Last December, William Ruto paid a three-day visit to India. Several partnerships were forged between the two countries, including one in the technology sector.
The Indian government has approved a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with Kenya, aimed at sharing digital solutions for large-scale digital transformation, according to a statement released on Thursday. The MoU, which was signed on December 5, will be effective for three years from the date of signature.
The agreement seeks to foster closer cooperation and exchange of digital technology-based experiences and solutions to drive digital transformation initiatives in both nations.
Kenyan President William Ruto (photo, left), who visited India in December, signed several MoUs, including the one approved, with the Indian government led by Prime Minister Narendra Modi (photo, right). Ruto is keen on leveraging the digital sector as the driving force of Kenya's economy and is actively seeking partnerships to this end.
Kenya, with its mature technological ecosystem, is a major attraction for investors on the continent. A report by CB Insights, published last January 4, projected that Kenyan start-ups would have raised approximately $228 million by 2023.
It's worth noting that several African nations, including Sierra Leone, Gabon, Mauritius, and Nigeria, have sought India's technological expertise and have entered into partnerships with the country.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
As Africa sees booming e-commerce, innovations in last-mile delivery are revving up efficiency, tightening transaction security, and slashing risks, playing a key role in the continent's economic ascent.
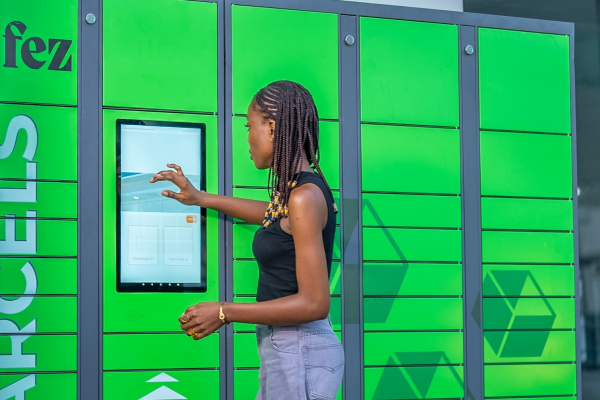
Nigerian logistics startup Fez Delivery is reshaping last-mile delivery with the introduction of Fez Safe Lockers. Launched on January 10, at the Ardova Plc filling station on Admiralty Way in Lagos, Fez Safe Lockers directly address challenges associated with the prevalent cash-on-delivery model in Nigeria.
Strategically positioned in high-footfall areas like filling stations, the Fez Safe Lockers offer seamless package drop-offs and pickups, functioning for a nominal fee of ₦999. User-friendly touchscreens and unique access codes simplify the package drop-off and retrieval process, improving the overall customer experience. Real-time monitoring, CCTV surveillance, and secure locations ensure the safety of packages, addressing concerns related to theft or loss.
Seun Alley, CEO and co-founder of Fez Delivery, emphasized the company's vision, stating, "At Fez, we're delivering a revolution. Fez Safe Lockers are more than just lockers; they're an investment in Nigeria's future. By modernizing logistics and promoting sustainability, we're building a delivery ecosystem that benefits everyone."
Fez Delivery's strategic evolution aligns with an industry shift towards innovative last-mile delivery solutions, marking a significant step forward in transforming Nigeria's logistics landscape.
Hikmatu Bilali
With the technology revolution quickly advancing across Africa, there is a growing number of startup support structures fueling that advance. Team@Solutions, a Cameroon-based incubator, is one of those structures.
Cameroon-based incubator Team@Solutions, specializing in new information and communication technologies (NICT), is a product of a partnership between German organization Brücke e.V and the International Association for Development and the Environment in the 21st Century (AIDE21). The organization, led by coordinator Touna Onguene Philippe, supports startups by providing a nurturing environment and professional guidance, aiding entrepreneurs in digitalizing their structures.
Team@Solutions operates in various sectors including trade, services, industry, agriculture, livestock, health, logistics, education, good governance, infrastructure, and renewable energies. It designs and implements IoT, big data, AI, and cloud solutions tailored to the African context. It has also established production and processing units to encourage local production and processing of raw materials, including agricultural products.
