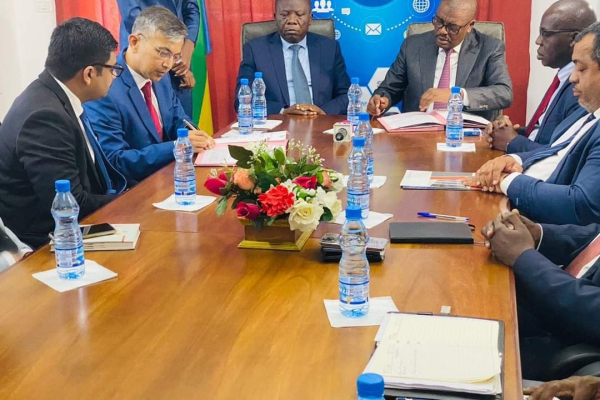
In 2021, Gabon started a three-year acceleration plan for economic transformation. This comprises several priority projects including the construction of a national datacenter to store all administrative data.
Last Thursday, June 29, Gabon's Minister of Digital Economy, Jean Pierre Doukaga Kassa, and the CEO of the Indian company Shapoorji-Pallonji, Ransit Gajave, signed a memorandum of understanding for the construction of a national data center in Gabon.
The Ministry of Digital Economy said on social media that the project is a high-priority one. Thus, “he instructed the general manager of the Digital Heritage and Infrastructure Company (SPIN) to sign the memorandum with Shapoorji-Pallonji, which holds a leading position in India for data center construction.”
Before the MoU’s signing, a delegation from the Indian contractor was in Gabon last March. At the time, the Asian firm said it wanted to help the African country design, build, and maintain its digital infrastructures, including data centers.
The national data center is extremely important for the Gabonese government and that is why the minister of digital economy quickly sealed the deal with Shapoorji-Pallonji. The official was well aware of the firm’s experience and achievements in Africa, including Egypt, Ghana, and the Democratic Republic of Congo.
Building the infrastructure, according to Doukaga Kassa, aligns with Gabonese authorities' ambition to make Gabon a digital hub in the Central African sub-region.
Samira Njoya
The adoption of technology in all government transactions is emerging as the solution to the bottlenecks caused by corrupt officials who divert government revenues from their intended destination in Africa's public sector.
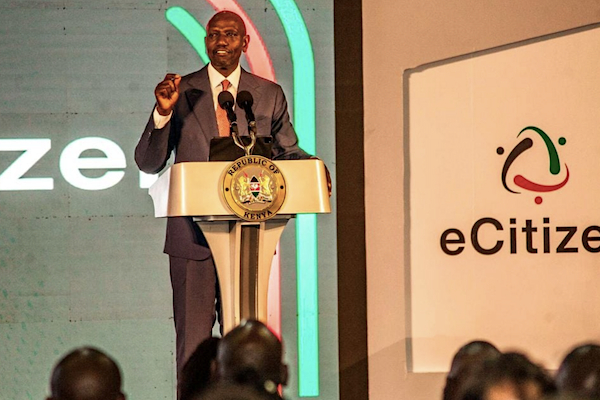
The Kenyan government launched the e-Citizen Portal, on June 30, providing citizens with access to over 5,000 government services. This digitalization initiative aims to streamline processes, foster transparency, and minimize corruption.
Under President Ruto's leadership, all ministries, departments, and agencies have digitized their services for the portal. The platform also offers easy access to essential healthcare services, revolutionizing healthcare delivery.
President Ruto announced that citizens can access the services through the e-Citizen platform's USSD code *2222# as well as Gava Express, an offline government service in collaboration with banks and fintechs.
“Gava Express will be available in more than 250,000 M-Pesa shops, 28,000 KCB shops, 40,000 Equity shops, and 22,000 Cooperative Bank shops to serve those without smartphones,” he said
The e-Citizen Portal enables citizens to own and manage their health records and engage in interactive sessions. According to the President, the system eradicates inherent inefficiency, corruption, wastage, and discrimination present in human interactions.
