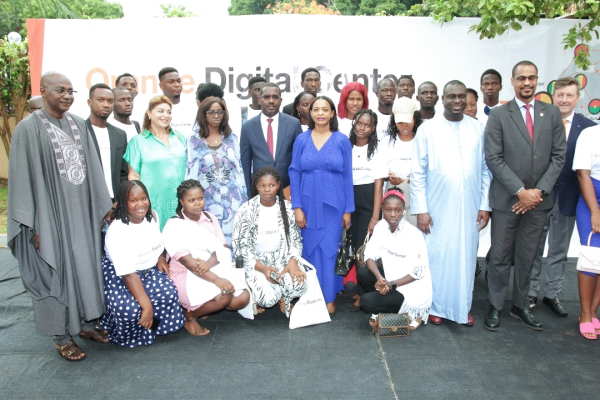
Orange continues to expand its Orange Digital Center network across the continent. Following launches in Dakar, Senegal; Bamako, Mali; Conakry, Guinea; and Freetown, Sierra Leone, Bissau, the capital of Guinea-Bissau, is now set to inaugurate this ecosystem dedicated to developing digital skills.
Orange, a leading telecom operator in Africa, has inaugurated the Orange Digital Center in Guinea-Bissau on June 28, 2024. The center, located in the capital Bissau, aims to train young people in digital skills, enhance their employability, and encourage innovative entrepreneurship.
The Orange Digital Center in Guinea-Bissau is part of a network of 26 similar centers across Africa, the Middle East, and Europe. It includes a coding school, a solidarity FabLab, a startup accelerator "Orange Fab," and is supported by Orange Ventures Africa, the group's investment fund dedicated to promising startups.
"This space is more than just a technological center; it is a promise of transformation and growth for the digital future of Guinea-Bissau and Africa. By providing free access to cutting-edge resources, we hope to inspire a new generation of creators and leaders, and contribute to an inclusive digital economy," said Brelotte Ba, Deputy CEO of Orange Africa and the Middle East.
The establishment of the Orange Digital Center in Guinea-Bissau aligns with the French telecom operator's strategy to position itself as a leader in digital transformation on the African continent. According to a World Bank report published in September 2022, the Bissau-Guinean government is committed to strengthening the country's digital skills, despite lacking the capacity to invest in the necessary resources. The absence of a national information and communication technology policy and strategy makes achieving several sustainable development goals by 2030 uncertain. Programs like Orange's help mitigate the issue while awaiting public authority actions.
Access to digital skills can improve access to basic public goods and services (e-government, telehealth, etc.), local financial services (online banking, digital payments, etc.), and promote better use of public information and digital platforms. It can also support an inclusive digital economy and contribute to the continuity of education by providing better access to distance or technology-assisted learning. As of early 2024, the internet penetration rate in Guinea-Bissau was 31.6%, according to DataReportal.
Adoni Conrad Quenum