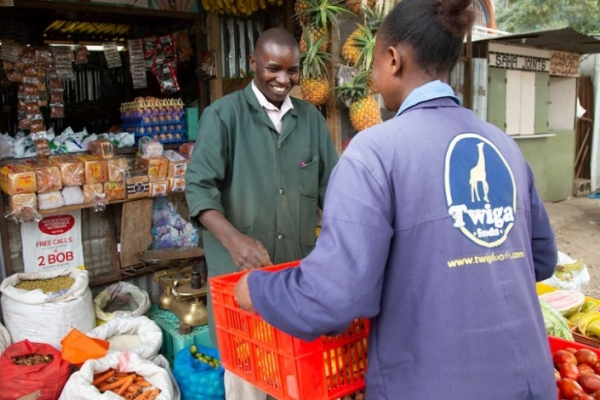
Kenyan platform Twiga Foods, which connects farmers with vendors, recently secured undisclosed funding during a refinancing effort following a KES 40 million debt collection lawsuit.
Investors, including Creadev, Juven, TLcom Capital Partners, and DOB Equity, who participated in Twiga's 2021 $50 million Series C, provided the funding. In a deleted Medium article, CEO Peter Njonjo announced the completion of the restructuring, ensuring suppliers that overdue payments would be settled, reversing Twiga's initial dispute over the debt collection.
Climate change is one of the main issues currently facing the globe. In Rwanda, Ghislain Irakoze is actively engaged in contributing to the fight against that problem by spearheading the collection and recycling of electronic waste.
Ghislain Irakoze (photo) is a Rwandan entrepreneur, activist, and sustainability researcher. As the co-founder and CEO of Wastezon, a green technology company specializing in machine learning-based material tracking solutions, he is dedicated to fostering innovation in support of material circularity.
Ghislain Irakoze, born in Rwanda, has been passionate about waste management since he was a child. After he almost lost his friend in a landslide caused by waste, he decided to do something to help. In 2018, he founded Wastezon with Jacqueline Mukarukundo.
The company developed a namesake digital app that connects consumers, manufacturers, and recyclers to process electronic waste and other materials. Wastezon uses machine learning to identify materials, track them through the supply chain, and facilitate recycling. This helps to create value from waste and reduce environmental impact.
To date, over 500 tons of electronic waste have been exchanged on the app, which has helped to reduce carbon emissions by over 4,100 metric tons. Before launching Wastezon, Ghislain Irakoze and his team launched the “Recycle for the Environment” campaign supported by Samsung Engineering-Korea. They managed to transform over 20 tons of household plastics into useful products.
Ghislain Irakoze holds a bachelor’s degree in business and international commerce from The African Leadership University, which he earned in 2021. He began his professional career in 2018 as a manager of the Circular Economy Club in Kigali. In 2019, he became a researcher at the Youth Think Tank of the Mastercard Foundation. Two years later, in 2021, he joined Global Resilience Partnership as an innovation and scaling consultant. The following year, he became a World Wide Web Foundation Sustainable Access Fellow.
For his impact on climate and sustainability, Ghislain Irakoze has received recognition and awards. He was a finalist in the Innovate4Climate pitch competition organized by the World Bank in 2019 and reached the finals of the Young Champion of the Earth award from the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) in 2020. He is also a finalist for the 2023 Commonwealth Youth Awards.
Melchior Koba
Africa's digital economy is poised to reach a staggering $712 billion by 2050, accounting for 8.5% of the continent's GDP. This prospect justifies the implementation of digital transformation initiatives across Africa, including Côte d’Ivoire which is accelerating its process.
Côte d'Ivoire and the United States are joining forces to foster the growth of the digital economy in both countries. US Ambassador to Côte d'Ivoire Jessica Davis Ba (photo, left) met with Ivorian Minister of Digital Transition and Digitization Kalil Konaté (photo, right) on Thursday, November 23, to discuss this collaboration.
During their meeting, Ambassador Davis Ba reaffirmed the United States' commitment to supporting the Ivorian government in implementing various digital projects. "We are delighted to assist Côte d'Ivoire in building a digital infrastructure that can create jobs for young people and establish Côte d'Ivoire as a model of technological innovation in the minds of Americans," stated the ambassador.
Côte d'Ivoire aspires to become a technology hub, mirroring the aspirations of several African countries, where digital technology serves as a cross-cutting sector driving economic dynamism and job creation. To achieve this goal, the government is collaborating with countries that share similar ambitions for the sector.
The United States was a natural choice given its long-standing position as one of the top five most technologically advanced nations. According to recent trade data released by the US Commerce Department's Bureau of Economic Analysis, the digital economy's share of US GDP increased from 11% in 2005 to 19% in 2022, and digital services exports accounted for 2.5% of GDP last year.