With the e-Citizen Portal, Kenya embraces technology for efficient public service delivery, transparency, and citizen empowerment. The government's vision of a digitized and inclusive future becomes a reality.
Hikmatu Bilali
The Democratic Republic of the Congo, like many other African countries, has a huge potential for tourism. Here, we take a look at a startup that showcases this potential, both to members of the Congolese diaspora and foreigners.
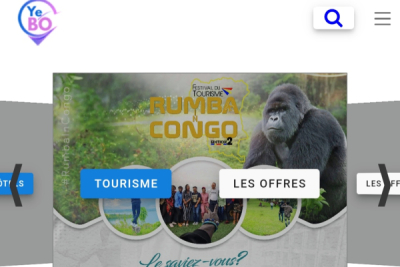
Yebo is a digital solution that enables users, mainly foreigners and members of the African diaspora, to visit the Democratic Republic of Congo on tailor-made tourist tours. The platform was developed by a Congolese startup, founded by Nelson Badibangi in 2021.
According to its developers, "Yebo is an innovative solution that brings together all tour operators in one place with the best tourism service offers, to make it closer to local and international consumers."
Users can access Yebo’s services via mobile, through a dedicated app. All they need to do is register and explore available offers. It is possible to choose a tour, based on one’s tastes and means. There is also a search bar which helps filter tours, based on users' preferences.
With Yebo, tourists do not have to go through any hassle. Transportation during the trip, short-stay accommodation, sightseeing and visits to private parks and/or tourist sites; the solution takes care of everything. The startup also assists with the administrative procedures necessary to obtain a visa. Users can access the Congolese embassy website from the Yebo platform.
At present, the startup offers over 52 tourist circuits. During the Canadian week in Kinshasa in June 2023, it won a prize for its great impact on cooperation between Canada and the Democratic Republic of Congo.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
ICT plays a central role in the digital transformation that is a priority for many governments worldwide. To accelerate the realization of their digital ambitions, countries are exploring avenues for collaboration.
The Angolan government announced on June 27 the start of tests on a fiber optic connection with Zambia. The Minister of Telecommunications, Information Technology, and Social Communication, Mário Oliveira (pictured), told the press about the tests during the visit of a parliamentary delegation from the Southern African Development Community (SADC).
According to the minister, the tests align with Angola's objective of becoming a telecom hub. A few days before the tests began, the two nations signed a memorandum of understanding to boost their cooperation in the field of fiber optics and space technology.
In this context, the minister stated that the country will provide satellite services to Zambia and South Africa in the coming months, specifically in the areas of agriculture, migration control, infrastructure, and the environment.
To achieve these goals, the minister called on financial partners who could support the strengthening of cooperation. "Without money, nothing can be done, but with the support of all, we can create robust systems for the continent and the world," said Mário Oliveira.
The new fiber optic connection will promote digital inclusion by improving traffic in the region and reducing the costs of accessing high-speed Internet in both countries. These efforts reflect the gradual progress the country is making in achieving its telecommunications objectives and promoting regional connectivity.
Samira Njoya
South Africa has one of the most advanced technology ecosystems in Africa. The country has numerous tech entities, including startups, incubators, and accelerators. Among them is Start with Seven (Sw7).
Start with Seven (Sw7) is Africa's first virtual acceleration platform for B2B. It brings together B2B tech founders, CEOs, COOs, CFOs, mentors, and investors.
Founded in 2014 by Odette and Keith Jones (CEO), Sw7 provides strategic guidance to pre-seed to Series B startups and funded companies. This South African platform also offers a comprehensive set of guidelines, resources, information, and expertise developed by and with founders, CEOs, mentors, and venture capital firms to boards of companies.
The support is delivered to business managers and entrepreneurs through tailored digital workshops, community calls, and 24/7 access to online resources and content. The platform's guidance extends throughout the fundraising journey. It provides insights on establishing and scaling offshore operations, as well as expanding into the United Kingdom, the United States, or other African markets.
