In Madagascar, the lack of newborn registration is a nationwide problem. By leveraging new technologies, the government wants to address the problem soon.
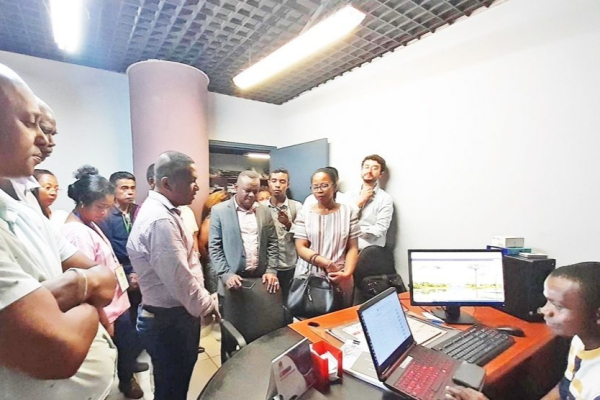
On Friday, June 15, the authorities of the urban commune of Toamasina in eastern Madagascar launched the trial phase of the digitized civil registration and identity system.
The new solution, which has been two years in the making, will be launched in the next few days in Toamasina, and by the end of 2023, it will be launched in several other communes in the country.
“... The official launch is scheduled for the end of June. Digitizing civil registration data means that birth information can be stored securely, to protect it from fire and loss,” said Volana Rakotonirina, Director General of the National Civil Registration Center at the Ministry of the Interior and Decentralization.
In Madagascar, as in many African countries, the identification of individuals remains a real problem. According to UNICEF data, nearly a quarter of children under the age of 18 in Madagascar have no birth certificate, i.e. some 2.5 million children. An estimated 1 million adults are unregistered and therefore invisible. The reasons for this shortfall lie partly in ignorance of the procedure, but also in structural problems such as administrative malfunctions.
Thanks to the new system, hospital data will be transferred directly to the communes, and the information will be validated by the registrar. Maternity wards will be equipped with connected tablets for this purpose. The aim is to interconnect at least 30 communes by the end of the year.
This digitization project is part of the Malagasy Digital Governance and Identity Management Project (Prodigy), launched in 2019 and financed by the World Bank. The project aims to increase inclusive access to legal identity for all Malagasy citizens and improve access to and the quality of key public services.
Samira Njoya