The incubator promotes cooperation, exchange, and knowledge sharing, offering coworking spaces, certified training courses in NICT and mechanical engineering technologies, and job opportunities in Germany for IT developers and mechanical engineers.
Supported by the German international development cooperation agency, GIZ, Team@Solutions has assisted several startups such as Health Map, which has established a hospital IT system to facilitate patient care, E-Gadget & IO-Tech, a builder of electronic equipment with AI and IoT capabilities, and Katika, a fintech firm.
Melchior Koba
In a move to widen cryptocurrency accessibility in Africa, leading platforms Coinbase and Yellow Card have announced a strategic partnership. This collaboration aims to simplify access to USDC, a stablecoin pegged to the US dollar, and other digital assets across the continent.
Through the partnership, Coinbase has integrated the Yellow Card Widget within its Wallet app. This integration grants Coinbase Wallet users seamless access to Yellow Card's extensive network of payment methods for buying and selling digital assets. The network reportedly spans 20 African countries, significantly facilitating crypto transactions in the region.
The Africa Stablecoin Consortium (ASC), a coalition of Nigerian banks and fintechs, announced it has postponed the launch of its cNGN stablecoin, originally slated for February 27.
"...We are engaging with the appropriate regulatory bodies, including the Central Bank of Nigeria, to participate in its regulatory sandbox program. Our goal is to showcase the potential benefits of the cNGN ecosystem, providing a secure, transparent, interoperable, and innovative solution for digital asset transactions in Nigeria," the ASC said in a statement.
Confronted with the challenge of high international export costs faced by African firms, Matthew Davey established TUNL as a solution.
South African entrepreneur Matthew Davey (photo), a University of Cape Town Civil Engineering graduate and Oxford University Geography and Environment PhD holder, is the co-founder of startup TUNL. Established in 2020 by Davey and COO Craig Lowman, TUNL aims to address export challenges for African manufacturers, designers, and retailers. The platform provides express courier options with global carriers to nearly all countries and has introduced TUNL Economy, a cost-effective export courier service from Africa.
Davey stated in December 2023 that cross-border shipping in Africa leads to an estimated annual business loss of $50 billion. Despite the presence of major carriers, high-quality products like textiles and camera accessories can be priced out of the market due to steep shipping costs. TUNL partners with these carriers, such as UPS and FedEx, to negotiate favorable rates and offer significant savings to merchants, with SMEs saving up to 50-75%.
In December 2023, TUNL secured $1 million in pre-seed financing from investors including Founders Factory, Digital Africa Ventures, E4E Africa, and Jozi Angels. This funding will facilitate the company's continued expansion in South Africa and preparation for entry into other African and emerging markets.
Before founding TUNL, Davey worked as a civil engineer for Jones & Wagener, a specialist engineering and scientific consultancy in South Africa, between 2013 and 2014. He served as an analyst with Sustainia, a consulting firm for companies and organizations, from January to June 2017. From August of the same year to February 2021, he was the managing director of Vesconite Bearings, a polymer bushings and wear materials manufacturer.
Melchior Koba
Morocco has stepped up efforts to modernize its government services through digitalization, launching several initiatives aimed at increasing service efficiency and promoting citizen participation through online channels.
Morocco has digitized over 600 public services, with a focus on improving access for citizens and businesses, Digital Transition and Administrative Reform Minister Ghita Mezzour (photo) announced on Monday.
Of the digitized services, 300 are dedicated to citizens, 200 to businesses, and 100 to public administrations, Mezzour told the House of Representatives. She emphasized the government's commitment to completing ongoing digital projects encompassing public service management, administrative reform, online content regulation, and support for emerging businesses, all part of the national digital strategy.
Morocco's new digital strategy, "Maroc Digital 2030," currently undergoing approval, is built on two pillars: complete digitization of public services and stimulating the digital economy. It aims to create 300,000 jobs and contribute $17 billion (170 billion dirhams) to GDP by 2030.
To achieve these goals, the strategy proposes a range of initiatives, including labeling 3,000 startups, a significant increase from the 380 registered in 2022 ; qualifying 45,000 digital talents annually ; retraining 50,000 young people in digital professions and attracting 6,000 foreign digital talents each year.