"We combine private one-on-one workshops, advisory, and mentoring sessions on priority areas with peer learning and knowledge-sharing that take place in our private roundtables, group webinars, and on our platform," the platform indicates.
Sw7 collaborates with various technology partners, including Amazon Web Services, HubSpot, Intercom, Miro, and Twilio. These partners offer several advantages, ranging from training and technical support to scaling assistance and enhanced market access.
Melchior Koba
After spending several years in the US, Afery Johnson (picture on the left) returned home to Togo, and set up his transport startup.
Lomé Taxi is a ride-sharing solution developed by a young Togolese company. It allows customers heading in the same direction to share transportation costs. Through this solution, users can travel around the city in cars at affordable rates. Already, the startup operates in 11 designated zones within the urban area of Lomé.
"The carpooling concept at Lomé Taxi emerged from the need to lower transportation costs for our customers. Faced with the repetitive rise in fuel prices, we had to increase our fares, and we noticed a decline in the use of our services due to the high cost of living. Through careful consideration, we found a solution that would allow our customers to continue using our services affordably," said Afery Johnson, founder of Lomé Taxi.
The solution does not require a mobile application. Users can easily access it through a web browser. To do so, they only need to provide information such as the departure date, departure time, departure neighborhood, destination, phone number, email address, and the number of passengers. The last piece of information is necessary to notify the start-up that you are open to sharing your ride with another person.
Besides the web platform, reservations can also be made through social media platforms like WhatsApp. SMS and direct calls are also available methods for contacting the start-up to make a reservation.
Lomé Taxi boasts a fleet of over 25 cars and operates from five offices across the Togolese capital. The fare for a trip downtown is CFA2,000, and CFA3,000 for trips to peripheral areas. The startup also offers a special service for people visiting the country.
"The driver picks them up from the airport to their place of residence. For those who no longer want to rent expensive cars during their stay, the company owner provides his car fleet at very affordable rates, tailored to their schedule," according to the platform.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
The evolving digital landscape in Africa is creating opportunities for governments to generate revenues for the development of their countries. These changes highlight the commitment of governments to keeping pace with the rapid growth of the digital economy.
On Monday, June 26, President Ruto signed Kenya’s Finance Bill 2023 into law. This new law brings significant changes to the digital economy, affecting digital content creators, crypto traders, and digital lenders. Effective July 1, 2023, the bill introduces new tax implications and regulations.
Digital content creators will now be taxed on their earnings from digital content, with a 1.5% withholding tax applied to their income. This expansion aims to include various forms of electronically offered content, such as advertisements, sponsorships, subscriptions, and merchandise sales, within the scope of taxation.
Crypto traders face the introduction of a digital asset tax (DAT) on earnings obtained from the transfer or trade of digital assets, including cryptocurrencies and Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs). Platform owners will deduct 3% of the digital asset's value, with non-resident owners required to remit the tax within 24 hours after deduction. The short period for deductions and the taxation of turnover rather than gains may pose challenges for crypto traders.
The bill also broadens the definition of 'fees' to cover charges associated with lending activities by digital lenders. This means that all costs linked to digital lending transactions, including fees charged by digital lending apps, will be subject to excisable duty. Consequently, borrowing from digital lending platforms may become more expensive.
Kenya's Finance Bill 2023 represents the country's adaptation to the evolving digital landscape, aiming to capture revenue and ensure fairness. Industry players must adjust their practices and business models accordingly to comply with the new regulations.
Digital Service Tax (DST) is a tax imposed on income generated from services offered through a digital marketplace (a platform facilitating electronic interactions between buyers and sellers). It was introduced in the Finance Act 2020. The rate of DST is 1.5% of the gross transaction value, which includes payments received for digital services and commissions or fees paid to digital marketplace providers for platform usage.
These changes highlight Kenya's commitment to keeping pace with the rapid growth of the digital economy and aligning its regulatory framework with global trends.
Hikmatu Bilali
To bolster access to financial services in Africa, which remains weak, fintech companies have been developing various solutions that fit the African market, and answer the needs of its people.
