Tech (802)
Ethiopian authorities aim to accelerate the development of the national space sector and harness it for socio-economic growth. The plan includes orbiting ten satellites by 2035.
Ethiopia plans to launch its third Earth observation satellite, the Ethiopian Remote Sensing Satellite-2 (ETRSS-2), in 2026, the Ethiopian Space Science and Geospatial Institute (ESSGI) said this week.
Developed in partnership with China, the new satellite will have a five-year lifespan and a resolution of 0.5 meters, the ESSGI said. It is expected to provide high-resolution imagery and enhanced monitoring capabilities compared to its predecessors, ETRSS-1 and ET-SMART-RSS, which were launched in December 2019 and December 2020, respectively.
The initiative is part of Ethiopia's national space policy, launched in December 2018, the institute said. The roadmap reflects the government's ambition to leverage space technologies to address the country’s socio-economic challenges. The government plans to launch ten new satellites by 2035.
Once operational, ETRSS-2 could facilitate decision-making in several sectors, including agriculture, by providing accurate data, the ESSGI said. The United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs (UNOOSA) considers space technology a key catalyst in the agricultural sector.
"Satellite imagery, global navigation satellite systems data and their integrated applications are now critical tools for agriculture, enabling stakeholders, ranging from local farmers to international policymakers, to monitor crop health, manage water resources, detect and control pests, and plan for weather uncertainties, among various other applications," according to the report "Leverage Space Technology for Agricultural Development and Food Security," published in January 2025 by UNOOSA.
By Isaac K. Kassouwi,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
Digital technology is revolutionizing education, enhancing accessibility, interactivity, and preparing students for 21st-century challenges. Senegal recognizes this transformation and is strategically investing to position itself as a global leader in education.
Senegal’s Ministry of National Education and the Sonatel Foundation signed a memorandum of understanding Tuesday, March 11, to modernize the nation’s education system, focusing on digital integration and equitable access.
The memorandum of understanding aims to improve school infrastructure, promote digital education, and provide opportunities for equal access and excellence.
“This partnership is a unique opportunity for Sonatel to continue actively contributing to the country's development by leveraging its expertise and resources in the education sector,” said Sékou Dramé, chairman of the Sonatel Foundation Council, in a statement. “We firmly believe that education is the key to the future, which is why we are committed to working alongside the government to provide a better future for future generations.”
Key initiatives include the “Digital Schools” program, which will equip 120 elementary schools with modern technology and digital educational content, officials said. The program aims to strengthen students’ early access to digital learning, with a focus on information technology.
Additionally, 500 women will receive free training in digital marketing and project management at seven Digital Houses, facilitating their integration into the digital economy and enhancing youth employability, according to the foundation.
The partnership aligns with the Sonatel Foundation’s mission to promote excellence, equal opportunities, and inclusion, and reflects the Ministry of National Education’s vision to transform Senegal’s education system into a modern, technologically advanced learning environment.
Senegal is also developing a $206 million strategy to modernize educational infrastructure and integrate cutting-edge technologies, officials said.
The partnership echoes the government’s recently launched digital strategy, the “Technological New Deal,” which includes training 100,000 graduates in the digital sector and integrating science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) into all educational cycles. The strategy promotes hands-on learning in disciplines such as robotics, coding, and artificial intelligence (AI).
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
To fully realize the potential of artificial intelligence, Africa needs to build robust infrastructure. Burkina Faso is actively pursuing this path, aiming to harness AI for national development, particularly in vital sectors like healthcare and education, with a focus on sustainable and independent innovation.
Burkina Faso is positioning artificial intelligence (AI) as a strategic driver of its digital and economic development, the government announced Tuesday. Minister of Digital Transition, Posts, and Electronic Communications, Aminata Zerbo/Sabane, outlined the nation's progress and ongoing initiatives to the Transitional Legislative Assembly (ALT), emphasizing a vision of sovereign AI innovation.