Côte d'Ivoire hopes to gain from the United States' experience to boost its digital economy, which currently contributes around 3% of GDP. The collaboration also aims to provide support for the development of digital infrastructure and services, cybersecurity, and entrepreneurship, among other areas.
Samira Njoya
Tunisian retail tech startup Winshot has announced the successful completion of a funding round for an undisclosed amount. The investment was led by 216 Capital, a venture capital firm based in Tunis. The capital will fuel Winshot's expansion efforts, with a focus on enhancing its technology platform and refining the customer experience for its partnered brands and retail chains.
In recent years, cybersecurity has emerged as a critical concern for African nations. Collaborating with strategic partners, they are embarking on specific cybersecurity initiatives to achieve predetermined goals.
Kenyan authorities welcomed an American delegation led by Ambassador-at-Large for Cyberspace and Digital Policy, Nathaniel C. Fick, to Nairobi on Monday, November 27, according to a press release issued by the US State Department. The visit marked the second U.S.-Kenyan Cyberspace and Digital Dialogue, which aims to bolster the partnership between the two countries in promoting a secure and stable cyberspace.
"U.S. and Kenyan officials discussed a range of topics, which included engagement on cyber and digital capacity building, implementation of the Framework for Responsible State Behavior in Cyberspace, collaboration on combatting cybercrime, promotion of secure and trusted information and communication technology infrastructure, and the advancement of digital freedom," stated the release.
Cybersecurity has become a crucial concern for African nations as they embark on their digital transformation journeys. Kenya, particularly since the inauguration of President William Ruto, has placed digital technology at the heart of its development strategy, fostering partnerships with various entities in the technology sector to support efforts in this domain. In terms of cybersecurity, Kenya holds a strong position, with a national cybersecurity strategy slated for implementation in August 2022 and a national computer incident response team in place. However, Nairobi has yet to ratify the African Union's Malabo Convention on cybersecurity.
Beyond cybersecurity, the two delegations also discussed topics related to achieving Kenya's objectives in the digital economy sector. Notably, Kenya, under President William Ruto, boasts one of the continent's most mature technological ecosystems, alongside South Africa, Egypt, and Nigeria.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
In an effort to streamline the vehicle breakdown experience for car owners, a tech entrepreneur has ventured into the breakdown market, developing a digital solution alongside his team.
Spana is a digital solution developed by a Tanzanian startup. It transforms the automotive landscape in the country by connecting vehicle owners with reliable mechanics and spare parts vendors through a mobile app. Founded in 2023 by Julius Mbungo, Spana addresses the challenges of Tanzania's used car market, which is heavily reliant on the spare parts market, a significant portion of which is unfortunately counterfeit.
“This influx of fake parts results in frequent breakdowns, compelling car owners to incur maintenance costs that are four times higher than necessary,” says Julius Mbungo. Spana wants to change that.
The Spana app, available on both Android and iOS, provides a convenient platform for vehicle owners to access a network of verified garages, mechanics, and spare parts vendors. Users can easily locate nearby service providers, compare prices, and make informed decisions based on their specific needs and preferences.
With an initial focus on Dar es Salaam and Dodoma, Spana has already established a network of approximately 50 garages and 100 mechanics. The startup plans to expand into several African countries in the coming months, with tests already conducted in Namibia and Kenya. Since its launch, the Android version of the Spana app has been downloaded over fifty times.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
To achieve the ambitious goals set out in its digital strategy, Morocco is fostering a collaborative environment that brings all the relevant stakeholders together. It offers a comprehensive suite of programs to entrepreneurs, providing them with the necessary support and enabling them to further develop their innovative ventures and gain access to increased funding opportunities.
On Friday, November 24, the Moroccan Ministry for Digital Transition and Administrative Reform and the Technopark Morocco management company (MITC) signed a partnership agreement on the sidelines of the inauguration of the Essaouira Technopark (the fifth in Morocco). This strategic collaboration aims to establish a comprehensive framework for providing targeted support programs to local startups.
The agreement, championed by Minister for Digital Transition Ghita Mezzour, underscores the government's commitment to fostering a vibrant startup ecosystem in Morocco. "We want to empower young entrepreneurs and project leaders to thrive in the national and international markets," stated Mezzour, expressing her aspiration to nurture a Moroccan unicorn shortly.
As part of this partnership, Essaouira Technopark will offer tailored programs designed to nurture startups throughout their lifecycle. These six-month and twelve-month programs will provide comprehensive support at every stage of development, empowering startups to overcome challenges and achieve their full potential. Over the course of the agreement, an estimated 70 startups will benefit from this specialized training and guidance.
The collaboration between the government and Technopark aligns with their shared vision of leveraging digital technology to drive Morocco's economic growth. The plan is to establish Technoparks in seven regions and increase the number of Technopark cities from four to ten by 2026.
