Tech (805)
In Africa, low birth registration rates prevent many people from accessing essential rights such as education, healthcare, and social protection. New technologies can play a crucial role in overcoming this challenge.
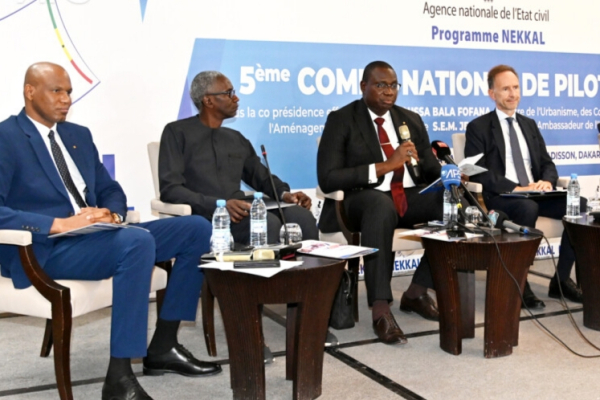
Senegal has already digitized and indexed over 19 million civil status records, announced Moussa Bala Fofana, the Minister of Urbanism, Local Government, and Land Management, on Tuesday, June 25, during the 5th meeting of the national steering committee for the project.
According to the minister, this initiative aims to ensure that every Senegalese citizen has an identification document enabling them to exercise their civil, political, and social rights, while also providing the state with the capability to plan and direct public policies more effectively.
The initiative is part of the "Nekkal" program launched in 2021, which aims to interconnect civil status centers and systematically digitize registers. The 42-month program is funded by the European Union to the tune of 18 billion CFA francs (27.4 million euros).
Once completed, the program is expected to address, among other issues, the problems of birth traceability and ensure data reliability. According to UNICEF figures, in 2019, one in five children (20%) in Senegal was not registered at civil status, thereby being deprived of their fundamental right to an identity. In rural areas, three out of five children (77%) are not officially recognized. For those who are registered, issues such as multiple identification numbers and loss of identifications due to file deterioration are common.
The second phase of the program, currently under consideration, will establish a service platform for all users, allowing citizens, whether in Senegal or abroad, to request civil status documents without needing to travel.
Samira Njoya
Across Africa, new digital technologies have enabled countries to move past outdated tools and progress toward modern innovations. This digital transformation has now reached all sectors, including identification systems, which have become fully digitized.
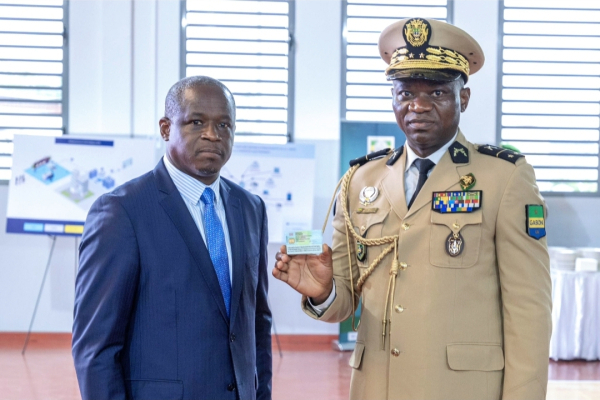
Gabonese citizens can now obtain the new Electronic National Identity Card, President of the Transition, Brigadier General Brice Clotaire Oligui Nguema, announced on Monday, June 24th.
The government touts the new ID card as "highly secure," featuring an electronic chip storing each citizen's digital identity and a unique 14-digit Personal Identification Number (NIP). This NIP certificate, issued upon capturing biometric data, serves as the key document for applying for the card.
This initiative fulfills the government's pledge to provide a secure and multifunctional national ID card to all Gabonese citizens. It comes after a near decade-long gap in card renewals, following the 2015 termination of a contract with a Belgian service provider.