"We are working to maximize AI's benefits while mitigating risks," Zerbo/Sabane stated. "Our goal is to establish Burkina Faso as a hub for independent AI innovation, developing solutions tailored to our unique needs and cultivating a generation of experts capable of competing regionally. Burkina Faso possesses the necessary assets to become a regional AI leader."
To achieve this, the government has established the Permanent Secretariat for Innovation and Monitoring of Emerging Digital Technologies (SPIVTEN), tasked with overseeing and regulating AI development. Infrastructure investments include a national backbone and a G-Cloud, providing secure data hosting and high-performance computing for AI applications.
Burkina Faso is also deploying AI-powered digital solutions to modernize public services. The DJAM platform and regulatory chatbots have been launched to streamline digital access and automate administrative processes. An AI action plan, currently under development, will be integrated into the national digital strategy to guide the technology's expansion.
A major focus on training and capacity building is planned. Through the Digital Transformation Acceleration Project (PACDIGITAL), substantial funding has been allocated to establish AI centers of excellence and offer scholarships for specialized training. A recruitment drive for 100 engineers will commence shortly, offering intensive training in AI and cybersecurity, bolstering local expertise and digital sovereignty.
A PwC study indicates AI could contribute $1.2 trillion to Africa's economy by 2030, boosting GDP by 5.6% through productivity gains in sectors like agriculture, health, finance, and education. Burkina Faso aims to leverage these advancements to become a leading West African AI player, developing localized solutions and fostering a competitive digital ecosystem.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
The role of North-South cooperation is critical in advancing innovation across Africa. Such partnerships enable technology transfer, provide crucial funding, and support entrepreneurial endeavors, thereby stimulating the growth of local startups and improving the continent's competitive standing.
France and Senegal are moving to strengthen their digital sector cooperation, with a focus on supporting young entrepreneurs. French Minister Delegate for Francophonie and International Partnerships, Thani Mohamed-Soilihi, visited Senegal's General Delegation for Rapid Entrepreneurship of Women and Youth (DER/FJ) on Monday, March 10, to review existing partnerships and explore new avenues for collaboration in digital technology and innovation.
The visit aimed to accelerate the growth of Senegalese tech startups and bolster support for young entrepreneurs.
"We are in Senegal to strengthen the partnership between France and Senegal. A win-win partnership, and I am very proud to see here that the French Development Agency (AFD) and other operators, including the African Development Bank (AfDB), are helping to promote these crucial and innovative projects for Senegalese youth. France is committed to establishing this new partnership agenda that respects our historical ties," Mohamed-Soilihi said.
The visit comes amid increased cooperation between the two nations in innovation and entrepreneurship. Through initiatives like Choose Africa 2, France is actively backing young African entrepreneurs. The DER/FJ, in partnership with the AFD and other stakeholders, has facilitated the creation of 74,000 jobs and supported 10,000 entrepreneurial initiatives, including 40 startups in collaboration with HEC Paris.
Projects such as Game Hub Senegal and Anim’Lab provide young talent with training and hands-on experience in digital creation.
The visit also raised the prospect of the AFD signing the second phase of the Innovation Valorization Support Program (PAVI 2), which would enhance young entrepreneurs' access to financing and technical assistance.
These potential partnerships align with Senegal's New Technological Deal, the country’s national digital transformation strategy. The ambitious program aims to certify 500 technology startups and create 150,000 direct jobs by 2034, positioning innovation as a key driver of Senegal’s economic growth and competitiveness.
Securing identity authentication is a critical challenge across online transactions, public services, and data protection. Given the swift evolution of fraud techniques, enhanced by technological progress, African nations are compelled to reinforce their systems without delay.
Generative artificial intelligence (AI), a rapidly growing technology, is revolutionizing numerous sectors. However, in Africa, as elsewhere, it is also being exploited for malicious purposes. Fraudsters are using these tools to create fake documents, synthetic voices, and hyper-realistic images, facilitating sophisticated scams and financial crimes. This new wave of AI-driven fraud presents major challenges in security and identity verification, according to Smile ID's report, "2025 Digital Identity: Fraud in Africa Report – Trends, Tactics, and Key Solutions to Tackle Fraud Effectively."