Since its inception in 2001, Technopark has established itself as Morocco's premier technology business incubator. Through its unwavering support, Technopark has nurtured over 3,500 innovative companies, creating more than 15,000 direct and indirect jobs.
Samira Njoya
Cameroonian e-health startup Waspito has completed a $2.5 million funding round, we learn from a LinkedIn post by founder, Jean Lobe Lobe. The funds will finance tech upgrades and expansion into new markets. "We intend to continue expanding in Cameroon and Côte d'Ivoire, and launch our activities in Senegal and Gabon," explained a Waspito executive.
Kenyan fish farming startup AquaRech announced last week the successful completion of a $1.7 million funding round. "The funding and partnership provided by our investors will promote the growth of our mobile-enabled platform, which is unlocking barriers faced by smallholder fish farmers and bringing the various value chain actors together while remaining farmer-centric," explained Dave Okech, who founded the startup in 2019.
In Côte d'Ivoire, this incubator dedicated to streamlining the agricultural value chain provides comprehensive support to agricultural entrepreneurs from the conception phase to the successful implementation of their projects.
Established in 2016 by three entrepreneurs from the Ivorian diaspora and members of the Club d'Affaires Afrique-Monde (CAAM), Incub'Ivoir is a specialized incubator fostering innovative projects in the agricultural sector. It is headed by Hermann Christian Kouassi (photo, right), one of its co-founders.
The incubator was created to inspire, train, structure, and support potential entrepreneurs to become catalysts for change in their communities. It offers a comprehensive six-month incubation program, equipping beneficiaries with the resources necessary to bring their projects to fruition. To date, a total of 82 projects have successfully undergone incubation.
Additionally, Incub'Ivoir provides a three-month acceleration program, granting startups access to mentoring, investors, and other crucial support to help them achieve stability and self-sufficiency. This Acceleration Program currently supports 38 companies.
When a company becomes a part of Incub'Ivoir's support system, it joins a vast network that includes other companies, major groups, institutions, investment funds, public players, and civil society.
Incub'Ivoir has spearheaded various initiatives, including Environnement Startup, a project call caravan endorsed by the Organisation Internationale de la Francophonie (OIF). This initiative provided support to ten project leaders in 2017-2018.
Another initiative, Speed Farmer –an acceleration program for agribusiness and foodtech entrepreneurs supported by the Netherlands– empowered ten entrepreneurs to enhance their skills in business management and product development in 2019.
With its diligent efforts, Incub'Ivoir has made a positive impact on the Ivorian entrepreneurial ecosystem, supporting over 120 structures and collaborating with 34 partners.
Melchior Koba
More...
Having observed the profound effect a small gesture can have on individuals living in rural Africa, the young Guinean residing in London decided to set up a platform, empowering diaspora members like himself to send airtime directly to their loved ones
Ibrahima Soumano (photo), a Guinean entrepreneur based in London and a graduate of Oxford Brookes University with a bachelor's degree in business administration, management, and operations (2005), serves as the co-founder and CEO of Senditoo. Originally known as Ozaremit, his platform was developed through collaborative efforts with his friend Takwana Tyranini. It primarily enables members of the diaspora to send airtime to their loved ones in their home countries.
The entrepreneur came up with the Ozaremit idea during a visit to his home country, Guinea, where he witnessed the profound impact even a simple gift like airtime could have on the local population.
Senditoo's services are characterized by their simplicity, speed, and accessibility through both a website and a mobile application. Users can effortlessly input the recipient's phone number, select the desired top-up amount, and make secure online payments. The chosen top-up amount is promptly delivered to the recipient's phone, confirmed via SMS.
Operating in over 140 countries globally, including 39 in Africa, Senditoo has expanded its services since 2020 to allow the diaspora to directly deposit money into mobile money accounts in Ghana, Guinea, Uganda, Cameroon, Côte d'Ivoire, Mozambique, Zambia, DR Congo, Zimbabwe, and Senegal. Additionally, the platform facilitates the payment of electricity bills for relatives residing in Zimbabwe.
In 2012, Ibrahima Soumano also founded Tafory, an Internet real estate search platform in Guinea. He served as the company's manager until 2016, the year Senditoo was founded.
Melchior Koba
Onix Data Centres aims to establish a pan-African data center network, beginning with West Africa, to address the burgeoning demand for digital services on the continent. To achieve this goal, the company is actively expanding its collaborative partnerships.
Ghanaian data center operator Onix Data Centres Ltd recently announced its integration into the Angola Cables network through its West African subsidiary TelCables. The initiative aims to improve international connectivity in Ghana and Senegal, two countries that host the operator’s data centers.
"Our intent has been to develop a reliable facility that can accommodate and deliver secure services to hyperscalers and carriers supporting terrestrial networks as well as existing and new subsea cables planned for the region," said Onix CEO, Michael Nahon.