Gabon joins a growing trend of African nations adopting biometric data collection through the national id card. According to a 2020 report by the American research firm Global Industry Analysts, the biometrics market in Africa and the Middle East is expected to experience a 21% annual growth rate, with the global industry projected to reach $82 billion by 2027.
Beyond secure identification, the electronic national identity card will empower citizens to access digitized administrative services while safeguarding their personal data. This card marks a significant milestone for Gabonese governance, with guaranteed nationwide coverage reflecting the government's commitment to modernization, efficiency, and transparency.
Samira Njoya
Digital transformation is enabling multinational companies to operate without a physical presence in the countries where they do business. This poses a significant fiscal challenge for African economies. As a result, it is urgent to regulate the activities of these digitally-enabled multinational firms.
The Senegalese Directorate General of Taxes and Domains (DGID) recently announced the introduction of a digital services tax, effective from July 1st. This measure aims to tax the revenues of foreign digital companies and platforms operating in the country, in accordance with Article 355 bis of the General Tax Code (CGI).
The tax will apply specifically to online marketplaces facilitating transactions between suppliers and customers, platforms for downloading and streaming music, movies, and online games, as well as data storage and processing services via cloud and database management services. It will also cover online learning and teaching platforms, and content hosting services such as websites, images, and text. Digital giants like Google, Apple, Meta, Amazon, and Microsoft are particularly targeted by this tax.
The taxable base will be determined based on the actual revenue of non-resident suppliers or foreign digital platform operators, evaluated according to the consideration received or to be received. The VAT rate in Senegal is 18%, with a specific reduction to 10% for the hospitality and restaurant sectors, which have struggled since the Covid-19 pandemic.
This regulation, introduced by the new government, is expected to have a positive impact on the Senegalese economy by generating additional tax revenue for the state and contributing to a fairer business environment. It will also allow the country to better regulate the activities of foreign digital companies on its territory and ensure they contribute fairly to the Senegalese economy
Samira Njoya
African nations are actively driving digital development to unlock its full potential. Close collaboration is key to maximizing these efforts.
Egypt and Burkina Faso are committed to bolstering their cooperation in the digital sector. The commitment was the focus of discussions between the Egyptian Ambassador to Burkina Faso, Shérif Abdel Kader Abdel Latif Nada, and the Burkinabe Minister of Digital Transition, Posts, and Electronic Communications, Aminata Zerbo/Sabane, on Friday, June 21.
"I came to discuss with the minister the opportunities for bilateral cooperation in the field of digitalization between our two countries. We want to further strengthen this cooperation. Egypt intends to share its expertise in digitalization with Burkina Faso," stated the Egyptian diplomat following the meeting.
This initiative is part of the Egyptian government's efforts to implement its digital transformation strategy, known as "Digital Egypt 2030." Cairo aims to develop its ICT sector and modernize its national telecom infrastructure, making digitalization the driving force behind the country's socio-economic development.
In this context, Egypt is seeking partnerships with countries like Burkina Faso, which is also actively working to develop its digital sector. Burkina Faso is striving to modernize its public services through various projects aimed at improving administrative efficiency and providing better services to its citizens.
The cooperation between the two countries could enable Burkina Faso to benefit from Egyptian expertise in implementing large-scale digital projects. It could also pave the way for technological partnerships, knowledge exchanges, and joint investments in digital infrastructure, creating new economic opportunities for both nations.
Samira Njoya
Gabon's transitional government is injecting fresh momentum into the country's development by prioritizing digital transformation. This modernization drive seeks the backing of key financial institutions, including the World Bank.
Gabon aims to make significant progress in digital projects this year. On Thursday, June 20, the Council of Ministers adopted a draft law authorizing the Gabonese state to borrow €56.2 million from the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD), a World Bank entity. This initiative is intended to fund the project titled "Gabon Digital."
According to the final communiqué from the Council of Ministers, this funding will catalyze the adoption of digitized public services and increase the number of citizens with a unique identifier. This identifier is crucial for facilitating inclusive access to various public services, thereby contributing to administrative efficiency and improving the quality of life for Gabonese citizens.