Biometric Fraud Explosion
One of the most concerning aspects of this trend is the increase in biometric fraud attacks. With the availability of free or low-cost AI tools, fraudsters can now produce deepfakes (fake videos or audio recordings) and high-quality fake selfies. According to recent data, deepfake-related incidents increased sevenfold between the second and fourth quarters of last year. Selfie anomalies, used to bypass verification systems, now account for 34% of emerging biometric fraud cases.
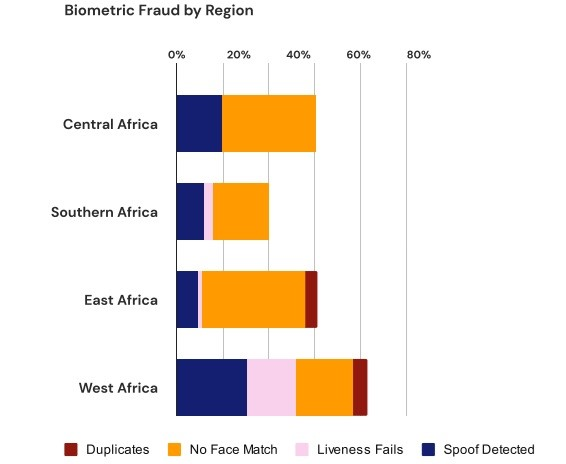
These techniques allow criminals to create fake identities or manipulate existing biometric data, making traditional security systems increasingly vulnerable. West Africa recorded the highest rise in biometric fraud cases in 2024. Cases of identity theft have increased in the region, representing 15% of biometric fraud cases, compared to less than 5% in 2023.
Traditional Verification Methods Under Threat
Faced with these technological advances, traditional identity verification methods seem increasingly outdated. Generative AI allows fraudsters to imitate individuals in real-time with unsettling realism. Security systems based on facial recognition or document verification are now vulnerable to high-quality falsifications.
Experts point out that the easy access to generative AI tools has paved the way for an industrialization of fraud. Criminals can mass-produce fake documents, photos, and videos, exposing major flaws in current protection systems. Among the most striking examples of this new era of fraud is OnlyFake, an underground platform that uses advanced neural networks to produce impressively high-quality fake identity documents. For just $15 per document, users can generate convincing documents capable of deceiving digital verification systems. OnlyFake perfectly illustrates how generative AI has eliminated the technical barriers once exclusive to expert counterfeiters.
Beyond the use of AI, which is growing in biometric fraud, Smile ID indicates that other techniques are also being implemented, notably document fraud and identity farming.
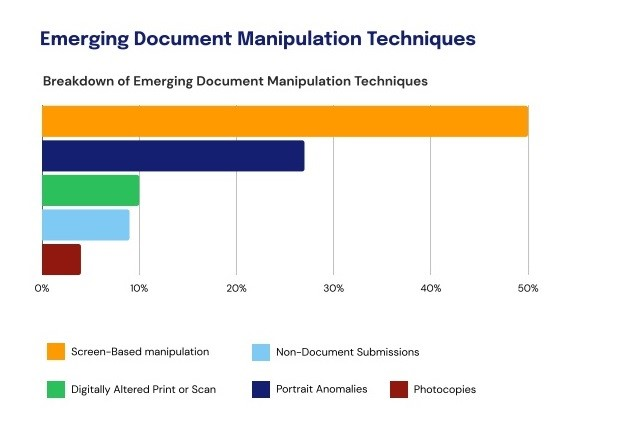
Document fraud involves manipulating or falsifying identity documents. This includes counterfeiting, altering genuine documents, and obscuring essential information. Emerging techniques include on-screen document manipulation, portrait anomalies, and the submission of altered photocopies or scanned documents.
As for identity farming, it involves collecting large amounts of personal information, often through illegal means, to facilitate fraud. This data is used to create synthetic identities, take control of existing accounts, or open fraudulent accounts.