With full service digitization, Morocco aims to climb from its current 113th position to the top 50 in the UN e-governance rankings. The country aspires to be a major player in the digital economy, driving job creation, economic growth, and improving citizens' lives through accessible and innovative public services.
Samira Njoya
The Meltwater Entrepreneurial School of Technology (MEST) has launched applications for its 12-month training program aimed at helping aspiring tech entrepreneurs in Africa turn their ideas into successful startups. The deadline for applications is March 18, 2024. More details about the program and the application process can be found here.
With a goal to democratize investment in Africa, an innovative entrepreneur has integrated finance and technology to ease access to African markets.
Cameroonian tech entrepreneur Boum III Jr (photo), co-founder and CEO of fintech startup Daba, is on a mission to democratize investment in Africa. A graduate of Southern Polytechnic State University with a bachelor’s degree in computer science, Boum III Jr earned an MBA from HEC Paris and an entrepreneurship-focused MBA from The University of Chicago Booth School of Business in 2021.
Daba, established in 2021 by Boum III Jr and Anthony Miclet, provides a unified investment platform aimed at facilitating high-quality investments in Africa for individuals and companies. With offices in the USA and Côte d’Ivoire, the company offers a more transparent, accessible, and efficient investment process.
In a 2022 interview, Boum III Jr outlined Daba’s ambitions, stating, “In the next five years, I envision Daba being the premier destination for any investor, whether an individual or an institutional investor when they want to start or manage their investments on the African continent.” He expressed a desire for Daba to have a significant presence in key African markets such as Kenya, Nigeria, Ghana, and South Africa, as well as emerging economies like Côte d’Ivoire and Senegal.
In addition to Daba, Boum III Jr founded Mbo’Wam in Atlanta in 2017, a platform offering hotel-style accommodations in apartments and private residences, primarily for business travellers. In 2020, He also co-founded Afrika Startup Lab, a non-profit organization supporting potential entrepreneurs.
Boum III Jr worked as a software engineer at Nasdaq eVestment, a Nasdaq division providing institutional investment data, analysis, and information on public and private markets, from 2015 to 2019. In 2022, he won the AFRICON pitch competition, earning a $10,000 prize.
Melchior Koba
More...
Kenya's ambitious Konza Technopolis project seeks to establish the East African nation as a leader in technology and innovation across the continent.
Kenya's Konza Technopolis, a sprawling project aiming to transform into a smart city, is betting on information technology (ICT) and innovation to propel the country to the forefront of Africa's tech scene.
Launched in 2012, the project has become a cornerstone of Kenya's Vision 2030 national development plan, with the government backing its development in partnership with the World Bank's International Finance Corporation.
It is led by John Paul Okwiri, a seasoned procurement and supply chain executive, through the Konza Technopolis Development Authority (KoTDA).
The project envisions a world-class city powered by a thriving ICT sector, robust infrastructure, and investor-friendly policies. It aims to attract businesses in outsourcing, software development, data centers, disaster recovery, call centers, manufacturing, and light assembly.
Konza Technopolis also fosters innovation through initiatives like the Jitume program, which equips young people with digital skills and access to services to leverage technology for job creation. In 2024, it will host the 41st world conference of IASP, a global network of innovation ecosystems.
The project has already generated 17,000 jobs and hosted events like the 2020 Africa Digital Influencer Awards (ADIA20). It was also recognized for excellence in smart city development at the 2023 Africa Public Sector Conference and Awards (APSCA).
Melchior Koba
Local authorities are encouraging smartphone manufacturers to shift a portion of their production to their region, a move aimed at boosting smartphone usage by reducing prices.
Uganda’s Minister of ICT and National Orientation, Chris Baryomunsi, has called on smartphone manufacturers to establish production facilities in Uganda, a move aimed at boosting smartphone penetration in the country. The invitation was extended during the launch of a 5G smartphone model by Tecno, in collaboration with a local mobile operator, in Kampala on Friday, January 12.
Baryomunsi highlighted the benefits for smartphone manufacturers investing in Uganda, citing the growing demand in a market of 50 million people. Furthermore, he suggested that Uganda could serve as a gateway to the African continent and its 1.4 billion population.