"Gabon Digital" will receive a total of $68.5 million in funding from the World Bank. It comprises several major components, including creating an environment conducive to rapid digital transformation, modernizing legal identity systems, and digitizing public administration and essential services.
This initiative is part of the transitional government's strategy to make the digital economy a strategic lever for economic and social growth. To this end, several priority projects have been reactivated, including the construction of a national data center, the development of a Cybercity on Mandji Island, and the digitization of key sectors of the country.
The support from the World Bank is expected to help the country realize these ambitious projects. The planned investments are likely to foster innovation, stimulate the creation of skilled jobs, and enhance the country's competitiveness on the international stage. According to a recently published report by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), titled "Measuring Digital Development: The ICT Development Index 2023," Gabon ranks as the most developed country in ICT in the Central Africa sub-region and holds the 10th place in Africa with a score of 72.9 out of 100 points.
Samira Njoya
After investing in several startups across the continent, the venture capital fund Breega has decided to set up a fund specifically dedicated to Africa.
Paris-based venture capital fund Breega has announced the closing of a $75 million fund dedicated to Africa, named "Africa Seed I." The fund aims to invest between $100,000 and $2 million in early-stage startups across the continent, targeting at least 40 investments.
“Reflecting on my experience, I struggled to find African investors who had built businesses without raising money. That’s why our goal is to be the investors we wished we had while building our businesses. Many entrepreneurs value having a sparring partner who has been there and done that before," Melvyn Lubega (photo, right), one of the leaders of Breega Africa, told TechCrunch.
The closing comes at a time when African startups are raising less capital. According to Partech Africa, African startups raised $2.3 billion in equity in 2023, a 54% decline compared to 2022. This downward trend continued into 2024, as highlighted by Africa: The Big Deal, a database tracking investments over $100,000 in African startups. It reported that African startups raised $466 million in the first quarter of this year.
Africa Seed I will focus on four major African markets: Nigeria, Egypt, South Africa, and Kenya, as well as Francophone African markets including Morocco, Senegal, Côte d'Ivoire, Cameroon, and the DRC. Breega has previously supported several African startups, including Numida, Hohm Energy, Socium, Klasha, Kwara, Coachbit, and Sava.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
The Ivorian government is continuing the implementation of its digital development strategy for 2025. The digitization of all public services stands as a fundamental pillar of this policy.
Côte d'Ivoire's digital transformation took a leap forward on Tuesday with the launch of four digital platforms designed to streamline operations across key government ministries.
The new platforms, DOB-connect, the Hospital Information System (SIH), E-Tribcom, and Trésor-PAY-Trésor-Money, aim to enhance service delivery and transparency in education, healthcare, justice, and finance.
DOB-connect, geared towards the Ministry of National Education and Literacy, provides a digital tool for tracking student performance and tackling academic failure. The Ministry of Health received the SIH, which will improve patient care by connecting over 160 healthcare facilities.
The E-Tribcom platform streamlines judicial operations, commercial registry management, and secure transactions for the Ministry of Justice and Human Rights. Finally, the Ministry of Finance and Budget received Trésor-PAY-Trésor-Money, facilitating state expenditure management and electronic revenue collection.
The launch aligns with the Governance Improvement Project for the Delivery of Basic Services to Citizens (PAGDS), an initiative within the National Digital Development Strategy 2021-2025. This World Bank-supported strategy encompasses 32 reforms and a substantial investment of 2,000 billion CFA francs (around $3.3 billion).
The Ivorian government anticipates this digital transformation to boost GDP by 6-7 percentage points and generate between 2,000 and 3,500 billion CFA francs. The World Bank further highlights the potential of the digital economy, estimating it could contribute over $5.5 billion to Côte d'Ivoire by 2025 and exceed $20 billion by 2050, contingent on continued investments in key digital infrastructure.
Samira Njoya
In Africa, access to electricity remains a major challenge, significantly hindering economic and social development. The initiatives by Orange and its partners are contributing to addressing this challenge in a sustainable manner.
