Public Management (481)
Last July, Ethiopian Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed launched a program aimed at training young people in digital skills. A few months after its launch, authorities are now assessing its progress.
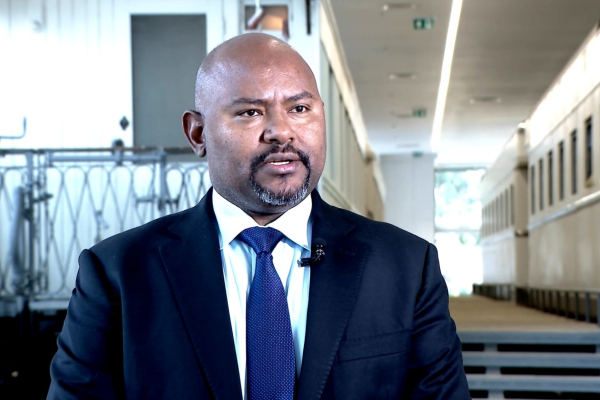
Ethiopian authorities have trained 31,000 citizens in coding within three months, according to a recent statement by Belete Mola, Ethiopia’s Minister of Innovation and Technology. He made this announcement while reviewing the results of the past fiscal year.
Belete Mola stated, “Over 246,000 citizens have enrolled in the training, and 31,000 of them have been certified. The young people trained as coders and the tech startups with creative potential will receive special support.”
The "5 Million Ethiopian Coders" initiative, launched last July by Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed in partnership with the United Arab Emirates, is part of the "Digital Ethiopia 2025" plan. Its aim is to provide training in programming, Android app development, data science, and fundamental digital skills in artificial intelligence.
This initiative aligns with Ethiopia’s broader goal to establish itself as a major tech hub in East Africa. The World Bank estimates that nearly 230 million jobs in Sub-Saharan Africa will require digital skills by 2030. Through the "5 Million Ethiopian Coders" program, Ethiopian youth are being prepared to meet this demand.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
To achieve universal health coverage for its population, Ghanaian authorities are relying on various technological solutions. They have opted for a public-private partnership to reach their goal.
Ghanaian authorities are set to launch, today Octyober 16, the electronic health management system, known as E-Health, which will create digital patient records accessible across all hospitals in the country.
The implementation of this system is a public-private partnership between Ghana’s Ministry of Health and Lightwave e-Health Solutions, a U.S.-based company specializing in e-health.
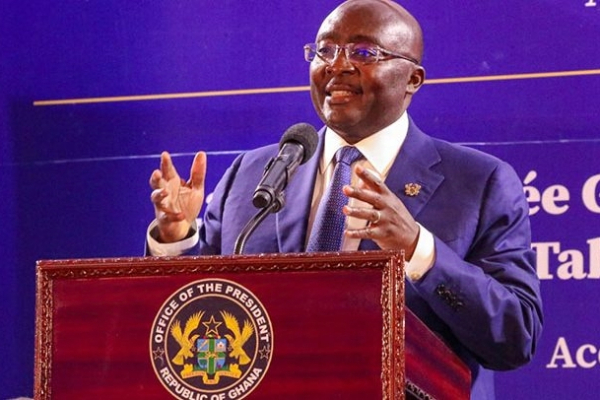
“Going forward, medical records and the history of patients can be gathered under a single database, which can be accessed by any networked hospital when the patient visits. This digitization effort has increased efficiency, effectiveness, and productivity in service delivery in our health facilities,” stated Ghana’s Vice President, Mahamudu Bawumia (photo).
This launch comes just months after the introduction of drone delivery solutions for medical supplies and online medicine purchasing from pharmacies. It aligns with the 2023-2027 Digital Health Policy and Strategy document, which aims to provide all communities in Ghana with timely, quality, and comprehensive healthcare through the use of information and communication technologies.
According to the Ministry of Health, the new system is expected to generate annual savings of between €50,000 ($54,000) and €300,000. It should also improve patient wait times by 35% to 40% in health centers and district hospitals, while regional and university hospitals could see a more than 40% reduction in wait times.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
Last March, the American company Pay Rem Group Africa announced several digital projects in Congo. It partnered with a key government ministry.
The Congolese government and Pay Rem Group Africa, a U.S. company specializing in modernizing financial services, signed, on October 11, a memorandum of understanding to support digital and technological projects in the country.
Jacqueline Lydia Mikolo, Minister of Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) and Handicrafts, announced the partnership, stating that Pay Rem Group Africa would provide training, design digital and technological solutions, and help secure funding for these initiatives.