Increasing Financial Losses
The growing use of identity fraud techniques in Africa has had significant consequences. Despite improvements in Know Your Customer (KYC) processes, financial losses due to fraud have increased in major markets. In Nigeria, banks reported losses of 42.6 billion naira ($28.2 million) due to fraud in the second quarter of 2024 alone, surpassing the total losses of 9.4 billion naira for the entire year 2023. Similar trends have been observed in South Africa, Ghana, Zambia, and other key African markets.
East Africa recorded the highest rate of reported biometric and document fraud attempts in Africa, at 27% in 2024. According to Smile ID, this phenomenon is mainly due to outdated, inconsistent, and low-quality identity documents in countries such as Zambia, Rwanda, and Sudan, which continue to hinder verification processes. West Africa saw a significant increase in its rate from 12% in 2023 to 22% in 2024, due to the rise in biometric fraud attempts. Central and Southern Africa recorded respective rates of 22% and 21%.
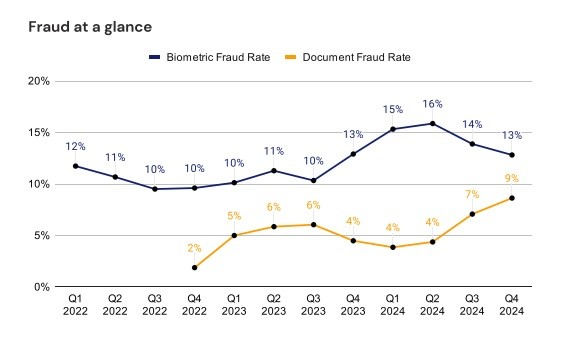
Digital banks recorded a peak in fraud attempts, accounting for 35% of all biometric and document verifications in 2024, followed by microfinance at 30%. These institutions remain prime targets for sophisticated schemes combining identity fraud, account takeovers, and money laundering.
National identity cards recorded the highest fraud rate in Africa in 2024, at 27%, reflecting their widespread use as the main form of identification. Driver’s licenses followed at 24%, due to their frequent use in both formal and informal contexts, increasing their exposure to misuse. Passports had a fraud rate of 20%.
Race Against Time
To address this threat, governments, financial institutions, and technology companies must step up their efforts. Innovative solutions, such as integrating AI to detect deepfakes or strengthening biometric verification systems, are already being explored. However, the speed at which fraudsters adapt their techniques makes this race against time particularly complex.
In Africa, where digital security systems are still developing in many countries, the impact of these frauds could be devastating. International collaboration and increased investment in detection technologies will be essential to counter this growing threat, Smile ID emphasizes. Generative AI, while promising in many areas, thus presents a dual challenge for the continent: harnessing its potential while protecting against its malicious uses.
Expanding access to cloud and AI tools paves the way for small businesses, startups, and government services to embrace digital transformation, enhancing efficiency and accessibility. With this investment, South African businesses will be better positioned to integrate AI and cloud computing, driving productivity gains and streamlining operations.
On March 6, Microsoft announced plans to invest ZAR 5.4 billion ($297,664,532) in South Africa to expand its cloud and AI infrastructure by the end of 2027. This investment will support the growing demand for Azure services while enabling businesses, government entities, and startups to harness the power of AI and cloud computing to drive efficiency and innovation.
Speaking on the announcement, President Cyril Ramaphosa emphasized the significance of Microsoft’s long-standing commitment to South Africa, stating: “The strategic investment announcements made by Microsoft today stands as further testimony to this enduring confidence. They signal to the business and investor community that South Africa’s economy continues to hold immense potential and that it is a favourable place to do business where their investments are secure.”
As part of its commitment, Microsoft plans to expand its digital skills initiative over the next 12 months by sponsoring 50,000 Microsoft Certifications in high-demand fields such as AI, data science, cybersecurity, and cloud computing.