Two weeks ago, Syca SAS, an Ivorian tech startup launched in 2015, joined the incubation and acceleration program of Scaleway, a cloud infrastructure services provider. The startup was selected with its first module, SycaPay, which launched in 2016.
"This collaboration provides us with an excellent opportunity to accelerate our development and strengthen our position in the market. We look forward to working closely with the Scaleway team and benefiting from their expertise and resources to continue providing innovative solutions to our customers," Mouhamadou Diop, CEO of SycaPay, said.
SycaPay is a fintech solution developed by the startup. It helps companies receive payments from their customers via mobile money, QR codes, and Visa and MasterCard bank cards. The mobile app is available on both iOS and Android.
After downloading the app, businesses must create an account providing the necessary information. Afterward, they can get payments and track their inflows and outflows from their dashboard.
For e-commerce operations, SycaPay offers an application programming interface (API) integration option. "Integrated into an e-commerce website, SycaPay allows merchants to accept mobile money payments without needing an account with every operator," as stated on the platform.
The Android version of the mobile application has been downloaded over 1,000 times. While currently available only in Ivory Coast and Senegal, the fintech company is working towards covering all UEMOA and CEMAC markets.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
He founded a company that digitizes the transportation sector and connects freight shippers and carriers. Backed by several investors, the company collaborates with major transport companies.
Moustapha Ndoye (see picture) is a Senegalese computer scientist and graduate of the Georgia Institute of Technology. With Alioune Ndoye, he co-founded Chargel, a logistics technology startup created in 2021. The company's mission is to make road transport more efficient, reliable, and transparent.
The startup helps carriers find freight at any time via its platform. This helps the users avoid empty trips while enjoying prompt payments. In addition, it offers value-added services such as the supply of GPS trackers, assistance in purchasing fuel at discounted rates, and support for repairs in case of breakdown.
With his startup, Moustapha Ndoye, its CEO, hopes to build the largest network of road freight transport in French-speaking West Africa. This will facilitate shippers' access to thousands of trucks at the best prices.
In April 2023, the company successfully raised $2.5 million to expand its operations in Senegal and neighboring countries such as Mali, Guinea, and Mauritania. Chargel has recently been selected for the Google for Startups Black Founders Fund and was ranked among the top 20 African startups to watch in 2023 by Jeune Afrique magazine.
Since its launch, Chargel has entered partnerships with several global giants, including Maersk and Grimaldi. In 2022, the company recorded a gross merchandise volume of $1.2 million.
Before starting Chargel, Moustapha Ndoye was the CEO of Xtreme Design and Engineering - an iOS mobile application development company, from 2009 to 2018. In 2013, he co-founded Teranga Solutions, a company that provides an outstanding hotel experience by leveraging mobile and cloud technologies.
After serving as CEO of Teranga Solutions, he became the Chief Operating Officer of HotelOnline in 2018. In 2020, he joined Wave Mobile Money as Director of Products until the launch of Chargel the following year.
Melchior Koba
African governments are embracing technology to revolutionize healthcare and enhance living standards.
Fujifilm South Africa and Uni Medical Supplies are collaborating to enhance healthcare in Namibia through the implementation of Fujifilm's advanced Synapse Radiology Information System (RIS) and Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS) platforms. This deployment is the country's largest and has transformative potential for healthcare services.
The project, launched Tuesday, June 27 connects geographically distant hospitals, including Katutura State, Onandjokwe State, Oshakati State, Rundu Intermediate, and Windhoek Central Hospitals, through the innovative Synapse RIS/PACS system.
Taro Kawano, Managing Director of Fujifilm South Africa, expressed optimism about the platform's impact on Namibian citizens' health. “We thank the Namibian Ministry of Health and Social Services for seeing the value of this platform and the benefits it holds for the country’s healthcare system,” he said.
The Synapse RIS/PACS system efficiently manages radiological information, streamlining appointment scheduling and reporting. Doctors can remotely access and diagnose patients using digital storage of imagery, such as CT scans and X-rays, on the PACS system. Additionally, four out of five hospitals have implemented Fujifilm's cutting-edge REiLI artificial intelligence (AI) platform, which provides advanced detection capabilities for breast and chest abnormalities, assisting radiologists in conducting further examinations.