In Ghana, Onix’s 2,000-square-meter data center currently serves major banking and financial customers. It currently has 3 kW and 5 kW racks and a dedicated pod of 50 racks for individual customers wishing to share infrastructure and reduce costs.
By connecting to Angola Cables, Onix will be able to offer its customers a variety of secure digital solutions and managed services thanks to the network’s state-of-the-art facilities comprising, among other things, 66 new data centers and 21 IXPs (Internet Exchange points).
The aim is to meet the needs of a wide range of customers who require secure storage and management of their digital assets and data. The partnership is part of Onix's commitment to providing neutral colocation services and high-quality connectivity in West Africa, as demand for digital services continues to grow in the region. In January, the company launched its second data center in Dakar, Senegal.
Meanwhile, Fernando Fernandes, CEO of TelCables Nigeria and West Africa, believes that “Partners like Onix are playing a vital role in developing the infrastructure necessary to expand digital services and provide the platform for ISPs, CDNs and other enterprises contributing to the explosive growth in data traffic, cloud services, and content distribution across the African continent.”
Samira Njoya
On the African continent where value-added digital services are getting appealing by the day, telecom operators are adapting their strategies to remain competitive. In that context, Orange is multiplying innovations, in line with its “Lead the Future” vision, to meet subscribers’ needs.
Earlier today, November 24, Orange Middle East and Africa (OMEA) announced the launch of Max it, its super app. Currently, the app is available in five African countries, namely Cameroon, Senegal, Mali, Burkina Faso, and Botswana. It will be gradually rolled out with functional updates in the twelve other countries that make up Orange’s market in the Middle East-Africa zone.
According to Orange CEO Christel Heydemann, "Max it perfectly reflects Orange’s spirit of innovation in Africa and the Middle East. By bringing together all our services and those of numerous partners, this application strengthens our position as a multi-service operator and our desire to offer the best of digital services to all our customers."
The digital solution aggregates three essential service offerings into a unified smartphone interface. Orange customers can seamlessly manage their mobile or fixed lines, and access a wide range of local and international financial services including money transfers, merchant payments, bank transfers, credit, and savings. Additionally, users can access diverse digital content such as online games, music, TV, videos, news, and more through an inclusive marketplace. The interface even facilitates the purchase of tickets for events like concerts and transportation services.
“Max it is accessible to all, regardless of operator, with Orange Money as the payment base, while accepting other solutions for paying for purchases via the super-app. Available in different languages and integrating local specificities for greater inclusion, Max it will enable the development of new uses while meeting the different needs of its users' daily lives,” Orange indicates in a release.
In sub-Saharan Africa, the mobile phone is the main gateway to the digital world. With a current smartphone adoption rate of 51%, projected to reach 87% by 2030, Orange is poised to capitalize on this potential by expanding its reach through its app over the next seven years. Aiming to connect with a wider audience, Orange has set a target of registering nearly 45 million active Max it users by 2025, building upon its existing base of 32 million monthly Orange Money users.
Digital transformation is now recognized as a driving force for growth across diverse sectors of the economy. Notably, the United Nations advocates for its role in accomplishing the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
At its 2023 Sustainability Forum held on November 21 in Dongguan, China, under the theme "Thrive Together with Tech: Realizing Sustainable Development", Huawei unveiled a fellowship program in collaboration with the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). This initiative targets young innovators between the ages of 18 and 28 worldwide who have impactful digital projects that empower community development.
Called the "The ITU Generation Connect Young Leadership Programme in Partnership with Huawei," the fellowship will open for applications early next year and run for three years. The 30 young people selected will be supported in carrying out their projects. This is an expression of the Chinese technology company's firm belief in the catalytic effect of digital talent in future technological innovation.
Jeff Wang, President of Huawei's Public Affairs and Communications Department, explains: “The support that participants will receive includes financial contributions to their projects, mentoring from ITU and Huawei experts, and opportunities to participate in joint events.”
The fellowship introduced by Huawei and ITU marks a significant development in the ongoing collaboration between the two entities, which commenced last year with the establishment of the Partner2Connect Digital Coalition (P2C). P2C is a program dedicated to advancing global connectivity and digital transformation, with a special emphasis on underserved communities in regions and countries facing digital accessibility challenges. As part of its commitment to this initiative, Huawei has pledged to extend connectivity to approximately 120 million individuals residing in these underserved regions across over 80 countries by 2025. Notably, the company reports that it has already made significant strides, reaching 90 million people as of now.
"Digital is a prerequisite for accelerating the achievement of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. We want the youth to push the envelope on the evolving global digital ecosystem and make their transformative contributions," said Dr. Cosmas Luckyson Zavazava, Director of ITU’s Telecommunication Development Bureau.