This investment builds on Microsoft’s 2024 achievements, where the company trained 150,000 people, certified 95,000, and helped 1,800 secure employment through its Skills for Jobs program. In January this year, Microsoft announced plans to provide 1 million people in South Africa with artificial intelligence (AI) training opportunities by 2026.
South Africa grapples with a significant digital skills gap, limiting its capacity to compete effectively in the global digital economy. A 2020 survey by Harambee, South Africa's Youth Employment Accelerator, titled Mapping of Digital and ICT Roles and Demand for South Africa, found that the country's shortage of technical skills led to the outsourcing of over 28,800 digital and ICT jobs each year. This resulted in an estimated annual loss of R8.5 billion ($55 million) in export revenue. Efforts like Microsoft’s initiative seek to bridge the gap by strengthening digital competencies across multiple sectors.
By strengthening its cloud and AI infrastructure, Microsoft aims to empower South Africa and the broader continent with the tools needed to compete globally, foster local enterprise development, and drive economic growth.
Hikmatu Bilali
The rising tide of cyberattacks poses a significant challenge to Africa's economic stability and digital development. Enhanced cooperation is essential to safeguard the continent's infrastructure.
Cybersecurity firm Kaspersky signed a three-year strategic memorandum of understanding with Smart Africa, an alliance of more than 40 African countries committed to the continent’s digital transformation, on Wednesday, March 5. The partnership aims to strengthen cybersecurity in Africa through skills development, policy harmonization, and the reinforcement of critical infrastructure.
"This MoU marks a significant milestone in our quest to secure Africa’s digital future. By joining forces with Kaspersky, we are not only building essential cybersecurity skills and bridging the gender gap but also setting the stage for robust regional cooperation and state-of-the-art cyber infrastructure," said Lacina Koné, CEO of Smart Africa.
The initiative is part of a broader effort to improve the digital resilience of African nations. According to the United Nations Economic Commission for Africa, the low level of cybersecurity preparedness costs African states an average of 10% of their GDP, amounting to nearly $4 billion per year, solely due to cybercrime. The African Network of Cybersecurity Authorities (ANCA), recently launched by Smart Africa, represents a first step toward more effective intergovernmental cooperation on cybersecurity.
Through the agreement, Africa will benefit from advanced training programs via the Kaspersky Academy, support in developing appropriate regulatory frameworks, and the establishment of security operations centers (SOCs). By making cybersecurity a priority in the continent’s digital transformation, the collaboration aims to create a safer, more inclusive, and resilient digital space for the years ahead.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
Global digital transformation is reshaping industries, and the automotive sector is no exception, with the increasing integration of information and communication technology (ICT) in vehicles. Tunisia is strategically positioning itself to capitalize on these emerging technologies, particularly electric and smart vehicles.
Tunisia is positioning itself to become a major player in the smart vehicle industry, as highlighted during the second steering committee meeting of the "Automotive Smart City" project on Tuesday, March 4. The initiative aims to establish a smart city dedicated to the electric and intelligent vehicle sector, enhancing Tunisia’s role as a strategic hub and boosting its global competitiveness.
The smart vehicle market is expanding rapidly, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, connectivity, and autonomous driving technologies. A report by consulting firm Modor Intelligence estimates that the automotive artificial intelligence market, valued at $2.3 billion in 2024, will grow to $16.2 billion by 2026, fueled by strong consumer demand and government efforts to reduce carbon emissions.
Tunisia’s Minister of Industry, Mines, and Energy, Fatma Thabet Chiboub, said the project aligns with the country’s national strategy for industry and innovation. It also supports the Pact for the Competitiveness of the Automotive Equipment and Components Manufacturing Sector by 2027. The initiative is expected to increase export revenues to 13.5 billion dinars ($4.4 billion) by 2027 and create 150,000 new jobs in the coming years.
The project is part of broader efforts to strengthen Tunisia’s automotive sector, which has already demonstrated significant growth. Tunisia ranks second in Africa for automotive component exports, underscoring the sector’s potential and its growing contribution to the national economy.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
Many small businesses still operate in cash-based systems with limited access to digital financial services. This initiative ensures that more businesses can participate in the digital economy, improving efficiency and security.