This agreement follows similar partnerships with the Digital Economy Development Agency (ADEN) and the Congolese Postal and Savings Company (Sopeco) aimed at promoting digital inclusion and bridging the digital divide. It is part of the "Congo Digital 2025" strategy, which seeks to ensure equitable access to digital services for all citizens.
The partnership could enhance the integration of digital technologies into SMEs, modernize the Congolese economy, and create jobs in the tech sector. It may also provide entrepreneurs with better training opportunities and access to financing solutions to support digital projects.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
Like most African countries, Ghana is following its digital transformation roadmap. Various projects are supporting the achievement of this goal.
Ghanaian authorities plan to launch a $5 million fund to support technological innovation in the country. This was announced by Finance Minister Mohammed Amin Adam on Tuesday, October 8, during a visit to the site hosting the digital center at the University of Ghana.
“We are also establishing a US$5million endowment fund to support the management of this hub. So, everything that’s required to make it a complete digital village in the provision of skills to the youth of Ghana will be done. […] We want to train a million youth in digital skills, and it is not a task that cannot be done,” he said.
This initiative comes as African countries increasingly require a skilled workforce to keep pace with the digital transformation that has been underway for several years. According to a study highlighted in the report "Digital Skills in Sub-Saharan Africa: Spotlight on Ghana," the International Finance Corporation estimates that around 20% of Ghanaian companies surveyed only recruit abroad for digital skills, mainly because they cannot find qualified local talent.
However, the same report estimates that $4 billion will be needed to train the local population in digital skills by 2030. In response, the government has set a goal to train 1 million young people in these skills. The construction of four digital centers is part of this effort. In addition to the University of Ghana, these centers will also be built at the Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology (KNUST) in Kumasi, the University of Cape Coast (UCC), and the University for Development Studies (UDS) in Tamale.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
In the first half of 2024, Moroccan startups attracted $14 million in funding, according to Africa: The Big Deal. The government has also committed to supporting these startups through its national digital strategy.
Moroccan Digital Minister Ghita Mezzour (photo) recently announced a 240 million dirhams (approximately $24.5 million) investment to boost innovation and support local startups. Announced, on October 8th, at the opening of the 6th edition of the African Digital Summit, the investment aims to boost demand for innovative services.
“We have allocated a budget of 240 million dirhams to stimulate domestic demand for innovative services, prioritizing purchases from local startups and giving them access to outsourcing opportunities, so they can export their solutions beyond our borders,” Mezzour stated.
This initiative comes at a time when African startups are increasingly struggling to attract capital. It is part of the "Digital Morocco 2030" strategy, which aims to boost the local tech ecosystem. According to data from Partech Africa, Moroccan startups secured $33 million in 2021, $26 million in 2022, and $93 million in 2023.
State support is expected to strengthen the country’s tech entrepreneurial fabric, stimulate job creation, attract foreign investors, and further solidify Morocco’s position as a regional tech hub.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
For several years, Kenya has been working to accelerate its economic development. The country has identified a few issues within its state apparatus that are slowing progress toward achieving this goal.
Margaret Ndung'u (photo, center), Kenya's Minister of Information, Communication, and Digital Economy, met last week with a United Nations delegation led by Stephen Jackson, the UN Resident Coordinator in Kenya. The discussions focused on the importance of partnering to leverage digital technology to track illicit financial flows and combat cybercrime.
According to the ministry, the UN also emphasized the need to develop the necessary infrastructure, train law enforcement to tackle cybercrime, create digital labor policies, and devise a strategy for digital job creation.
This initiative follows Kenya’s request for an International Monetary Fund (IMF) audit to assess the impact of corruption and mismanagement of state resources on public finances. In Transparency International’s latest Corruption Perception Index, Kenya ranks 126th out of 180 countries.
On the cybersecurity front, Kenya is a global leader, ranking in Tier 1 with a score of 98.59 out of 100, according to the International Telecommunication Union’s "Global Cybersecurity Index 2024" published in September. However, cybercrime losses in Kenya could reach $383 million, according to the "Reimagining the African Cybersecurity Landscape" report released in 2023 by Serianu, a Kenyan cybersecurity consultancy.
UN support could help effectively combat these challenges and position digital technology as a driver of social development, as outlined in Kenya's national strategy. This UN assistance hinges on conditions such as media freedom, the protection of information integrity, the regulation of digital platforms and combating misinformation.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
As part of its digital transformation ambitions, Ghana is ramping up initiatives to digitize services and make them more accessible to the public. In September, the country launched a digital platform specifically designed for rent control.