Orange Smart Energies, a specialized digital platform by the telecom operator Orange, is now open to all energy producers in Africa. This pay-as-you-go solution, combined with Orange Money, allows them to manage the prepaid electricity provided to populations through their solar kits and smart meters. This initiative will significantly enhance energy inclusion in Africa.
"Using digital technology to improve the energy inclusion of African people has been our ambition since day one. By opening up our Orange Smart Energies platform to all energy producers, we are taking a major step forward in our commitment to universal access to energy in Africa and the Middle East," said Jérôme Hénique, CEO of Orange Middle East and Africa (OMEA).
In its "Electricity 2024: Analysis and Forecast to 2026" report, the International Energy Agency (IEA) indicated that 600 million people, primarily in sub-Saharan Africa, lacked access to electricity in 2023, accounting for over 40% of Africa's population. Off-grid gasoline or diesel generators have become a common solution for accessing electricity on the continent due to their low initial costs compared to grid connection. However, their operating costs have significantly increased, particularly since 2021, following the surge in oil prices.
On the other hand, since 2015, the adoption of modular decentralized home solar systems (SHS) has steadily increased, according to the IEA. "Countries like Ghana and Kenya have multiplied their SHS capacity more than twentyfold between 2015 and 2019. SHS providers have enabled the implementation of the system through financial incentives such as a pay-as-you-go business model," notes the International Energy Agency.
Given this context, the Orange Smart Energies platform — operational in 12 African countries with over 300,000 households benefiting from its services daily — positions itself as a valuable asset for the French telecom operator in the fight against energy poverty in Africa. In addition to facilitating access to energy for remote populations, it also addresses the profitability challenges of energy producers by reducing the risk of non-payment.
Orange wants to connect one million households to solar energy by 2026. Furthermore, the company covers a dual advantage. The connection between Orange Smart Energies and Orange Money allows it to further monetize its mobile finance service, while also promoting internet usage, a strong revenue segment for Orange, through increased access to electricity.
By creating a hub that attracts regional entrepreneurs, governments can drive technological innovation across Africa, fostering a collaborative ecosystem that benefits the entire region.The project will create numerous jobs and opportunities for skills development in technology, business process outsourcing, and related fields, contributing to workforce empowerment and economic stability.
Sierra Leone is dedicating $150 million to a cutting-edge Tech City hub in Tikonko, Bo District, to transform the nation into a digital innovation powerhouse. Announced at the Orange-sponsored Sierra Leone Innovates Tech Summit (11-13 June 2024), the hub will offer facilities to incubate and accelerate programs, supporting the transition of start-ups from ideation to commercialization.
Speaking on the matter, President Bio said: “The City will foster the development of new technologies, products, and services that will serve as catalysts for sustainable development, promote economic diversification and reduce the country’s over reliance on the traditional sectors.”
The Tech City, set in a 130-acre economic zone, marks a significant step in Sierra Leone’s digital transformation efforts. Technology Minister Salima Bah, who spearheads the project, envisions the hub as a catalyst for the country’s technological advancement.
Key telecom operators Africell and Orange Sierra Leone are supporting the project, with Africell planning to establish an on-site data center, as confirmed by a memorandum of understanding (MoU) signed during the summit. The Ministry of Communication, Technology, and Innovation announced today, via their Facebook page, the signing of an MoU with Orange. This agreement paves the way for the construction of the "Orange Village" community project within the Tech and Innovation City.
The Tech City is designed to generate jobs, with new opportunities in business process outsourcing and device assembly. This multifaceted strategy aims to boost Sierra Leone’s tech capabilities and solidify its role in West Africa’s innovation landscape.
The investment comes at a crucial time as African nations increasingly leverage digital solutions to spur economic and social progress. Sierra Leone’s bold move could set a precedent, demonstrating that smaller nations can significantly impact the digital stage.