Payments technology company Flutterwave has partnered with the Small and Medium Enterprises Development Agency of Nigeria (SMEDAN) to enhance digital payment solutions for micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) across the country. This collaboration aims to provide businesses with the tools they need to thrive in an increasingly digital economy.
Flutterwave CEO Olugbenga ‘GB’ Agboola emphasized the company’s dedication to supporting Nigerian businesses. “As a business with Nigerian roots, we understand the challenges that small businesses face daily. This partnership ensures they have the financial tools they need to succeed in today’s digital economy.” By leveraging Flutterwave’s technology, MSMEs will be better equipped to navigate the evolving business landscape.
Aligned with SMEDAN’s Grow Nigerian initiative, the partnership will provide MSMEs with secure digital storefronts, seamless payment solutions, and improved financial access. Through this, businesses will be able to accept payments globally via mobile wallets, card payments, and bank transfers enhancing their reach and competitiveness.
Highlighting the impact of this initiative, SMEDAN Director-General and CEO Charles Odii noted, “One of the biggest challenges MSMEs face is access to digital tools, financial resources, and training that can help them scale. With Flutterwave as our partner, we have a solid ally providing Nigerian businesses with innovative solutions that will enable them to compete effectively on a global scale.”
Building on its longstanding support for small businesses, Flutterwave has consistently introduced initiatives such as the Flutterwave Store, small business grants, annual trade fairs, and the ‘Keeping the Lights On’ campaign, which has helped thousands of businesses remain operational despite economic challenges. The partnership with SMEDAN further strengthens Flutterwave’s commitment to empowering entrepreneurs.
This latest development follows NITDA’s February announcement of a partnership with Flutterwave, Alami a fintech offering sharia-compliant financing for SMEs and SMEDAN. Together, these initiatives signal a broader push toward digital and financial inclusion for small businesses in Nigeria.
The significance of this collaboration is further underscored by the role SMEs play in Nigeria’s economy. According to the International Labour Organization (ILO) Country Office in Nigeria, SMEs contribute 48% of the national GDP, make up 96% of all businesses, and provide 84% of employment. As digital solutions become increasingly critical to business success, partnerships like this one will help ensure that Nigerian MSMEs remain competitive and continue to drive economic growth.
Hikmatu Bilali
The increasing prevalence of fake diplomas, driven by readily available technology, seriously undermines global education standards. However, blockchain technology presents promising solutions to combat this growing issue.
The Tunisian government has adopted a blockchain-based diploma verification system across its higher education institutions, aiming to combat widespread fraud.
The move follows a 2023 investigation by the Tunisian Association for the Fight Against Corruption, which revealed that an estimated 120,000 to 200,000 civil servants were allegedly hired between 2011 and 2021 using fake diplomas.
On Friday, February 28, Tunisia implemented the Unified Arab System for Diploma Authenticity Verification, utilizing blockchain technology. The system stores each diploma as a unique, secure, and tamper-proof block, protecting academic records from forgery, fraud, and unauthorized modifications. Institutions, employers, and stakeholders can instantly verify diploma authenticity, bypassing lengthy administrative processes.
The use of blockchain in higher education is not new. The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) implemented a secure digital diploma program on blockchain in 2017. In Africa, similar initiatives are emerging. Some Nigerian universities are experimenting with blockchain-recorded diplomas to ensure authenticity and simplify verification.
A study by Market Research Future projects the blockchain market applied to education could reach $1.3 billion by 2030, with an estimated annual growth rate of 33.7%. This growth reflects increased adoption of the technology by educational institutions seeking secure and simplified diploma management.
In Tunisia, the project is part of the Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research’s digital transformation strategy. It aims to ensure diploma integrity, develop digital skills, and modernize the education sector. The initiative stems from a November 2024 cooperation agreement between Tunisia and the Arab League Educational, Cultural, and Scientific Organization (ALECSO). A pilot project in three Tunisian institutions demonstrated the solution's effectiveness, leading to nationwide implementation.