On Monday, October 7, Ghana’s Vice President Mahamudu Bawumia launched a new unified mobile digital services platform. Baptized CitizenApp, the application allows Ghanaian citizens to access various government services, report issues, and receive real-time updates on public matters.
“What Ghana has done many advanced countries have not yet done it. So we are moving in a direction that has major opportunities…Once the system comes in doing business in Ghana will be very easy and smooth, paying taxes will be very easy, getting your passport, will be very easy, registering a business is very easy,” Bawumia stated.
The initiative is part of the Ghanaian government's broader strategy to accelerate the digitization of public services and improve their accessibility. In September, a digital platform dedicated to rent control was introduced. In July, the Ministry of Roads and Highways launched a mobile app enabling citizens to report road issues, enhancing safety and infrastructure development. Earlier, in February, another app was launched to formalize and harmonize the informal transport sector. Additionally, the digitization of the national population census process is currently in preparation.
These efforts have positioned Ghana as a leader in e-government implementation. According to the “E-Government Survey 2024: Accelerating Digital Transformation for Sustainable Development,” published in September 2024 by the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (DESA), Ghana ranks first in West Africa and seventh on the African continent.
However, the adoption of the new platform and the use of digital services will largely depend on Ghanaians' access to smartphones and the internet. While specific data for Ghana is not provided, the GSM Association (GSMA) reports that smartphone penetration in the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) is at 51%. In Ghana, according to the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), 69.8% of the population owns a mobile phone, and 68.6% uses the internet.
Isaac K. Kassouwi
The digital transformation is progressing across the continent. Morocco is ramping up partnerships and investments in the digital sector, aiming to establish itself as a key player in the industry within Africa.
On Friday, October 4, in Rabat, Moroccan authorities launched a digital procedures and services platform. This project, developed in partnership with the International Labour Organization (ILO) and supported by the Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency, aims to streamline various administrative processes.
Younes Sekkouri, Minister of Economic Inclusion, Small Business, Employment, and Skills, highlighted that the objective is to digitize 55 administrative procedures and services. The platform will leverage data management and extraction technologies to optimize public policies, particularly in employment and skills development.
This initiative follows the launch of the "Digital Morocco 2030" strategy, which places e-government at its core. Morocco aims to become Africa’s leading digital hub by 2030. According to the "E-Government Survey 2024: Accelerating Digital Transformation for Sustainable Development," published in September, the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UN DESA) ranks Morocco 11th on the continent and 100th globally in the Online Service Index (OSI), with a score of 0.5618, above the African average of 0.3862.
The implementation of this platform is expected to improve interactions between the government and citizens, strengthen the relationship between businesses and employees by simplifying administrative procedures, reducing processing times, and enhancing productivity. It will also improve how businesses manage human resources and interact with public authorities.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
By adopting blockchain technology in May 2024 to modernize and optimize several of its state operations, Guinea-Bissau made a bold decision. This ambitious move aimed to enhance transparency, security, and efficiency in administrative and financial processes.
Guinea-Bissau is set to expand its blockchain-based salary management platform to cover all public sector employees. By November 2024, the solution could track the data of the country’s 26,600 civil servants and 8,100 retirees, according to Concha Verdugo Yepes, lead economist for Africa at the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and head of the institution’s Blockchain Solution program. She shared this information in an interview published on Wednesday, October 2, by IMF Country Focus, the IMF's news platform.
“The platform offers a secure, transparent digital ledger for managing the public service’s wage bill data, enabling almost real-time monitoring of salary and pensions eligibility, budgeting, payment approvals, and salary and pensions disbursements. It significantly improves data integrity and supports the production of timely and accurate fiscal reports for use by policymakers and the public. It’s one of the first platforms in sub-Saharan Africa to use blockchain technology to improve government operations, particularly in managing salaries and pensions,” Verdugo Yepes explained.
When the project was first conceived in 2020, 84% of the state’s tax revenues were used to pay the salaries of Bissau-Guinean public servants—the highest ratio in the region, according to José Gijon, the IMF’s mission chief for Guinea-Bissau. He noted, “For every hundred dollars collected in taxes, eighty-four dollars were spent on salaries. This ratio has now declined to 50 percent—a huge improvement, but still high compared to the West Africa Economic and Monetary Union (WAEMU) regional fiscal convergence criteria of wages not exceeding 35 percent of tax revenues.”
The government of Guinea-Bissau adopted blockchain technology to combat various issues, including poor governance in state finances, embezzlement, and corruption. The system aims to eliminate ghost workers, payroll fraud, and other schemes that persisted due to poor traceability of public funds. The platform securely records, stores, and shares information in a way that prevents tampering. Every transaction is inviolable, and the system detects any discrepancies in salary data, flagging them for the relevant authorities.
