency," said Openserve.
Because of the break in the three undersea fiber optic cables, Internet service providers and consumers have been deprived of a total of 154.5 terabits per second (Tbps) of data capacity for over a month. That's 20 Tbps for the ACE system, which connects ten African countries; 120 Tbps for SAT3 and 14.5 Tbps for WACS, which together connect eleven African countries.
For some countries, such as Benin, Cameroon, and Côte d'Ivoire, which host all these cables, the inconvenience caused by the incident to telecoms infrastructures was somewhat more severe. However, the alternative solutions adopted by operators enabled Internet services to continue uninterrupted.
This is not the first time that the SAT3, WACS, or ACE cables have been damaged. In 2017 and 2020, the cables were severed, hampering business continuity in several countries. To remedy the situation once and for all, many countries are increasing their access to subsea systems, while others are opting for satellite technologies.
At a time when the United Nations considers the Internet to be a basic service capable of contributing to the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), the diversification of connectivity sources is more than just an economic issue for African countries.
Samira Njoya
Since 2011, Congo has been served by a single international fiber subsea cable, the WACS. Frequent outages on this infrastructure disrupt Internet services.
On Thursday, September 7, the Congolese Minister of Posts, Telecommunications and the Digital Economy, Léon-Juste Ibombo, launched the construction of a second national backbone network, resulting from Congo's recent connection to the new 2Africa subsea cable.
The 2Africa subsea cable, initiated by Meta (Facebook's parent company), will enable data transmission between Pointe-Noire and Brazzaville at a very high speed of up to 10 gigabytes per second.
According to the Minister of Telecoms, the new network will improve and further strengthen the capacity of what already exists. "The construction of the new Matombi backbone network, which will serve Pointe-Noire, Brazzaville, and the other cities, is the concrete expression of a strong ambition to improve the speed and reliability of electronic communications, facilitate trade and access to international markets, foster technological innovation and encourage the emergence of startups, and strengthen Congo's participation in the global digital economy," he said.
2Africa is the second international subsea cable the Republic of Congo is connected to. In 2011, the country connected to the WACS (West Africa Cable System) cable, on which it mainly depends for broadband Internet services. However, frequent outages on this infrastructure cause disruption to Internet services.
When completed in 2024, the 2Africa cable will be 45,000 km long, making it the longest in the world. It will serve a geographical area (Africa, Middle East, Europe) home to some three billion people, or 36% of the world's population.
In Congo, 2Africa should not only reduce the cost of Internet services but also extend access to these services to millions more people. According to the latest data from the regulator, the country currently has 3.05 million Internet users, equivalent to a penetration rate of 54%.
Samira Njoya
Broadband Internet service provider Starlink has expressed its interest in conquering the African market by 2024. So far, the company has launched operations in five countries on the continent and is looking to do the same in Zimbabwe with plans to extend its reach to 23 African markets.
Starlink, Elon Musk’s satellite internet company, will have to comply with applicable regulations if it is to operate in Zimbabwe. The Postal and Telecommunications Regulatory Authority of Zimbabwe (POTRAZ) recently issued a warning to users and resellers cautioning them against using unlicensed operators and internet service providers based abroad.
According to the telecoms regulator, to launch operations in the country, Starlink can either apply for a license or partner with a local company registered as a public network operator. In this case, "the Satellite Operator and the local network Operator enter a Virtual Network Operator (VNO) agreement, that must be approved by the authority, to ensure that the public network operator meets legal and regulatory requirements stipulated in the license," POTRAZ wrote in a public notice.
In December 2022, Starlink announced the launch of its activities in Zimbabwe. On its website, Starlink indicated it was planning to start serving the region in the fourth quarter of 2023. So, for the regulator, if this timetable remains unchanged, the company should have submitted a license application by now.
Starlink's arrival in Zimbabwe is expected to boost the digital sector and provide high-speed Internet connection to the population, who constantly complain about the poor quality and high cost of Internet in the country.
Samira Njoya
We are in the digital economy era, and the impact of tech entrepreneurship on wealth and job creation keeps growing in Africa. However, African innovators still face many challenges, and encouraging local talent and promoting access to certain resources is becoming more and more urgent.
The Tanzania Communications Regulatory Authority (TCRA) and the Tanzania Commission for Science and Technology (COSTECH) recently signed a partnership agreement to provide free communications resources to emerging ICT companies. The move aims to foster an environment that is conducive to digital innovation and allows these companies to thrive.
"The collaborative effort aims to nurture the country's thriving digital innovation landscape, ensuring that start-ups have the tools they need to thrive and contribute positively to society through their technological advances," said TCRA CEO Dr Jabiri Bakari (pictured, right).
"The distribution of these resources makes it possible to offer high-speed Internet services, an important factor in the digital economy," he added.
Two months ago, the TCRA allocated resources to four innovative startups to enable them to submit their ideas to COSTECH for further development. The move also contributes to the Tanzanian government's ambition to provide 80% of the population access to high-speed Internet by 2025, consequently fostering innovation in areas such as entrepreneurship, agriculture, and transport.
Support from TCRA and COSTECH will enable Tanzanian startups to communicate their projects free of charge. Among other things, TCRA provides numbering resources, frequency spectrum, zip codes, residential addresses and mobile money services.
Samira Njoya