Beyond combating fraud, the innovation is expected to facilitate academic and professional mobility by ensuring immediate and unquestionable recognition of diplomas nationally and internationally. It also represents a strategic advancement for Tunisia’s education system, strengthening the credibility and competitiveness of its universities globally.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
More...
Successful digital transformation requires identifying challenges and implementing effective solutions. In Madagascar, key obstacles include limited infrastructure access, high connectivity costs, and a digital skills shortage.
Madagascar's Ministry of Digital Development, Posts, and Telecommunications, in collaboration with the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), launched a Digital Readiness Assessment (DRA) on Feb. 27 in Antsirabe. This initiative aims to provide a comprehensive diagnosis of the country's digital sector and identify priority actions to address existing gaps, supporting Madagascar's goal of full integration into the digital economy.
In recent years, the has made significant progress, notably through the development of mobile money and the rise of local tech startups. However, several challenges remain. The country continues to face major structural obstacles, including limited access to digital infrastructure, high connectivity costs, and a digital skills gap.
According to DataReportal, in January 2024, the internet penetration rate in Madagascar was 20.6%, with 6.31 million users out of a total population of 30.68 million. However, this coverage remains uneven, particularly in rural areas. Regarding the cost of connectivity, the Malagasy government announced last October its intention to reduce telecommunications service tariffs to improve the population’s access to the internet. Despite these efforts, the cost of mobile internet access still represents 15.5% of the monthly gross national income (GNI) per capita, well above the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) recommendation of 2% of the monthly GNI per capita.
The digital skills gap also remains a major obstacle. The 2023-2028 Digital Strategic Plan highlights a shortage of approximately 40,000 specialized technicians needed to enable an effective digital transformation of the country. In this context, the Ministry of Digital Development has launched a program aimed at training 6,000 people in emerging digital professions over the next three years to address this urgent need.
To meet these challenges, the DRA represents a fundamental first step. This assessment is based on five key pillars: connectivity, to strengthen infrastructure and reduce the digital divide; governance, to improve coordination between sector stakeholders; regulation, to create a legal framework suited to the digital economy; businesses, to encourage innovation and technological entrepreneurship; and human capital, an investment in digital skills training.
The DRA is not limited to a simple assessment of the situation. It also serves as the basis for a strategic roadmap, aligned with Madagascar’s sustainable development priorities. Through this assessment, the country hopes to define a coherent digital vision that will not only accelerate its transformation but also help reduce inequalities in access to opportunities offered by the digital sector.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
Digital applications help authorities vet travelers in advance, improving security while reducing administrative burdens. By allowing travelers to apply for visas online before arrival, Namibia reduces congestion at borders, improving the overall travel experience.
Namibia has introduced an online application system for visas on arrival, marking a major step toward modernizing its visa process. Minister of Home Affairs, Albert Kawana, officially launched the initiative on March 3, 2025, at the ministerial conference hall.
Minister Kawana emphasized that while this new system enhances travel convenience, the visa application process for countries that do not qualify for visas on arrival remains unchanged. These travelers must continue to apply in advance via the Ministry’s online platform and await approval before entering Namibia.
The system allows eligible travelers to apply for visas before arrival, ensuring a smoother and more efficient entry process. The minister also reaffirmed Namibia’s commitment to fostering diplomatic and economic ties by engaging with nations interested in reciprocal visa agreements.
Starting April 1st, the new policy will apply to countries such as Benin, Burundi, Chad, the Central African Republic, Ghana, Guinea, Niger, Rwanda, and Togo. Citizens of African nations will pay approximately $70 for a tourist or holiday visa application.