For the IMF, the solution offers additional benefits by simplifying audit reporting and reconciliation processes. It also provides reliable, up-to-date, and high-quality data for artificial intelligence models.
According to the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), governments must have credible public finance management frameworks to build trust with international donors and local and foreign investors. A crisis of confidence in government threatens the financial resources it needs for the country’s economic and social development.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
Agriculture is vital to African economies. With the technological revolution, digitizing the sector has become a priority for many countries, offering opportunities for greater efficiency, sustainability, and inclusive growth.
On Tuesday, October 1, Morocco's Minister of Agriculture, Maritime Fisheries, Rural Development, Water and Forests, Mohammed Sadiki (photo, right), signed an agreement with David Li (photo, left), CEO of Huawei Morocco, to support the digital transformation of the agricultural sector. This initiative, finalized during the 15th edition of the El Jadida Horse Show, aims to introduce connected platforms, develop agricultural e-services on pilot sites, enhance farmers' skills, and promote youth entrepreneurship.
The partnership aligns with the "Green Generation 2020-2030" strategy launched by the government in February 2020. One of the key goals of this strategy is to connect two million farmers to public services by 2030, fostering a more modern and inclusive agriculture.
Huawei's support is expected to facilitate the digitalization of the sector through the introduction of technologies that will optimize the use of inputs, expand market access, improve transaction transparency, develop mobile banking, and strengthen food safety through better traceability.
According to the 2023 report by the NGO Agra Africa, titled Empowering Africa's Food Systems for the Future, digital technologies will be crucial in addressing three persistent challenges in African agriculture: inefficiency, exclusion, and unsustainability. Meanwhile, a study by Mordor Intelligence estimates that the global digital agriculture market will reach $20.01 billion in 2024 and could grow to $32.96 billion by 2029, with an annual growth rate of 10.5%.
Samira Njoya
More...
Morocco aims to become one of Africa’s leading technological hubs. To achieve this, the country is ramping up projects to meet the goals outlined in its national strategy document by 2030.
On Tuesday, October 1, Moroccan authorities inaugurated a digital skills complex in Lahraouyine, in the province of Mediouna. The goal is to train young Moroccans in digital professions and strengthen the capacities of businesses in this field.
The center provides training in software development, programming languages, app and website development, data analysis, digital marketing, cybersecurity, performance analysis, and artificial intelligence.
This initiative comes just days after the unveiling of the national strategy "Digital Morocco 2030," which aims to create 240,000 direct jobs in the technology sector by 2030. It is an integral part of the National Initiative for Human Development (INDH), which will contribute to achieving this goal. According to the International Telecommunication Union, Morocco ranks second in Africa in the 2024 Development Index with a score of 86.8 out of 100—well above the continental average of 50.3.
Ultimately, this complex could help create economic opportunities, reduce the digital divide, and bridge the gap between urban and rural areas.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
In The Gambia, the government is stepping up efforts to accelerate digital transformation. This affects all sectors of the economy, including education.
Last week, the Gambian government launched an initiative to provide laptops to the principals of all schools across the country. This effort, in partnership with the Global Partnership for Education (GPE), UNICEF, and the World Bank Group, is expected to drive the digitalization of school administration.
“The initiative marks a significant step in our efforts to enhance quality education and empower school managers with the tools needed for efficient service delivery in the digital age,” said Pierre Gomez, Minister of Higher Education, Research, Science, and Technology.
The Gambian government aims to digitize the national education system as part of its broader ambitions for digital transformation. According to Minister Gomez, the government is working to develop digitized information systems, enhance the digitalization of public services, and expand the use of electronic record management systems across all public administrations.
In September 2023, the government launched the Gambia Research and Education Network (GAMREN), in partnership with the World Bank, to provide high-speed internet connectivity to schools and research institutions nationwide. As early as July 2022, the Ministry of Higher Education, Research, Science, and Technology had begun efforts to develop a national strategy for digitizing technical and vocational education and training, with support from UNESCO.
UNESCO believes technology can significantly enhance educational management. "It enables a wider range of data collection on schools and students, allowing for precise analysis of learning paths and influencing factors. This data can be used to personalize learning, identify marginalized children, and prevent disengagement and early dropout," the organization stated in its 2023 Global Education Monitoring Report.
Isaac K. Kassouwi
The Senegalese government is positioning artificial intelligence (AI) as a key driver of economic growth across various sectors. On September 19, the Ministry of Digital Economy unveiled a plan to reform the educational system to meet the evolving challenges and opportunities presented by AI.
Senegal's Minister of Communications, Telecommunications, and Digital Economy, Alioune Sall, met with Meta's Vice President Nick Clegg on September 25 to discuss a potential partnership for an AI data center in Senegal. The meeting took place on the sidelines of the 79th United Nations General Assembly in Washington.
The AI data center would enable the processing of large volumes of data and the execution of advanced algorithms, thereby accelerating the development and deployment of AI applications in the country. The Senegalese government has already launched several initiatives, including the creation of a national AI strategy. In January, former President Macky Sall unveiled a roadmap outlining priority actions, with a budget of 7 billion CFA francs (about $11.9 million) allocated for the next two years.
Digital technology is a key pillar of Senegal’s socio-economic development, and the government views AI as a "catalyst for the Plan for an Emerging Senegal, youth employment, economic performance, public sector transformation, sovereignty, and the attractiveness of the country." A July 2024 study by the Global System for Mobile Communications Association (GSMA) estimates that AI could boost Africa's economy by $2.9 trillion by 2030, equivalent to an annual GDP increase of 3%.
However, while AI holds significant economic potential for Senegal, its adoption faces challenges, such as limited internet access. According to DataReportal, the country's internet penetration rate stood at 60% for its approximately 18 million inhabitants at the beginning of 2024. This presents a hurdle to fully harnessing AI’s transformative potential in Senegal.
Isaac K. Kassouwi
Morocco aims to build an information society by significantly integrating ICT into all sectors of the economy by 2030. To realize this vision, a strategic roadmap has been developed, with clear objectives and concrete actions to be implemented.
On Wednesday, September 25, Morocco officially unveiled its national strategy, "Digital Morocco 2030," an ambitious roadmap aimed at transforming the kingdom into a regional and international digital hub by 2030. The strategy is built around two main pillars and key objectives to accelerate economic and social development through digital transformation, while enhancing the country's global competitiveness.
Digital Job Creation and Training
A major goal of this strategy is the large-scale creation of jobs in the digital sector. To support this initiative, the government has allocated an investment of 11 billion dirhams ($1.14 billion) between 2024 and 2026. Prime Minister Aziz Akhannouch outlined Morocco’s aim to train 100,000 young people annually in digital professions, a significant increase from the 14,000 trained in 2022. The objective is to create 240,000 jobs in the digital sector by 2030, addressing the growing demand for skilled workers.
Digitization of Public Services Through AI
Another critical pillar of the strategy focuses on the digitization of public services. Morocco aims to improve its global ranking in the United Nations' e-Government Development Index, seeking to move from 90th to 50th place by 2030. The country has already taken concrete steps by digitizing 600 public services: 300 for citizens, 200 for businesses, and 100 for government agencies. Artificial intelligence (AI) will play a crucial role in optimizing these services. Planned AI-based solutions will automate administrative processes and analyze data to anticipate user needs and improve service quality.
Boosting the Digital Economy and Promoting Exports
The "Digital Morocco 2030" strategy also emphasizes developing the digital economy. One key objective is to increase digital export revenues, which are expected to rise from 17.9 billion dirhams in 2023 to 40 billion by 2030. To achieve this, Morocco plans to expand outsourcing services, establish 3,000 startups by 2030 (1,000 of them by 2026), and raise 7 billion dirhams in funding. The country also aims to foster the emergence of one or two unicorn companies, which would significantly enhance its attractiveness in technology and innovation.
Strengthening Digital Infrastructure: 5G and Fiber Optics
Developing digital infrastructure is another central aspect of the strategy. Morocco aims for 70% nationwide 5G coverage and plans to connect 5.6 million households to fiber optics. Additionally, improving internet access in 1,800 rural communities is a priority, ensuring an inclusive digital transition and bridging the digital divide between urban and rural areas. The government also intends to establish a sovereign cloud, a crucial infrastructure to enhance the country's technological independence and secure national data.
Strategic Partnerships and Offshoring Development
The rollout of "Digital Morocco 2030" began with the signing of several partnership agreements between the Ministry of Digital Transition, public institutions, and private sector stakeholders. Among these partnerships is a program contract for developing offshoring, a sector in which Morocco seeks to become a leader. Other partnerships focus on strengthening vocational training in digital professions and attracting more investments in information technology. In the coming years, Morocco aims to forge numerous strategic partnerships across various digital fields.
The "Digital Morocco 2030" strategy represents a major turning point for the country, as it strives to become a key digital hub in Africa and beyond. By combining efforts in training, infrastructure, strategic partnerships, and the growth of the digital economy, Morocco is well-positioned to achieve its ambitious goals.
Samira Njoya