The minister expressed the government’s support for technological innovation, stating, “We support the innovation and the government has deliberately promoted the policy of legalizing communications and airwaves. So far, we have since moved from traditional means of communication and have created space for innovations and technologies in Uganda so that we move with the rest of the world in this era of digital transformation. Continue making the innovations and technologies and we are ready to embrace all these cutting-edge technologies including these devices.”
The call for multinational smartphone manufacturers to establish assembly plants in Africa is becoming increasingly common. The goal is not only to create local jobs but also to reduce smartphone costs and increase affordability for the population.
In line with this trend, Kenya commissioned a smartphone assembly plant last October. The plant is expected to produce between 1.2 and 1.4 million smartphones annually, with retail cost at 7,500 Kenyan shillings ($46.58). Earlier that year, Angola signed a memorandum of understanding with China’s ZTE to establish a mobile phone factory, set to be operational this year.
It’s worth noting that, according to DataReportal, Uganda is projected to have 30.55 million active mobile subscriptions in 2023, accounting for 63.8% of the total population.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
While the digital economy booms elsewhere, the Central African Republic (CAR) faces a persistent challenge in bridging its own digital divide. Yet, amidst ongoing national struggles, the government is actively taking steps to equip young people with the digital skills they need to thrive in the global job market.
In a significant push towards a digital future, President Faustin Archange Touadéra of the Central African Republic (CAR) inaugurated a state-of-the-art digital training center and incubator at the University of Bangui on Monday, January 15. This launch coincided with the official nationwide rollout of broadband internet for the first time in the country.
Financed jointly by the European Union and the African Development Bank (ADB), the center aims to equip young people with the skills and tools to drive the creation of jobs and economic diversification through the burgeoning digital sector.
"This center marks a new chapter for fiber optic development in the Central African Republic. Its completion paves the way for high-speed internet access and positions CAR to become a smart nation, recognizing that internet access is a cornerstone of national development," stated the Prime Minister’s office.
The initiative forms part of CAR's national fiber optic backbone project, a key component of the broader Central African Backbone (CAB) program. Alongside the training center, the project encompasses a cybersecurity and electronic certification platform as well as technical assistance for the Ministry of Digital Economy, Posts and Telecommunications in establishing the Central African Digital Development Agency, which will spearhead the nation's digital strategy implementation.
The new center boasts cutting-edge equipment, including a training room, technical facilities, offices, an incubator, a database processing lab, and more. This infrastructure will empower young Central Africans to design, develop, and market digital products addressing the population's needs.
Samira Njoya
Universities around the world are rapidly accelerating their transition to digital education, driven by the urgent need to prepare students for a job market increasingly reliant on digital skills and qualifications. This shift necessitates the adoption of new technologies and pedagogies that go beyond simply replicating traditional classroom experiences online.
In Côte d’Ivoire, Minister of Higher Education and Scientific Research Adama Diawara, officially presented 16 mobile studios for recording digital teaching resources to the country’s public universities and grandes écoles.
Valued at XOF275 million ($458,125), these acquisitions aim to foster an environment conducive to integrating digital technology into the education system. “Digital technology is a powerful lever of transformation to support public education policies in all their dimensions,” Diawara stated.
The initiative is part of the AMRUGE-CI n°2 project, which seeks to stimulate the development of digital education. Mobile studios will be delivered to all the country’s universities to reinforce flexible educational production and digital documentation.
Since 2013, the government has collaborated with the French Development Agency (AFD), which has mobilized over XOF10 billion for the development of digital education in Côte d’Ivoire through the Debt Reduction-Development Contract (C2D).
By digitizing the education system, the Ministry aims to renovate the higher education offering to better meet job market demands, guarantee education quality, and comply with international standards.
The first beneficiaries include the Universities of Félix Houphouët-Boigny in Cocody, Nangui Abrogoua in Abobo-Adjamé, Alassane Ouattara in Bouaké, Jean Lorougnon Guédé in Daloa, Péléforo Gon in Korhogo, Man, Bondoukou, San Pedro, the Université Virtuelle de Côte d’Ivoire, the Ecole Normale Supérieure in Abidjan, and the Institut National Polytechnique Félix Houphouët-Boigny in Yamoussoukro.
Samira Njoya