Namibia has been actively digitalizing its immigration processes to enhance efficiency and accessibility. Key initiatives include the launch of an online application system for Short-Term Employment Permits (Work Visas) and Namibian Ordinary Passports in 2023, allowing applicants to apply, schedule appointments, and monitor application statuses online, reducing the need for in-person visits. Also, in 2022, Namibia introduced the Digital Nomad Visa to attract remote workers. The Visa permits eligible individuals to reside in the country for up to six months while working remotely for foreign-based employers.
These initiatives mark significant progress in Namibia’s digital transformation, enhancing security, modernizing services, and facilitating seamless travel.
Hikmatu Bilali
Niger, like many African nations, is pursuing digital technology as a key driver of development. The government's roadmap prioritizes modernizing administration, strengthening infrastructure, and expanding access to digital services.
Niger will adopt a national policy for the development of its digital sector next month, the government said last Wednesday. Speaking on Radio Télévision du Niger (RTN), Minister of Communication, Posts, and Digital Economy Sidi Mohamed Raliou said the policy aims to structure and accelerate the country’s digital transformation, making digital technology a driver of growth and modernization.
The national policy will encompass all sectors and government administrations, he explained. The objective is to digitize public services, gradually eliminating paper documents and optimizing service management. The policy will be supported by connectivity infrastructure, including fiber optic deployment to interconnect different regions.
The initiative is part of a broader set of strategic projects designed to strengthen Niger’s digital sector. These projects include the launch of three satellites for communications, remote sensing, and airspace surveillance, as well as the construction of a national data center to secure and centralize digital data.
Additionally, the government plans to establish a National Cybersecurity Agency to oversee IT system protection, combat cyber threats, and raise public awareness about cybersecurity best practices. Efforts are underway to improve nationwide internet access, particularly in rural areas.
The policy aligns with Niger’s ambition to modernize digital services and attract investment in the telecommunications sector. In 2024, the country scored 0.1578 out of 1 on the Telecom Infrastructure Index (TII), significantly below the African average of 0.4534, according to the United Nations. In terms of e-governance, Niger ranked 187th out of 193 countries with an index score of 0.2116. These figures highlight the significant efforts needed to enhance the country’s digital transformation.
Once adopted, the national digital policy is expected to transform Niger’s digital ecosystem by strengthening infrastructure, expanding access to online services, and improving cybersecurity. The development of broadband and the expansion of internet coverage will foster greater digital inclusion, enabling citizens and businesses to benefit from modern tools.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
The Moroccan government has prioritized digital technology as a cornerstone of the country's socioeconomic development. In addition to investing in infrastructure, the administration is committed to equipping the population with the necessary digital skills to achieve these goals.
Morocco will open a new school specializing in programming and coding in the Fès-Meknès region, the government said Friday. An agreement to establish the "YouCode Fès" school was signed under the leadership of Amal El Fallah Seghrouchni, Minister Delegate in charge of Digital Transition and Administrative Reform.
"Under this agreement, the ‘YouCode Fès’ school will offer a two-year training program in information technology and digital fields. Each cohort will welcome 80 students, contributing to the expansion of employment opportunities in the digital sector within the region and improving young people’s employability in tech-related professions," the ministry said in a Facebook announcement.
The initiative aligns with Morocco’s Digital Maroc 2030 strategy, which aims to develop a high-quality talent pool in the digital sector. The government's long-term goal is to enhance its outsourcing and digital export hub. By 2030, the country aims to increase employment in the sector to 270,000 jobs, up from 130,000 in 2022. Rabat is also targeting digital export revenues of 40 billion Algerian dinars ($296.13 million) by 2030, compared to 15.8 billion dinars in 2022.
According to the World Bank, nearly 230 million jobs in Sub-Saharan Africa will require digital skills by 2030. While Morocco is not part of this region, the trend highlights the critical role of digital training in Africa’s technological transformation.
The timeline for the new school’s launch has not been announced. Similar programs may be expanded to other regions. YouCode already operates campuses in Safi and Youssoufia (Marrakech-Safi region) and in Nador (Oriental region).
By Isaac K. Kassouwi,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji















