Cybercrime is gaining ground in Africa. Sub-Saharan Africa is presented as a region particularly vulnerable to the issue of online scams and large-scale cyberattacks on the rise. Nevertheless, industry players are moving to provide adequate responses.
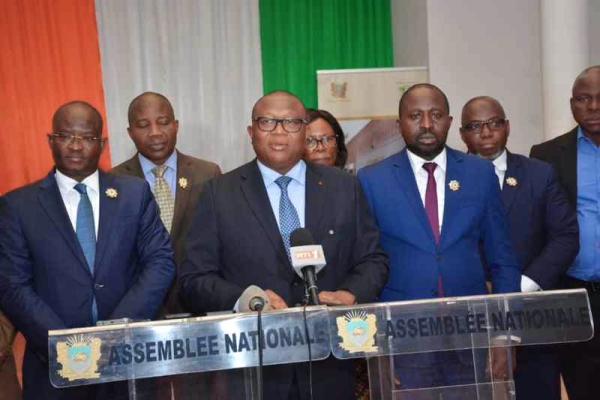
Last week, the Ivorian parliament approved the draft law amending articles 17, 33, 58, 60, 62, and 66 of the law N° 2013-451 of January 19, 2013, on the fight against cybercrime.
According to Minister of Communications Amadou Coulibaly (Photo, center), who defended the draft law before the parliament, it was necessary to overhaul the rules punishing cybercrime in an environment where the number of such acts is ever-rising with the rise of social media.
Like its African peers, Côte d'Ivoire is confronted by the scourge of cybercrime. The most recurrent acts are sextortion, sexual harassment, identity, and payment fraud.
In 2011, the Ivorian government established a Platform for the Fight against Cybercrime (PLCC). In March 2019, it ratified the Budapest Convention on Cybercrime, which allowed it to benefit from international collaboration in its fight for greater effectiveness. About two years later, it adopted a new strategy to better secure its cyberspace and accelerate its digital transformation to become the African leader in cybersecurity
The amended articles increase the maximum sentences for cyber acts that violate human dignity, honor, and intellectual property rights as well as any illegal act carried out using ICT tools. For example, Article 17 consecrates a one to six years prison sentence and between 20 to 40 million fine for anyone who publishes or distributes child pornography.
Samira Njoya