The government has been actively seeking ways to drive economic development through the combined forces of entrepreneurship, innovation, and technology. Initiatives include the Sierra Leone Medium Term National Development Plan (2019-2023), the National Digital and Innovation Strategy, and the establishment of Small and Medium Enterprises (SME) development agencies, among others.
A study by the African Development Bank (AfDB) highlights that nations with diversified economies are more resilient to global economic shocks. Sierra Leone’s investment in Tech City supports this diversification, enhancing economic resilience and creating a sustainable growth model.
Hikmatu Bilali
With the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) across the globe, African nations have a critical opportunity. They can harness AI's potential to fuel economic growth, but must also consider strategies to mitigate potential risks.
African ICT and Communication ministers have unanimously approved a Continental Artificial Intelligence (AI) Strategy and an African Digital Pact. Both documents aim to accelerate the continent's digital transformation by harnessing the potential of new digital technologies. They were approved during the second extraordinary session of the African Union's Specialized Technical Committee on Communication and ICT, held from Tuesday, June 11, to Thursday, June 13.
According to the African Union's communiqué, the Continental AI Strategy "provides guidance to African countries to harness artificial intelligence to meet Africa's development aspirations and the well-being of its people, while promoting ethical use, minimising potential risks, and leveraging opportunities."
The strategy also identifies key priorities and actions to ensure that African countries fully benefit from AI's capabilities. These include enhancing infrastructure, talent development, data institutions, innovation, and partnerships, while ensuring adequate safeguards and protection against threats.
The African Digital Pact outlines the continent's digital future and leverages the transformative potential of digital technologies to promote sustainable development, economic growth, and societal well-being across Africa. According to Amani Abou-zeid, the African Union Commissioner for Infrastructure and Energy, the pact represents the continent's strategic commitment to using digital transformation as a catalyst for inclusive progress and sustainable development in Africa.
Both documents align with the African Union's Digital Transformation Strategy (2020-2030) and Agenda 2063. Developed through consultations with a wide range of stakeholders, they represent Africa's contribution to the Global Digital Compact and the upcoming United Nations Summit on the Future in September. Before that, they will be submitted to the African Union Executive Council in July for review and adoption.
More...
Government support for startups nurtures talent and creativity, enhancing skills in technology and entrepreneurship. These initiatives align with African development goals by addressing unemployment, poverty, and economic diversification.
The Lagos State government has allocated N1 billion ($654,000) as a seed fund for startups through the Lagos State Science, Research, and Innovation Council (LASRIC), Governor Babajide Sanwo-Olu announced on June 14.
“We are committed to increasing these success metrics with the provision of LASRIC seed fund to the tune of N1,000,000,000 – in the first tranche of funding to the council,” Sanwo-Olu said.
a SEED Fund of N1Billion was provided for this cause. This is another marquee achievement for our dear State and indeed a greater Lagos that is ever evolving. Congratulations LASRIC. 2/2 pic.twitter.com/fq8KwMNaPL
— LASRICLAGOS (@Lasriclagos) June 15, 2024
The funding was revealed during the inauguration of the newly reconstituted LASRIC members, who include experts from industry, academia, and the public sector.
For Sanwo-Olu, Lagos is a burgeoning hub for early-stage and unicorn startups, noting that the city’s startup ecosystem has outpaced many other African cities in success metrics and foreign direct investment. He also emphasized LASRIC’s achievement in securing the government’s first patent through a team from the University of Lagos, which developed the Ambu Bag Ventilator.
According to the Global Startup Ecosystem Report 2023, Lagos ranks high among African cities, attracting significant investment and producing innovative solutions. The seed fund aims to support Lagos' thriving startup ecosystem and maintain its status as a leading innovation hub in Africa.
Hikmatu Bilali
In Guinea, a large portion of its population lacks access to formal banking. To spur economic development, initiatives that improve financial inclusion are crucial.
On Tuesday, June 18, Guinea's Minister of Posts, Telecommunications, and Digital Economy, Rose Pola Pricemou (photo, center), met with a delegation from the Canadian company EZO, led by co-founder Charles-André Bergeron. The visit aimed to propose a financial solution tailored to the Guinean market, addressing the growing need for the digitalization of financial services in the country.
According to the Ministry of Digital Economy, discussions focused on the potential implementation of the EZO financial application in Guinea, the digitization of financial services, and the development of financial inclusion. Ms. Pricemou emphasized the importance of such initiatives in improving access to financial services for both rural and urban populations.
EZO's visit to Guinea is part of its international expansion strategy. The company plans to establish itself in Tunisia in the coming months and offers an automated and autonomous solution covering all financial activities. Its system comprises three main components: customer inclusion (swap system), payment, and savings. The application also allows users to receive money directly on their phones, with payment options available regardless of the currency origin.
Moreover, EZO integrates portfolio management and microcredit features, which could transform Guinea's financial landscape by offering comprehensive banking services via a digital platform.
In Guinea, the EZO delegation also met with officials from the Central Bank and other major banks to discuss solutions for providing all citizens with access to essential financial resources for their development.
Samira Njoya
The Moroccan government aims to connect educational institutions as part of its digital transformation ambitions. Starting in 2021, approximately 1.2 million SIM cards have been distributed to students, allowing them free access to the internet.
American wireless network provider Cambium Networks announced on Tuesday, June 18, the deployment of 18,000 Wi-Fi access points to provide high-speed internet connectivity in 12 major public universities in Morocco. The project covers over 200 campuses and benefits 1.3 million students, educators, and administrative staff.
The campuses are equipped with Cambium Networks' Wi-Fi 6 solutions, both indoors and outdoors. These solutions were designed and deployed in collaboration with 3GCOM, a service integrator and partner for the project. The partners integrated planning tools, contactless provisioning, streamlined installation, and centralized cloud management into the existing systems to ensure optimal performance.
The deployment of Wi-Fi access points in Moroccan universities is part of the "Connected Campus" program launched in 2021, aimed at providing students with free and secure access to digital tools. Over 1.2 million SIM cards have been distributed to students in partnership with telecom operators. This effort is part of the government's initiatives to accelerate the transformation of the higher education, scientific research, and innovation ecosystem.
"Flexible learning, online testing, and video collaboration with media-rich content requires stable, reliable and affordable performance. Our purpose-built technologies uniquely address density and scale while delivering best in class experience—ensuring uninterrupted learning while remaining affordable," said Morgan Kurk, CEO of Cambium Networks.
Isaac K. Kassouwi
The Ivorian government is intensifying its efforts to enhance the employability of young people and women through information and communication technologies (ICT). The goal is to reduce unemployment and stimulate technological innovation in the country.
The United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), in partnership with the Ministry of Commerce and Industry and the Ministry of Digital Transition and Digitalization, launched the development of the National Industry 4.0 Strategy in Côte d'Ivoire on Friday, June 14. This initiative was introduced during a dedicated workshop.
The strategy, currently under development, will focus on skill development, support for investment and financing, and assistance to innovation and startup ecosystems to deliver 4.0 technological solutions tailored to business needs. It also emphasizes partnerships, alliances within the ecosystem, international cooperation with technical and financial partners, and awareness-raising efforts.
This initiative is part of the "Employment4Youth: Industry 4.0 to foster youth employment in Tunisia and Côte d'Ivoire" project, led by the Ivorian government and implemented by UNIDO. Launched in 2022, the project aims to increase youth employment and improve working conditions by structuring and consolidating a digital ecosystem, particularly within Industry 4.0. The project is funded by the German Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development (BMZ) under the special initiative "Decent Employment for a Just Transition."
In Côte d'Ivoire, this project is expected to create 13,000 jobs, including 3,000 direct jobs, by 2025 across various private sectors such as social and ecological transformation, renewable energies, ICT, and agro-industry, with a total investment of USD 30 million.
Samira Njoya