The immediate availability of data and imagery enables accurate and timely diagnoses, eliminating distance barriers for healthcare services in remote areas. Fujifilm's Synapse RIS and PACS platforms have a successful track record globally.
In that light, Namibia's healthcare system is set to undergo a remarkable transformation with this project. The collaboration between Fujifilm South Africa and Uni Medical Supplies promises improved healthcare services, enhanced patient care, and a more connected healthcare network throughout the country.
Uni Medical Supplies, a Namibian-owned company, delivers affordable, high-quality medical products directly to customers while prioritizing customer satisfaction and ethical business practices. Meanwhile, FUJIFILM South Africa (Pty) Ltd, a subsidiary of FUJIFILM Holdings Corporation, serves the Sub-Saharan region with a diverse range of award-winning products, including Photographic Film and Paper, Film and Digital Cameras, Photofinishing Products, Healthcare Systems, Graphic Systems, and Data Management Systems.
Hikmatu Bilali
More...
The rapid advancements in technology, surging data consumption, and the deployment of 4G and 5G networks in Africa intensify the need for telecom infrastructures. In response, the government and international partners are working diligently to address these needs within the digital transformation landscape.
The International Finance Corporation (IFC) loaned $60 million to telecom tower manager Eastcastle Infrastructure. This was made public in a press release issued on Monday, June 26. The funds will be used to enhance digital connectivity in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), one of the least connected countries in Sub-Saharan Africa.
News Release 📢 Trigon Granted Permits to Highly Prospective High-Grade Silver Lead Ground in Morocco – Addana Project
— Trigon Metals (@trigonmetals) June 28, 2023
View it here: https://t.co/pxDYTjCtHz
Watch the full video: https://t.co/8LbSNk2Ql3$TM.V | $PNTZF pic.twitter.com/ktIHtJ2u25
Expressing his satisfaction with the IFC's investment, Peter Lewis, Co-founder and Director of Eastcastle Infrastructure Ltd., said: "We are delighted that following their equity investment in Eastcastle, the IFC has made $60 million in long-term financing available to our operations in the DRC. Together with the $34 million from Standard Bank of South Africa, this will enable us to surpass 1,000 towers in the DRC."
According to the release, the funding includes $30 million from IFC and an additional $30 million mobilized from the Emerging Africa Infrastructure Fund (EAIF). This is in line with Eastcastle's strategy to construct a maximum number of shared towers in the DRC. The main goal is to promote the digital economy in the region.
Back in 2021, the IFC had provided financing to support Eastcastle’s growth plans in Sub-Saharan Africa. Now with the new financing, the company will be able to lease its new towers to mobile network operators and other digital service providers in the DRC, thus helping expand their coverage, reduce operating costs, and minimize energy consumption through infrastructure sharing.
It is worth noting that the DRC has 48.4 million mobile phone subscribers. According to the latest data from the Regulatory Authority for Post and Telecommunications of Congo (ARPTC), the rate of penetration is 50.9%. However, the number of mobile internet users stands at 22.6 million, with a penetration rate of 23.8%. The expansion of Eastcastle's telecom towers network will improve the quality and coverage of telecom services in the country.
Samira Njoya
Kenya has introduced its digital sex offender registry as part of ongoing digitization efforts across all sectors, including the justice system. By doing so, the government aims to significantly reduce sexual assaults on women and children and facilitate the identification of perpetrators.
On Monday 26, Martha Koome, the Chief Justice of Kenya, unveiled the country's first digital sex offender registry at the Kibera Law Courts. The registry comprises a comprehensive database containing crucial information about convicted sex offenders.
11. The Register, established under the Sexual Offences Act, serves as a crucial database, holding the records of all convicted offenders. By automating this Register, we will ensure easy access to information on convicted sex offenders, facilitating expedited justice. pic.twitter.com/OW7FArbZvC
— Hon. Justice Martha K. Koome, EGH (@CJMarthaKoome) June 26, 2023
During this ceremony, she stated: "The implementation of the automated registry is a vital tool for protecting the public from sex offenders. By providing accessible information, we empower individuals to take necessary precautions and create an environment that discourages such offenses."
In recent years, Kenya faced an upsurge in sexual offenses. This created so many challenges to the safety and well-being of its citizens. The digital registry will bolster government efforts against this menace.
Before this action, the government took some measures to fight sexual offenses in Kenya. In 2008 for example, Legal Notice No. 133, supplementing the Sexual Offenses Act, mandated the director of the Criminal Investigations Department to establish a DNA database of dangerous sex offenders.
This digital tool will be useful for key stakeholders in Kenya's justice system in tracking and monitoring sex offenders after their release from prison. It will also help the public to access information about sex offenders residing in their neighborhoods. Thus, they can take precautionary measures to protect themselves and their children.
Through this, Kenya joins other countries that have implemented sex offender registries. In 2007, South Africa established a similar registry. Unfortunately, it is kept confidential and not open to the public.
Samira Njoya
He is a tech entrepreneur with two successful companies in Liberia. Thanks to his solution My Watchman, he was celebrated at the Global Startup Awards as West Africa's Founder of the Year 2023.
Oliver Wleh Klark (photo) is a Liberian entrepreneur who graduated from Hamline University School of Business in 2012 with a Master's in International Conflict Management. Recently, at the Global Startup Awards, he received the 2023 West Africa Founder of the Year award for his tech solution My Watchman.
“This award is a win for Liberia because it gives the country the platform to showcase innovations and different technologies, developed locally, which can be scaled across the continent. So, we are proud to have won this, but more importantly for us, we think this is a big win for all Liberians,” he said after receiving the award.
The solution that earned him the award is a full-service emergency app, with an around-the-clock emergency response network and an emergency dispatch command center. It's a smarter, safer way to protect family and property, with access to help anywhere, anytime. As the winner of this award in the West African zone, My Watchman and Oliver Wleh Klark will represent the whole zone at the grand final where the continental founder of the year will be named.
The solution is a registered trademark of technology company Advanced Converged Technologies LLC, founded and currently headed by Oliver Wleh Klark. The entrepreneur is also the CEO and one of the co-founders of RoviaGate Technology, a Liberia-based information and communication technology (ICT) company offering integrated smart data-centric solutions.
Melchior Koba
Africa's youth-dominated population presents a prime opportunity for the continent to emerge as a digital hub. Governments are actively tapping into this valuable resource to drive progress and foster economic development.
Nigeria's Vice President, Kashim Shettima, unveiled on Monday June 26, a plan to generate one million digital jobs for the youth. During talks with a Korean delegation led by Special Envoy Jang Sungmin (photo), he stressed the importance of strategic collaborations to achieve this objective.
Reaffirming Nigeria's commitment to bolstering ties with Korea, Shettima highlighted the potential for learning from Korea's successes in manufacturing and agriculture. The Vice President also pointed out that with 75% of Nigerians under the age of 35, Nigeria sees an opportunity to address global talent deficits, while also emphasizing the need for Korea's assistance in digital skills training and technology support. “We need the skills set, we need the technology to drive the process and yours is a technology that we can embrace,” he said.
The Nigerian government, focusing on security and economic development, expressed its commitment to supporting Korean businesses operating in the country and creating a favorable business environment for foreign investors.
The partnership between Nigeria and Korea in skills training and technology support is expected to play a crucial role in achieving the government's target of one million digital jobs. This collaboration opens doors not only to addressing talent shortages but also to Nigeria's integration into the global digital landscape.
According to the "Africa's Development Dynamics 2022: Regional Value Chains for a Sustainable Recovery" report by the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, “Africa's thriving digital sector presents an opportunity for governments to drive post-COVID-19 growth. By promoting the adoption of digital technologies, and data sharing [… ], African countries can expedite economic transformation and generate productive employment, aligning with the African Union Agenda 2063 aspirations.”
Hikmatu Bilali